Parts of Speech
advertisement

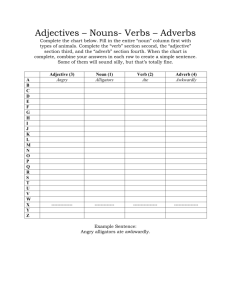
Parts of Speech in the English Language There are thousands of words in any language. But not all words have the same job. For example, some words express "action". Other words express a "thing". Other words "join" one word to another word. These are the "building blocks" of the language. Think of them like the parts of a house. When we want to build a house, we use concrete to make the foundations or base. We use bricks to make the walls. We use window frames to make the windows, and door frames to make the doorways. And we use cement to join them all together. Each part of the house has its own job. And when we want to build a sentence, we use the different types of word. Each type of word has its own job. We can categorize English words into 8 basic types or classes. These classes are called "parts of speech". It's quite important to recognize parts of speech. This helps you to analyze sentences and understand them. It also helps you to construct good sentences. Following is an overview of the eight parts of speech, and a quiz to check your understanding: Parts of Speech Table This is a summary of the 8 parts of speech*. You can find more detail if you click on each part of speech. Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example Sentences Verb action or state (to) be, have, do, like, work, sing, can, must EnglishClub.com is a web site. I like EnglishClub.com. Noun thing or person This is my dog. He lives in my house. We live in London. Adjective describes a noun pen, dog, work, music, town, London, teacher, John a/an, the, 69, some, good, big, red, well, interesting 1 Toshiba SATELLITE | 1 My dog is big. I like big dogs. LTC. MOHAMMAD ABU ZAID Adverb describes a verb, adjective or adverb quickly, silently, well, badly, very, really My dog eats quickly. When he is very hungry, he eats really quickly. Pronoun replaces a noun I, you, he, she, some Tara is Indian. She is beautiful. Preposition links a noun to another word to, at, after, on, but We went to school on Monday. Conjunction joins clauses or sentences or words and, but, when I like dogs and I like cats. I like cats and dogs. I like dogs but I don't like cats. Interjection short exclamation, sometimes inserted into a sentence oh!, ouch!, hi!, well Ouch! That hurts! Hi! How are you? Well, I don't know. * Some grammar sources categorize English into 9 or 10 parts of speech. Examples of other categorizations are: Verbs may be treated as two different parts of speech: o Lexical Verbs (work, like, run) o Auxiliary Verbs (be, have, must) Determiners may be treated as a separate part of speech, instead of being categorized under Adjectives. Parts of Speech Examples Here are some sentences made with different English parts of speech: verb noun verb noun verb verb Stop! John John is working. works. 2 Toshiba SATELLITE | 2 LTC. MOHAMMAD ABU ZAID pronoun verb noun noun verb adjective noun She animals. Animals like kind people. loves noun verb noun adverb noun verb adjective noun John English well. John good English. speaks speaks pronoun verb preposition adjective noun She to the station quickly. ran adverb pron. verb adj. noun conjunction pron. verb pron. She likes big snakes but I hate them. Here is a sentence that contains every part of speech: interjection pron. conj. adj. noun verb prep. noun adverb Well, she young John to school slowly. and walk Words with More than One Job Many words in English can have more than one job, or be more than one part of speech. For example, "work" can be a verb and a noun; "but" can be a conjunction and a preposition; "well" can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection. In addition, many nouns can act as adjectives. To analyze the part of speech, ask yourself: "What job is this word doing in this sentence?" 3 In the table below you can see a few examples. Of course, there are more, even for some of the words in the table. In fact, if you look in a good dictionary you will see that the word but has six jobs to do: Toshiba SATELLITE | 3 LTC. MOHAMMAD ABU ZAID Verb, noun, adverb, pronoun, preposition and conjuction! word part of speech example noun My work is easy. verb I work in London. conjunction John came but Mary didn't come. preposition Everyone came but Mary. adjective Are you well? adverb She speaks well. interjection Well! That's expensive! noun We ate in the afternoon. noun acting as adjective We had afternoon tea. work but well afternoon 4 Toshiba SATELLITE | 4 LTC. MOHAMMAD ABU ZAID Quiz Determine which part of speech is the underlined word: 1. I bought a beautiful dress at the mall. 2. What did she ask you to do? 3. I left my shoes under the kitchen table. 4. If we finish our work quickly we can go to the movies. 5. On Saturdays I work from nine to five. 6. I want to go to a university in the United States. 7. I'm sure I have met your girlfriend before. 8. Well, I don't think I will be here to answer the phone. 9. Andy knocked on the door but nobody answered. 10. After lunch let's go out for a coffee. Answer Key: (1) adjective, (2) pronoun, (3) preposition, (4) adverb, (5) verb, (6) noun, (7) verb, (8) interjection, (9) conjunction, (10) preposition 5 Toshiba SATELLITE | 5 LTC. MOHAMMAD ABU ZAID