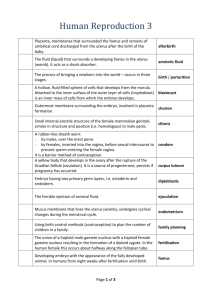
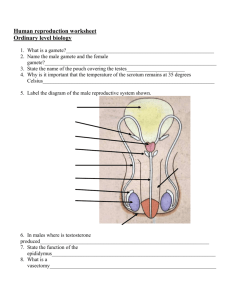
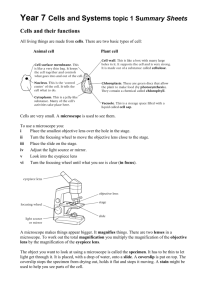
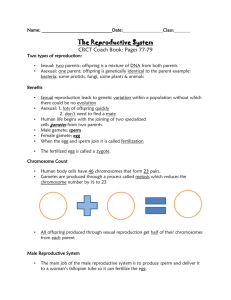
Human Reproduction 1 Found at the tip of the sperm above the
advertisement

Human Reproduction 1 Found at the tip of the sperm above the nucleus. It contains enzymes that break down the jelly coat surrounding the female egg thus allowing the sperm nucleus entry into the egg. A method of testing the foetus in the uterus (womb) for chromosomal disorders. A sample of amniotic fluid is withdrawn from the uterus using a needle and the fluid and foetal cells it contains are analysed. acrosome amniocentesis A fluid-filled sac/bag, found in the uterus of pregnant females, containing the developing embryo. amniotic sac Holds the erect penis during intercourse. Also, the new baby arrives into the world from the uterus (womb) through here. birth canal / vagina Suckling a child at mother's breast. It gives a baby the best possible start in life. breast-feeding Finger-like projections of the chorion of the embryo. chorionic villi The first milk produced by a mammal after parturition (birth). It is a thick, yellowish liquid containing proteins and antibodies, and is colostrum later replaced by breast milk. The act of preventing the fertilisation of an egg or implantation or pregnancy. Different methods include: natural, mechanical, chemical contraception and surgical. Situated below the prostate and is involved in the manufacture of seminal fluid and provides nourishment and a medium for sperm to Cowper’s gland swim. Outer of the three primary germ layers. Gives rise to skin, hair and nails. ectoderm Fertilised egg or immature animal in uterus (up to eight weeks in humans). embryo Sperm storage organ in the male testes. epididymis All the organs involved in gamete formation, copulation, fertilisation and development of the young in the female. female reproductive system An egg whose nucleus has joined with the nucleus of a male gamete. fertilised egg / zygote Fluid-filled sac in the ovary in which the egg develops. follicle Page 1 of 3 Any cell which must fuse with another cell in order to produce a new individual. A haploid reproductive cell, i.e. it contains half the required genetic information for the formation of a new individual or half the somatic number of chromosomes (in humans = 23), e.g. sperm cell, egg. gamete Length of time from conception to birth, i.e. length of pregnancy, gestation period carrying foetus in womb (uterus). In humans = 40 weeks or 266 days. Hormone secreted by an implanting fertilised egg (blastocyst). It maintains the corpus luteum in the ovary (until the ninth week of the gestation period, after which the placenta takes over) and prevents the breakdown of the endometrium. The analysis of urine for the presence of this hormone is used to confirm pregnancy. The inability to produce sufficient gametes and conceive or produce children. May be caused by a low sperm count or low sperm mobility in males, blocked fallopian tubes in females or endocrine gland failure in either or both. HCG / human chorionic gonadotrophin infertility Growth and maturing of embryo or foetus within the uterus or womb. intrauterine development An event or process occurring inside a living organism, e.g. fertilisation. in-vivo Cells found between the seminiferous tubules of the testis, which secrete testosterone. Leydig cells Period in a woman’s life between the ages of 40 and 50 during which menopause menstruation stops. The middle layer of the three primary germ layers of a triploblastic organism, from which muscles, skeleton, kidneys, etc. develop. A female sex hormone produced by the ovaries. · Stimulates proliferation of uterine wall (endometrium). · Inhibits FSH production. · Stimulates LH production, and · Maintains the female secondary sexual characteristics. In animals, female reproductive organ producing eggs and is also an endocrine gland producing the hormones oestrogen and progesterone. mesoderm oestrogen ovary The male urinogenital organ, i.e. used in excretion and copulation. Eliminates urine through the urethra and deposits sperm in vagina. penis Carrying developing young in womb (uterus). pregnancy A hormone produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary, which stimulates milk production in mammary glands (breasts) and inhibits FSH production by the pituitary. prolactin Page 2 of 3 The ability of an organism to produce new individuals of its own kind by either sexual or asexual means and pass on genetic information to the next generation. The physical characteristics that appear during puberty and adolescence. In the male they include the broadening of the shoulders, growth and enlargement of the penis, deepening of the voice, body and facial hair, etc. In the female they include enlargement and growth of the breasts, growth of body hair under arms and pubic regions. reproduction secondary sexual characteristics Small coiled tubes in the testes that produce sperm by meiosis. seminiferous tubules Reproduction involving the production, transfer and union of sex cells or gametes and development of the embryo. Two parents involved (plant or animal), one male and one female. sexual reproduction The male organ that at maturity produces gametes (sperm). Also an endocrine gland that produces the hormone testosterone. testis Surface layer of cells of blastocyst, part of which forms the placenta. trophoblast Technique used where very high frequency sound waves are passed into the body and the echo which returns is converted into a visible picture of the internal organs. Used on women during pregnancy to monitor embryo and foetal development. ultrasound scanning Holds the erect penis during intercourse. Also birth canal, i.e. new baby arrives into the world from the uterus (womb) through here. vagina Any disease that is passed on through sexual intercourse. venereal disease Page 3 of 3