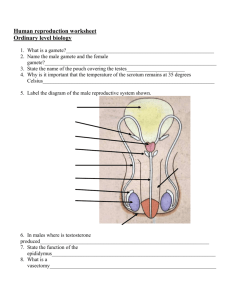
Testes – makes and stores sperm via meiosis. The testes are also
advertisement

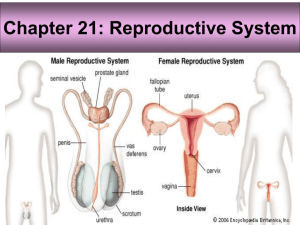
Male Reproductive Structures Testes – makes and stores sperm via meiosis. The testes are also responsible for produces testosterone, the male hormone. Sperm-male sex cells. Scrotum- Pouch that encloses the testes. Penis- organ where sperm leaves the body. Urethra- where urine leaves. Seminal Vesicle and Prostate Gland- release liquids into the vas deferens when sperm is moving through it. Testosterone is responsible for many of the "male" characteristics. Epididymis – Where the sperm matures until it’s expelled or reabsorbed. Vas deferens - tube where sperm travels to the outside of the body. Bulbourethral gland / Cowper’s gland- adds fluid to the semen during ejaculation. Semen- a mixture of fluids that looks milky white. Female Reproductive Structures * 2 important functions- nourishes, produces, and protects the egg cells. Vagina-birth canal, tube that leads from an opening outside the body. Uterus- strong, thick, muscular walls that holds and nourishes the growing embryo. Cervix- opening of the uterus at the top of the vagina, stretches during birth. Fallopian Tubes- connects the ovary to the uterus. The tubes where the eggs travel down. Ovaries- produce, store, and releases eggs. Eggs-female reproductive cells. Ovum- egg cell. * Estrogen is the hormone responsible for secondary sex characteristics. * Progesterone is the hormone responsible for initiating menstruation. * Testosterone is the hormone that initiates sperm production and male secondary sex characteristics. * Fertilization produces a new cell= zygote. 23 chromosomes from mom and 23 from dad= complete set! * An egg is usually a few days old before it implants in the uterus. At this point, it has already divided several times and is called a blastula. * The period from fertilization to birth = gestation. If the zygote has the incorrect number of chromosomes, it may never start growing. An extra chromosome #21 will result in the baby having Down syndrome. First Trimester Up to 3 months Zygote divides several times to form a hollow ball called a blastocyst. Embryo is implanted into the uterine wall – takes about 8-9 days. Nourishment begins. Gastrula forms-> make up the germ layers-> which develop into different structures. Ectoderm-= outer layer-> forms skin, nerves, and sense organs. Mesoderm=middle layer> forms bones, muscles, and tissues. Endoderm= inner layer-> digestive system and lungs. All three layers developing in different ways is called differentiation. After 8 weeks the major organs have begun to develop and then it is called a fetus Second Trimester Month 3 to 6 Fetus starts to move. By the end it has fully developed eyes. Lungs are starting to develop. Third Trimester 6 months- end Brain develops rapidly. Regular breathing Lungs aren’t fully developed until the 36th week.