Halogens
advertisement

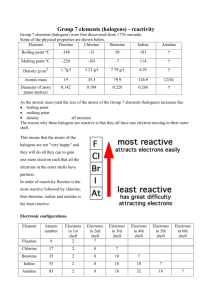
What are Halogens? Halogens are a series of non-metal elements located in group 7 of the periodic table. The term “halogen” means “salt-former”. All halogens have seven electrons in their outermost shell. They are therefore just one short of a full outer shell. This is what makes them reactive with other elements. They are not found in their pure state like gold, but are found tied up in covalent or ionic compounds. They have low melting and boiling points and do not conduct electricity at all. Halogens All halogens have 7 electrons in their outermost shell, giving them an oxidation number of -1. This group contains, Fluorine- a pale yellow gas, Chlorine- a pale green gas, Bromine- a dark brown liquid, and Iodine- a dark purple solid. Properties of Halogens The vigor of the reactions in halogens decreases as we go down the group, whereas the melting and boiling points increase. Fluorine is one of the most reactive existing elements, attacking inert materials such as glass, and forming compounds with the heavier noble gases. The high reactivity of fluorine means that once it does react with something, it bonds with it so strongly that the resulting molecule is very inert and non-reactive to anything else. For example, Teflon is fluorine bonded with carbon. The Halogens at Room Temperature The halogens exist, at room temperature, in all three states of matter: Solid- Iodine. Liquid-Bromine. Gas- Fluorine, Chlorine. Reactions of Halogens Halogens may either gain electrons to form negative ions or they can form a single covalent bond with other non metals. They do this to become like noble gases, having a full outer shell. The halogens can react with many metal and non metal elements forming a number of different ionic and covalent compounds. Example: sodium chloride (NaCl) and carbon tetra chlorine (CCl4). Ionic and Covalent Bonds During the formation of sodium chloride, a single electron from the outer shell of sodium is transferred to the outer shell of a single chlorine atom. Both ions (Na+ & Cl-) are now stable having the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. This is an Ionic Bond. During the formation of the covalent hydrochloric acid, both atoms form a single covalent bond. This sharing of electrons fills the outer shell of both hydrogen and chlorine atoms making them both stable. Uses of Halogens All the halogens are potentially harmful substances. Fluorine and chlorine in particular are highly toxic. It is very dangerous to ingest or breathe halogen vapor or their solutions. They are used to kill bacteria, which is why they are used as a sterilizer for water in swimming pools. Chlorine compounds are used in disinfectants like ‘dettol’. Our toothpastes contain fluoride to kill the bacteria in our mouth. Iodine water is also used as a disinfectant prior to surgery or to sterilize dirty drinking water.