PTTb
advertisement

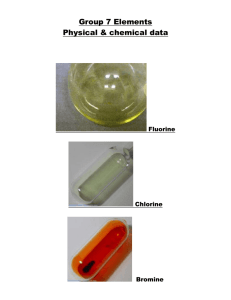
Group 7 elements (halogens) - reactivity Group 7 elements (halogens) were first discovered from 1776 onwards. Some of the physical properties are shown below. Element Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Astatine Boiling point oC -188 -35 58 183 ? Melting point oC -220 -101 -7 114 ? Density g/cm3 1.7g/l 3.21 g/l 7.79 g/l 4.93 ? Atomic mass 19 35.5 79.9 126.9 (210) Diameter of atom (nano-metres) 0.142 0.198 0.228 0.266 ? As the atomic mass (and the size of the atom) of the Group 7 elements (halogens) increases the: boiling point melting point density all increase. The reason why these halogens are reactive is that they all have one electron missing in their outer shell. This means that the atoms of the halogens are not "very happy" and they will do all they can to gain one more electron such that all the electrons in the outer shells have partners. In order of reactivity fluorine is the most reactive followed by chlorine, then bromine, iodine and astatine is the least reactive. Electronic configurations. Element Atomic number Electrons in 2nd shell 7 Electrons in 3rd shell 9 Electrons in 1st shell 2 Fluorine Electrons in 4th shell Electrons in 5th shell Chlorine 17 2 8 7 Bromine 35 2 8 18 7 Iodine 53 2 8 18 18 7 Astatine 85 2 8 18 32 18 Electrons in 6th shell 7 Electronic configurations (diagrams) for fluorine and chlorine are shown below. NOTE As the atom becomes bigger and bigger the ability to attract an electron into the outer shell becomes less and less. So for fluorine (size 0.142 nm) the outer electron shell is very close to the attracting nucleus. an electron is easily attracted. Fluorine IS very reactive. So for Iodine (size 0.266 nm) the outer electron shell is a long way away from the attracting nucleus. it is very hard to attract electrons to the outer shell.. Iodine is NOT very reactive.