Revision Guide
advertisement

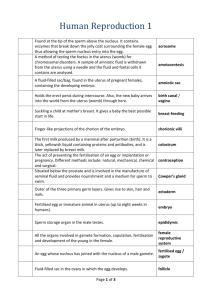
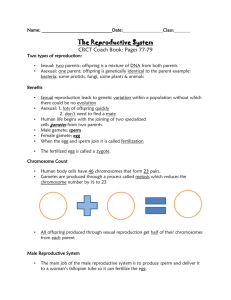
LOWER 4th REVISION BOOKLET 2014 This revision booklet provides students with notes and diagrams that are to be used to SUPPORT their revision for the summer exam 2014. Topics covered that will be present on the exam paper are : 1. Lab Safety 2. Characteristics of Living things (Mrs Grenc) 3. Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems 4. Microscopy 5. Variation 6. Keys 7. Classification 8. Puberty and reproduction Biology = The study of living things 1 Flammable Oxidising agent Corrosive Explosive Irritant Harmful 2 What do ALL living things have in common? Movement Respiration (release energy from food source) Sensitivity (Respond to stimuli) Growth (Increase in size and complexity) Reproduction (Produce offspring of the same species) Excrete (Removal of waste products) Nutrition (Take nutrients for energy, growth and repair) Control (their internal environment) A plant is living because it respires, it is sensitive (to light, Carbon dioxide levels) it moves (leaves), grows, reproduces, excretes and needs nutrients to survive. MAGNIFICATION = Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. It is used for very small objects and we use a MICROSCOPE. Eg. Sand, cells. 1. Eyepiece 7. Objective Lenses 6. Stage 5. Mirror 2. Arm 3. Focus adjustor 4. Base Remember if the eyepiece lens has a magnification of 10 and the Objective lens has a magnification of 20 the TOTAL MAGNIFICATION = 10 x 20 = 200 The diagram below shows how we are organised – All organisms are made up of cells. Theses cells have organelles inside them. 3 ORGANISM A ‘whole being’. Humans are organisms SYSTEM A collection of organs eg. the nervous system, the respiratory system ORGAN A collection of tissues eg Heart (mixture of muscle and nervous tissue) Bundles of cells with similar use eg muscle TISSUE CELL The basic unit of living organisms ORGANELLE Found within a cell. Has specialised job eg. chloroplast Main differences and similarities between plant and animal cells PLANT ANIMAL (US!) Nucleus Nucleus Chloroplasts Mitochondria (energy) Mitochondria (energy) Cell membrane Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Permanent vacuole PLANT CELL Cell membrane Cytoplasm – chemical reactions take place here Nucleus – Contains DNA (genetic material Cell wall – cellulose – strong for protection Permanent vacuole (contains cell sap – salts, wastes, sugar etc) Chloroplast – Site of Photosynthesis Mitochondria – ENERGY production 4 ANIMAL CELL Cell membrane Cytoplasm – chemical reactions take place here Nucleus – Contains DNA (genetic material Mitochondria – ENERGY production Different kinds of specialised animal cells white blood cell Amoeba red blood cell muscle cell cheek cells sperm nerve cell Paramecium SPECIALISED CELLS ANIMALS 1. EGG – Ovum • FUNCTION = Sex cell of female animals • FUNCTION = Carries genetic material and joins sperm • FEATURE = Very large because contains large amounts of stored food 5 2. SPERM • • • • • FUNCTION = Sex cell of male animals FUNCTION Carrier genetic material in large nucleus FEATURE = Long Tail for swimming FEATURE = The head of the sperm is the acrosome – stores enzymes to break down egg cell wall FEATURE =Mid section is full of mitochondria, which provides energy for swimming. Vacuole with Enzymes Strong tail for swimming 3. RED BLOOD CELL • FUNCTION = Carry Oxygen around the body in the chemical haemoglobin • FEATURE = Biconcave discs to increase surface area increase oxygen entry into cell • FEATURE = NO nucleus increase oxygen transport 4. CILIATED EPITHELIAL CELL FUNCTION = cleaning airways by trapping dust and dirt FEATURE = Covered in lots of tiny hairs to increase Surface Area 5. NEURONE FUNCTION = Carry nerve impulses around the body FEATURE = Long axon PLANTS 1. PALISADE CELL a. FUNCTION = ‘Catch’ light from sun PHOTOSYNTHESIS b. FEATURE = Found in leaves & stems c. FEATURE = Contain lots of chloroplasts (which contain chlorophyll) 2. ROOT HAIR CELL a. FUNCTION = Take water & nutrients from the soil for distribution around plant b. FEATURE = Thin cell membrane c. FEATURE = Their extensions INCREASE surface area Larger surface in contact with water to uptake into the plant from the soil d. FEATURE = They have a large permanent vacuole 6 e. FEATURE = Close to xylem tissue which carries water up to the rest of the plant f. FEATURE = They grow out of the root just behind the root tip VARIABLES • Variation is how things are different. VARIATION can occur between: the same species (Eg. HUMANS – we are not all the same!) = INTRASPECIFIC VARIATION or between different species (eg. between a dog and a cat!) = INTERSPECIFIC VARIATION Individuals of the same species can reproduce to make more individuals of the same species. • Two individuals belonging to different species cannot normally reproduce together. If they do, their offspring is usually infertile and unable to reproduce. TYPES OF VARIATION 1. Continuous variation A characteristic with a range of values, that changes gradually. Examples include: a. height b. weight • 2. Discontinuous variation A characteristic with only a limited number. • Gender (male or female) • blood group (A, B, AB or O) • eye colour 7 Some characteristics are INHERITED (from parents) eg. Eye colour, blood group Some characteristics some from the parents AND the environment eg. Height & weight When performing an experiment there are VARIABLES that can change. Independent: What we chose to change Dependent: measured for each change in our independent variable • But there are 4 different types!! – CATEGORIC - Best described as a label Eg. Eye Colour – DISCRETE - Whole numbers (eg. cows in a field) – CONTINUOUS - One that we measure Eg. Temperature (37.4°C) – ORDERED - Where you can put the data into order CLASSIFICATION We classify organisms to enable us to identify which species they are closely related to. Classification is a world wide language – latin names are recognised everywhere. 5 kingdoms - split into Vertebrates (animals WITH a backbone) and Invertebrates (animals WITHOUT a backbone) VERTEBRATES: (you need to know more detail for each than in given) Reptiles: Lay leathery eggs & have dry scaly skin amphibians: cold blooded, moist skin fish: scales & gills birds: have feathers & wings mammals: live young that feed on milk INVERTEBRATES coelenterates (jellyfish) flatworms (tapeworm) annelids (worms, leeches) molluscs (snail, oyster) echinoderms (starfish) arthropods – Jointed legs/ Exoskelton eg: (crab (10-14legs), spider(8legs), fly (6legs), centipede(20+legs)) NOTE: You need to know a little about each – ie. Arthropods have segmented limbs with a hard outer layer and molluscs bodies are soft Classification of HUMANS KINGDOM – Animal PHYLUM – Chordate (Vertebrates) CLASS - Mammal ORDER - Primate FAMILY - Hominid GENUS - Homo SPECIES – sapiens 8 DICHOTOMOUS KEY They help us identify organisms by looking at their PHYSICAL characteristics Yes/No answers narrow a species down from Kingdom to Species PUBERTY • • • • • 9 Puberty is the period of time when children begin to mature biologically, psychologically, socially and cognitively. Girls start to grow into women and boys into men. Reproduction is one of the eight life processes. All living things reproduce. Humans use sexual reproduction to produce their young. In order to reproduce, the two parents (male and female) have different reproductive systems and organs that produce different sex cells (gametes) male reproductive system Female reproductive system In the female, one of the ovaries produces an egg every 28 days. This is called ovulation. During sexual intercourse millions of sperm are ejaculated into the vagina. If a sperm meets the egg, the sperm’s nucleus can join with the egg’s nucleus. This fusing of the nuclei is called fertilization. 10 CHANGES IN GIRLS TO TURN TO WOMEN 1. Breasts start to develop 2. Hips start to widen 3. Pubic and underarm hair 4. Sexual organs and eggs mature, 5. Ovulation and then, 6. Menstruation begins (get their period) 7. Emotional changes 8. Growth spurts THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE A 28 day cycle that involves the production of EGGS ready to be fertilised by sperm to produce offspring. If the egg is NOT fertilised, the lining of the uterus shed in a monthly ‘period’ or menstruation 11 CHANGES IN BOYS TO TURN TO MEN 1. Facial & body hair 2. Pubic hair 3. Voice deepens 4. Penis and testes grow larger and darker 5. Starts to produce sperm experience erections and wet dreams. 6. Emotional changes 7. Shoulders broaden 8. Become more muscular. 9. Growth spurts Day 1 – 7 The menstruation cycle starts with the first day of a woman’s period. This is the name given to the time of the month when the lining of the uterus comes away and exits through the vagina as blood. Day 7 - 13 The blood flow stops. The lining of the uterus begins to build up again. At this time an egg starts to mature in one of the ovaries Day 14 (The Middle) On the 14th day which is the middle of the cycle, an egg is released by an ovary into the oviduct. This is called Ovulation Day 14 - 17 The egg can last up to 2 days after it is released from the ovary. During this time the egg travels down the oviduct and into the uterus hoping to be fertilised. Day 18 - 28 If the egg is not fertilised then the lining of the uterus begins to break down. Day 1 – the cycle starts again Target words 12 FERTILISATION – Fusion (joining) of an egg and a sperm to produce a ZYGOTE SPERM – The male reproductive cell (Gamete) containing HALF the GENES EGG – The female reproductive cell (Gamete) containing HALF the GENES PUBERTY – Hormonal changes in boys and girls when they are changing into men and women. o Boys to Men – 12-16yrs o Girls to Women – 10-14 yrs OESTROGEN – The female hormone that causes the release of an egg from the OVARY TESTOSTERONE – The male sex hormone that results in the development of his sex organs (penis, testes & development of sperm) UTERUS – The major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ. It is within the uterus that the foetus develops for 9 months during gestation. MENSTRUATION – The shedding of the uterus lining if NO fertilisation occurs. Also known as a ‘period’ and on average lasts 28 days FALLOPIAN TUBE – The tube that joins the ovary to the uterus. The area where fertilisation must take place 13