The collision theory of reactions
advertisement
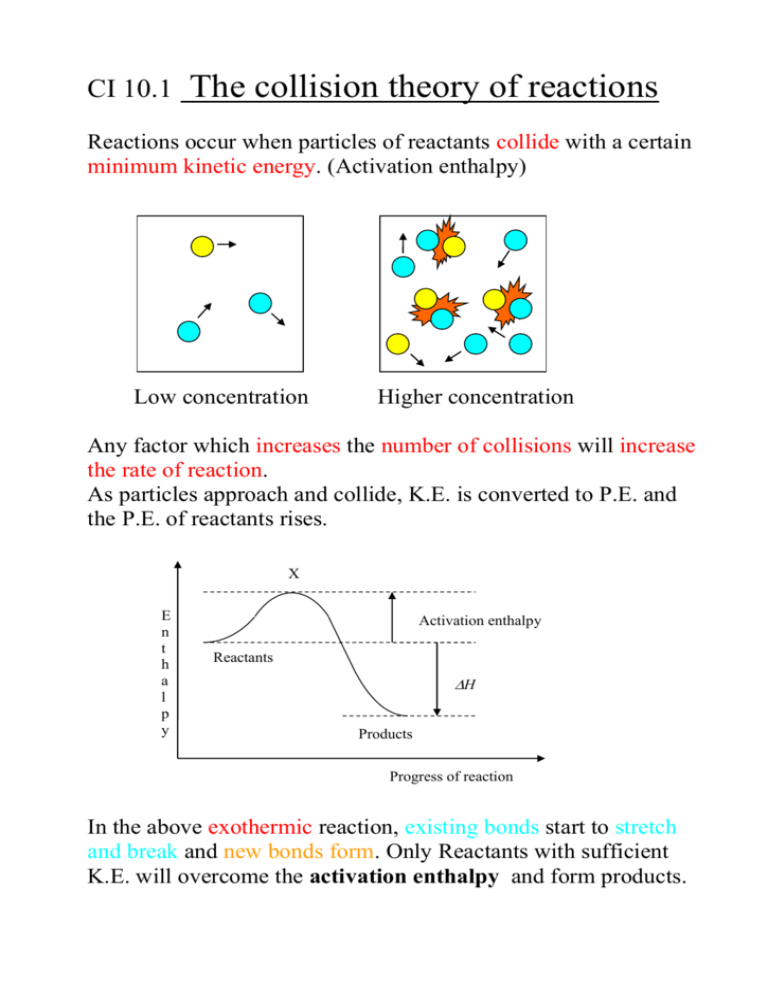
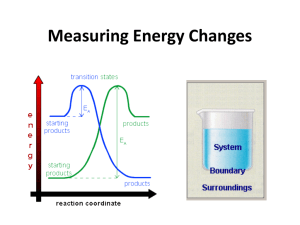
CI 10.1 The collision theory of reactions Reactions occur when particles of reactants collide with a certain minimum kinetic energy. (Activation enthalpy) Low concentration Higher concentration Any factor which increases the number of collisions will increase the rate of reaction. As particles approach and collide, K.E. is converted to P.E. and the P.E. of reactants rises. X E n t h a l p y Activation enthalpy Reactants H Products Progress of reaction In the above exothermic reaction, existing bonds start to stretch and break and new bonds form. Only Reactants with sufficient K.E. will overcome the activation enthalpy and form products. At higher temperatures, more of the colliding particles have enough energy to react. Enthalpy profiles X E n t h a l p y Activation enthalpy Reactants H Products Progress of reaction The curved line is the energy pathway for a pair of colliding molecules (called the energy or enthalpy profile for the reaction). X corresponds to the arrangement of atoms where old bonds are stretched and new bonds are starting to form. Eg. For chlorine atoms and ozone, the oxygen – oxygen bonds in ozone break and a new bond between oxygen and chlorine is forming. Cl + O3 Cl------O------O O ClO + O2 At X (this is a very unstable arrangement and only lasts for a very short time). The enthalpy profile is shown as a single curve (this is only true for single-step reactions). Other reactions have several steps, so the enthalpy profile would show several steps, too. do problems for 10.1 ‘Rates of Reactions’ p. 222-223 questions 1 to 4. 1. For each of the following reactions, say how, if at all, you would expect its rate of reaction to be affected by the following factors: a) Temperature b) Total pressure of gas. c) Concentration of solution d) Surface area of solid a b C A Rate will Rate will Rate will increase with increase with increase with temperature temperature temperature B Rate of Rate increases Rate of forward forward reaction not reaction not affected affected C Increasing the Solutions not Increasing the concentration involved concentration of acid will of peroxide increase the will increase rate the rate D The more The more Solids not finely divided finely divided involved the the catalyst the magnesium, faster the rate the faster the rate 2.) Both the acid and the enzyme can act as catalysts for the hydrolysis of a protein. 3. a) The greater the concentration of reactants, the greater the rate of collisions and hence the faster the reaction proceeds. 3 b) A change of temperature has little effect. Most collisions result in a reaction. 4 a) B and C b) A and D c) D d) B e) B f) D