CELLS AND REPRODUCTION
advertisement

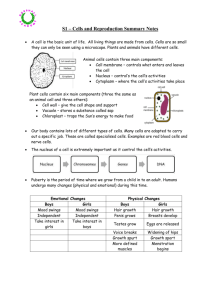
CELLS AND REPRODUCTION What you should know. WORDBANK ACID ANTHERS ANTIBODIES BACTERIA CELL WALL CELLS CHARACTERISTICS CHLOROPLASTS CHROMOSOMES COLOUR CYTOPLASM DISEASE DNA FERTILISATION FUNCTIONS FUSE GAMETES GROUP INSECTS MEMBRANE MICROBES MONTHS MOTHER NUCLEUS (X2) OVARIES (X2) OVIDUCT (X2) OVULES POLLEN PROTECT SIGNALS SPERM (X2) SPERM DUCT STIGMA STYLE TAIL TUBE UMBILICAL UTERUS VACCINATIONS VACUOLE VAGINA WALL WHITE WIND 1. All living organisms are made up of _________. All cells, both plant and animal cells, contain a ___________, which controls cell activities, a ____________ which controls the entry and exit of materials, and ____________ where chemical reactions occur. 2. Plant cells also have _____________ for photosynthesis, a _______ _________ for support and a ____________ filled with fluid. 3. There are many different types of cells, all of which have different ____________. A sperm cell has a ______ which allows it to swim. A nerve cell is branched to allow it to send ________ around the body. 4. _____________ are tiny single celled organisms that can be seen using a microscope. The type of microbe used to make yoghurt is ____________. Some microbes are harmful and can cause ____________. Our bodies can defend themselves against these using saliva, skin, stomach ______, and _______ blood cells which produce _______________ to fight the invaders. 5. ___________ give us a harmless version of the microbe, so that we produce antibodies which stay in our system and __________ us from the disease. 6. Sex cells in plants and animals are also known as ________. Flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. __________ produce the male sex cells called _____________. The female sex cells are called _________ and these are produced in the __________. Petals attract _________ which will transfer the pollen onto the __________, usually of another flower. Sometimes pollen is carried by the _______. The pollen then grows a pollen _________ which grows down the _________ and into the ovary where fertilisation takes place. This is when the male and female sex cells ________. 7. Human egg cells are produced in the ________ of females. The egg cell then enters the ___________ or fallopian tube, and travels towards the ___________. 8. __________ are produced in the testes. They leave the body through the ________ ______ and the urethra, and during sexual intercourse are deposited inside the female’s ____________. They then swim up through the uterus and into the ___________ to find the egg cell. This is where fertilisation occurs, when the nucleus of the __________ joins with the __________ of the egg. 9. The fertilised egg divides many times before implanting in the ________ of the uterus for about nine __________. During this time it develops into a human baby, with the help of nutrients and oxygen it gets from the ___________ through the placenta and_________________ cord. 10. The nucleus of a cell contains ___________ which are made of the chemical _____ which is tightly coiled up. Chromosomes carry the genetic information of an organism. This genetic information is passed on during ____________ of the egg and sperm, and it controls all the ____________ of an organism. We have inherited our eye ________, skin colour and blood ________ from our parents.