SCOS Objective: The atmosphere can be studied to
advertisement

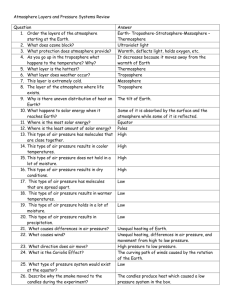
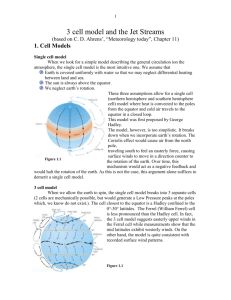
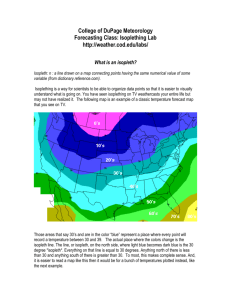
A 2.2 The atmosphere has wind patterns Two-Column Notes Name Topic: A2.2 The atmosphere has wind patterns. Period Uneven heating causes air to move (A47). Date _______ Weather is the __________________ of Earth’s atmosphere at a particular ______________ and _________________. _______________ is a very important part of weather. Wind is air that moves _____________________, or parallel to the ________________________. Uneven ____________________ of Earth’s surface causes such pressure differences, which set air in ________________. How wind forms (A48) Sunlight is concentrated _____________ the equator because it strikes the surface _______________. Sunlight is more _______________ out near the poles because it ____________ at a ______________ angle. The warm air _________________, and an area of low _______________ forms. The cooler, _________________ air ___________slowly, and an area of ____________ pressure forms Air moves as ________________ across the surface, from ______________ pressure to _________________ pressure. When the difference in _____________________ between two areas is small, the wind may move ________ ______________ to be noticeable. A very large __________________ difference can produce wind _____________ enough to uproot trees. Global Winds (A48) Global winds travel _______________ of km in ___________ ________________. Uneven heating between the ____________________ and _______________ ___________________ causes global winds. Earth’s rotation affects wind direction (A49) If Earth did not _______________, global winds would flow directly from the _____________ to the _____________. A 2.2 The atmosphere has wind patterns Earth’s rotation __________________ the direction of winds and other objects moving _____________ the Earth. Earth’s rotation affects wind direction (A49) The influence of Earth’s rotation on free moving objects is called the ___________________ __________________. In the N. Hemisphere, winds curve to the __________________ in the direction of the motion. Winds in the S. Hemisphere curve to the _______________. Because the Coriolis Effect causes _______________ winds to ______________, they cannot flow directly from poles to the equator. Instead, global winds ______________ along __________ routes in each ____________________. Global Wind Belts (A50-51): Trade winds: Blow from the _____________, moving from the horse latitudes ___________the ____________. (0o to 30o N & S of equator). Westerlies: Blow from the _____________, moving from the horse latitudes _____________ the _____________. (30o to 60o N. & S. of equator) They bring ____________ across much of the _____________ ______________. Easterlies: Blow from the ______________, moving from the _____________ regions toward the mid- _____________ (60o to 90o N. & S. of equator) Jet Streams flow near the top of the troposphere (A52) Jet streams usually flow in the ________________ troposphere from ___________ to ____________for thousands of kilometers. Each hemisphere has ________ jet streams, a ____________ jet stream and a __________________ jet stream. The polar jet stream has a _______________ influence on weather in _________________ America. Scientists must know ________________ the jet stream is flowing to make _________________ weather predictions. A 2.2 The atmosphere has wind patterns