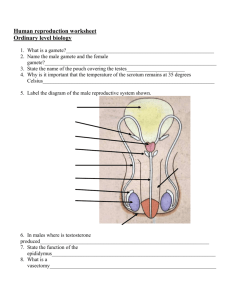
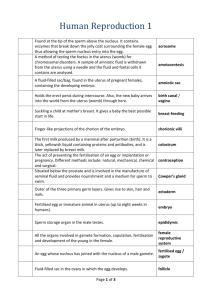
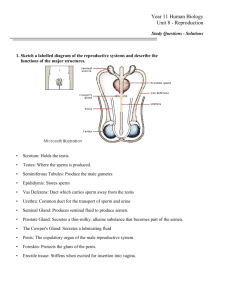
Human Reproduction 3 Placenta, membranes that surrounded the
advertisement

Human Reproduction 3 Placenta, membranes that surrounded the foetus and remains of umbilical cord discharged from the uterus after the birth of the baby. afterbirth The fluid (liquid) that surrounds a developing foetus in the uterus (womb). It acts as a shock absorber. amniotic fluid The process of bringing a newborn into the world – occurs in three stages. birth / parturition A hollow, fluid-filled sphere of cells that develops from the morula. Attached to the inner surface of the outer layer of cells (trophoblast) is an inner mass of cells from which the embryo develops. blastocyst Outermost membrane surrounding the embryo, involved in placenta formation. chorion Small internal erectile structure of the female mammalian genitals similar in structure and position (i.e. homologous) to male penis. clitoris A rubber-like sheath worn: · by males, over the erect penis · by females, inserted into the vagina, before sexual intercourse to prevent sperm entering the female vagina. It is a barrier method of contraception. A yellow body that develops in the ovary after the rupture of the Graafian follicle (ovulation). It is a source of progesterone, persists if pregnancy has occurred. condom corpus luteum Embryo having two primary germ layers, i.e. ectoderm and endoderm. diploblastic The forcible ejection of seminal fluid. ejaculation Mucus membrane that lines the uterus (womb), undergoes cyclical changes during the menstrual cycle. endometrium Using birth control methods (contraception) to plan the number of children in a family. family planning The union of a haploid male gamete nucleus with a haploid female gamete nucleus resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote. In the human female this occurs about halfway along the fallopian tube. fertilisation Developing embryo with the appearance of the fully developed animal. In humans from eight weeks after fertilisation until birth. foetus Page 1 of 3 The loose skin that covers the end of the penis. Removed during circumcision. foreskin A portion of a group of cells capable of developing into the various different tissues and organs of a new individual. Cells in the human blastocyst arrange themselves into three layers and give rise to the following tissues: · ectoderm – skin, hair, nails · mesoderm – muscles, skeleton, kidneys · endoderm – linings of the alimentary canal, trachea and bronchi. germ layer Fluid-filled vesicle in ovary of female mammal containing an egg. Graafian follicle Funnel at end of oviduct that catches the egg after ovulation and directs it into the oviduct. infandibulum Cells situated within the testes that secrete testosterone. interstitial cells A method used to treat infertility and help a woman conceive. It involves the union of the male gamete nucleus with the female gamete nucleus outside the woman’s body (in a ‘test tube’ or other laboratory environment). in-vitro fertilisation Milk production by the breasts of mammals. lactation The organs involved in gamete formation and copulation in the male. male reproductive system The discharge of menstrual fluid consisting of blood, lining of womb (endometrium) and unfertilised egg, which occurs monthly from puberty to menopause. menstruation / period The outer muscular wall of the uterus. myometrium The changes that take place in an ovary from the beginning of one menstruation to the onset of the next. ovarian cycle A hormone produced by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland in response to the sudden fall in the levels of oestrogen and progesterone. It stimulates contractions of the uterus during labour. A structure attached to the inner surface of the womb (uterus) of pregnant mammals, which helps to nourish the foetus, and discharges its waste. oxytocin placenta A hormone produced by the ovaries. Stimulates endometrium (lining progesterone of womb) growth in preparation for and during pregnancy. Page 2 of 3 A hormone secreted by the placenta. Relaxes the joints of the pelvic girdle and aids in the dilation of the cervix. relaxin External pouch in most male mammals that contains (holds) the testes outside the body at a temperature slightly lower (35°C ) than body temperature (37°C in humans) for the efficient production of sperm. scrotum Manufactures seminal fluid (semen) which nourishes the sperm and allows them swim. seminal vesicle Occurs in three phases—arousal, copulation and orgasm. sexual intercourse Tube through which sperm travel from their place of storage (the epididymis) to the urethra in humans. sperm duct / vas deferens Embryo having three primary germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. triploblastic One of a pair of animals born at the same time to the same mother. There are two types: identical and fraternal. twin Holds the developing embryo during pregnancy. Another name for the womb. uterus Cutting and tying, or removal of part of, the vas deferens for sterilisation of the male. vasectomy A diploid cell resulting from the union of two haploid gametes, i.e. a fertilised egg. zygote Page 3 of 3