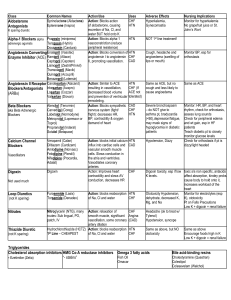
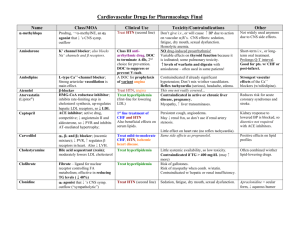
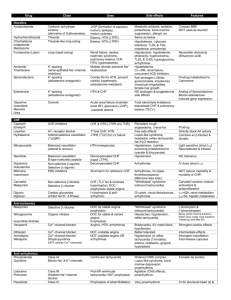
Post Operative Hypertension
advertisement

Drugs Mechanism of Action Labetolol Alpha 1 and Beta 1 & 2 receptor blockers Esmolol Beta 1 receptor blocker, little or no B2 except @ high doses. No ISA Uses Mild to severe HTN or hypertensive emergencies SVT, A-fib, Aflutter, HTN Onset 2-5 minutes 2-10 minutes Metoprolol B1 competetive inhibitor. No ISA Hydralazine Direct vasodilation of arterial smooth muscle. Decreases diastolic > systolic, increases HR, CO , SV, also causes Na and H20 retention. Nitroglycerin Organic nitrate: vasodilating agent, releases tension on vascular smooth muscle and dilates peripheral veins and arteries. Converted to nitric oxide intracellularly Increases cGMP in smooth muscle. Decreases preload and afterload Ventricular Moderate to HTN, CHF, MI arrythmias, severe HTN, with HTN, angina, precomplications, A-flutter, A-fib, eclampsia, Angina symptomatic tx with of hypertropic isosorbide subaortic dinitrate in stenosis African American in CHF 20 minutes 5-20 immediate minutes Nitroprusside Direct arterial and peripheral vasodilation Hypertensive crisis, CHF < 2 minutes Peak 5-15 minutes Duration Metabolism 2-4 hours Hepatic 10-30 minutes Red blood cell esterases 5-8 hours Hepatic T 1/2 Excretion Dose 5.5 hours urine Up 20mg, 0.25mg/kg, may use 4080mg in 10 minutes intervals, max dose of 300mg 9 minutes urine Loading: 500mcg/kg over 1 minute. Follow wit a 50mcg/kg/minutes over 4 minutes. Can rebolus with 500mcg/kg over 1 minutes and increase infusion to 100mcg/kg/minute. Usual dosage range is 50200mcg/kg/min Cardiogenic shock, uncompensated CHF, bradycardia, Contraindications Cardiogenic shock, uncompensated 10-80 minutes 2-6 hours Hepatic immediate 3-8 hours urine 5mg q 2-3 minutes for 3 doses for MI 2-4 hours urine 5-20mg 1-4 minutes urine Start 5mcg/min, then can increase 5mcg until get to 20mcg/min, if no change, then can start increasing by 10mcg intervals up to 100-200mcg Cardiogenic shock, uncompensated Severe AS Hepatic ,rbc’s, vascular walls 1-10 minutes Hepatic cyanide prussic acid thiocyanate (monitor acid/base status-acidosis of cyanide toxicity). Drug is broken down by UV light so must be wrapped in foil. <10 minutes urine Initial: 0.30.5mcg/kg/minute. Increase by 0.5 mcg/kg/minute. Usual dose is 3 mcg/kg/min. Up to 10mcg/kg/min Coarctation of aorta, caution in increased ICP. Most common Side effects CHF, bradycardia, pulmonary edema, heart block pulmonary edema, heart block Orthostatic hypotension, dizzyness Hypotension, diaphoresis, nausea CHF, bradycardia, pulmonary edema, heart block, severe COPD, syst bp <100, AV conduction ABN Fatigue, dizziness, weakness H/A, palpation, tachycardia, lupus like syndrome Hypotension, tachyarrythmias, rash xerostomia, lightheadedness, H/A H/A, palpitations, hypotension, thyroid suppression, metheglobinemia, cyanide toxicity