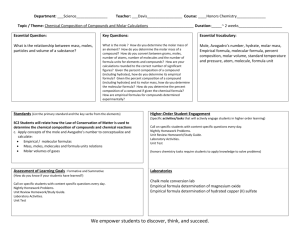
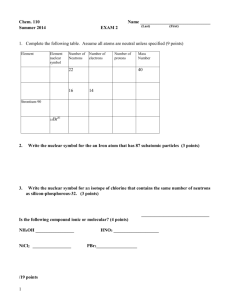
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry
advertisement

Unit 6: The Mathematics of Chemical Formulas Name: _________KEY____________ Text Questions from Corwin 1. Why do we count atoms in groups? they are too small to count individually 2. Avogadro’s number of marbles would be the size of… the Moon 9.1 3. Avogadro’s number is sometimes referred to as… the chemist’s dozen 9.2 4. How do we define a mole? the amount of substance that contains Avogadro’s number of particles 5. The mole relationship allows us to convert between what? the number of particles and the mass of substance 9.3 6. What is the molar mass? the atomic mass of a substance expressed in grams 7. The atomic mass of iron is _55.85 amu_; the molar mass of iron is _55.85 g_. 8. How can we calculate the molar mass of a compound? by adding the molar masses of each element in it 9.4 9. What is the central unit in chemistry? the mole 9.5 10. What did Avogadro propose in 1811? that two gases containing equal numbers of molecules occupy equal volumes under similar conditions 11. Standard temperature is _0oC_. Standard pressure is _1 atm_, which is… the atmospheric pressure exerted by air at sea level 12. What is the molar volume? the volume occupied by 1 mol of any gas at STP 9.6 13. Write the three interpretations of the mole. 1 mol = 6.02 x 1023 particles, 1 mol = molar mass, 1 mol = 22.4 L at STP 9.7 14. What does the percent composition of a compound list? the mass % of each element 15. What two things are compared in finding the percent composition of, say, water? the molar masses of hydrogen (and oxygen) and the molar mass of the whole compound 9.8 16. What two things did chemists measure in determining the formula of a compound containing oxygen? the mass of the element and the mass of the oxide after reaction 17. The empirical formula of a compound corresponds to what? the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a molecule 18. We determine the ratio of the empirical formula from the _moles_ of each element. 19. What did the EPA discover about benzene? it is a carcinogen 9.9 20. Molecular compounds are represented by what? individual molecules composed of nonmetal atoms 21. The molecular formula is some _multiple_ of the empirical formula. 22. The two things you need to calculate the molecular formula of a compound are the compound’s _molar_ _mass_ and the mass of the _empirical_ _formula_. Unit 6: The Mathematics of Chemical Formulas Name: _________________________ Text Questions from Corwin 1. Why do we count atoms in groups? 2. Avogadro’s number of marbles would be the size of… 9.1 3. Avogadro’s number is sometimes referred to as… 9.2 4. How do we define a mole? 5. The mole relationship allows us to convert between what? 9.3 6. What is the molar mass? 7. The atomic mass of iron is _________; the molar mass of iron is _________. 8. How can we calculate the molar mass of a compound? 9.4 9. What is the central unit in chemistry? 9.5 10. What did Avogadro propose in 1811? 11. Standard temperature is _____. Standard pressure is ________, which is… 12. What is the molar volume? 9.6 13. Write the three interpretations of the mole. 9.7 14. What does the percent composition of a compound list? 15. What two things are compared in finding the percent composition of, say, water? 9.8 16. What two things did chemists measure in determining the formula of a compound containing oxygen? 17. The empirical formula of a compound corresponds to what? 18. We determine the ratio of the empirical formula from the ________ of each element. 19. What did the EPA discover about benzene? 9.9 20. Molecular compounds are represented by what? 21. The molecular formula is some ____________ of the empirical formula. 22. The two things you need to calculate the molecular formula of a compound are the compound’s _________ ________ and the mass of the ______________ ____________.