Drugs Exam 2
advertisement

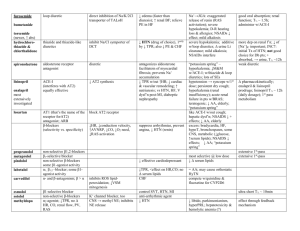
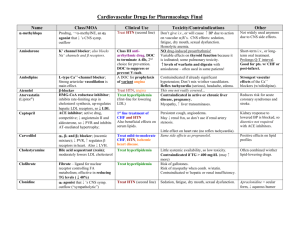
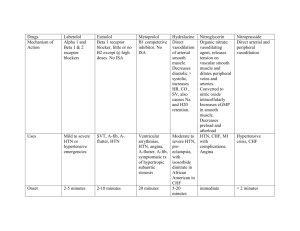
Drug Diuretics Acetazolamide Hydrochlorothiazide Chlorhalidone Indapamide Metolazone Furosemide (Lasix) Amiloride Triamterene Spironolactone Class Uses Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (derivative of Sulfonamides) Thiazide Thiazide-like long acting IOP (formation of aqueous humor); epilepsy; motion sickness Edema, HTN (TPR) Edema, HTN (TPR) Loop (rapid-acting) Renal failure, ascites, nephrotic syndrome, pulmonary edema, CHF, HTN, hypercalcemia Modest diuretic prevents Na+ reabsorption K+-sparing (renal epithelial Na+-channel inhibitors) K+-sparing (aldosterone antagonist) Combo Rx for HTN, prevent cardiac hypertrophy (aldosterone-mediated) Side effects Metabolic acidosis, sedation, parasthesia, bone marrow suppression, allergic rxn Same as below Hypokalemia, glucose tolerance, LDL & TGs, impotence, arrhythmias Hypotension, hypokalemia, ototoxicity, hyperuricemia, LDL & HDL hyperglycemia, arrhythmias Hyperkalemia CI—DM, renal failure, concurrent ACE-inhibitors Anti-androgen (libido, gynecomastia, impotence) menstrual irregularities, female hair growth NO androgen & progesterone side effects Eplerenone K+-sparing (aldosterone antagonist) HTN & CHF Glycerine Isosorbide Mannitol Urea Osmotic Acute renal failure (maintain renal BF), glaucoma (IOP), cerebral edema Total electrolyte imbalance, exacerbate CHF & pulmonary edema (ECV) ACE-inhibitors CHF & HTN (TPR w/o HR) AT1-receptor blocker Arterial-selective vasodilator (cGMP) 1st-line CHF; HTN TPR (CO) for LV failure Nitroprusside Balanced vasodilator (arterial & venous) HTN emergencies Nesiritide Balanced vasodilator B-type natriuretic peptide Non-selective -agonist Selective 1-agonist PDE-inhibitors Decompensated CHF (rapid TPR) Decompensated CHF Persistent cough, angioedema, renal fxn Few side effects Lupus-like syndrome, headache, reflex tachycardia, Na+/H2O retention Hypotension, cyanide poisoning (metabolized to cyanide & thiocyanate) Hypotension Carvediol Metoprolol Non-selective -blocker Selective 1-blocker Digoxin Digitoxin Cardiac glycosides (inhibit Na+/K+ ATPase) CHF (LV fxn & reverses hypertrophy); DOC prophylaxis stable angina (+)inotropism & antiarrhythmic Anti-ischemics Metoprolol Selective 1-blocker Nitroglycerine Organic nitrates Isosorbide dinitrate Verapamil Ca2+-channel blocker DOC for stable angina prophylaxis DOC for stable & variant angina Prophylaxis Angina, HTN, arrhythmias Diltiazem Amlodipine Nifedipine Ca2+-channel blocker Ca2+-channel blocker Dihydropyridines NOT unstable angina NOT unstable angina OR arrhythmias CHF Captopril Enalapril Losartan Hydralazine Dopamine Dobutamine Milrinone Inamrinone Short-term for refractory CHF (NOT cardiac Ca2+-channels) Anti-arrhythmics Procainamide Quinidine Lidocaine Phenytoin Flecainide Features Crosses BBB NOT used as diuretic! Reversible ototoxicity (Ethacrynic acid) Prodrug metabolized to Canrenone Analog of Spironolactone Blocks aldosteroneinduced gene expression Prodrug Directly block AII activity Combine w/ -blocker & diuretic Light sensitive (short t1/2) Reconstituted & infused NO tolerance Arrhythmias IV dose (short t1/2) Arrhythmias, GI upset, thrombocytopenia (Milrinone less toxic) “Withdrawal” syndrome (rebound tachycardia) NOT reduce morbidity & mortality of CHF! GI upset, visual disturbances, arrhythmias Carvediol racemic mixture antioxidant & antiproliferative t1/2=42h, renal metabolism t1/2=5d, hepatic metabolism “Withdrawal” syndrome (rebound tachycardia) Headaches, hypotension, reflex tachycardia (-)inotropism & (-)chronotropism Bradycardia, AV nodal block, hypotension Better tolerated Hypotension w/ reflex tachycardia (mortality), edema, headache, gingival hyperplasia Strongest cardiac effects Torsade de pointes CI for structural heart dz & Class IA Blocks Na+ & K+-channels Ventricular tachycardia Class IB Weakest Na+-channel blocker Class IC Post-MI ventricular tachycardia; NOT prophylaxis Widened QRS complex, Lupus-like syndrome, bone marrow depression, proarrhythmic Agitation (CNS effects), proarrhythmic Prophylaxis of atrial fibrillation Very proarrhythmic Spray (short onset & duration) Patch (slow onset, long duration) Tablets go bad after 6m Intermediate effects Strongest vasodilation Fast-release capsules Propranolol Amiodarone Sotalol Verapamil Adenosine HTN Prazosin Hydralazine Minoxidil Nitroprusside Hyperlipidemia Simvastatin (Zocor) Atorvastatin (Lipitor) Cholestyramine Colesevelam (WelChol) Strongest Na+-channel blocker Class II -blocker Class III K+-channel blocker Class III -blocker & K+-channel blocker Class IV Ca2+-channel blocker G-protein receptor agonist (-)inotropism DOC for rate control of atrial fibrillation Most arrhythmias (especially structural heart dz) mortality following MI Warfarin & Digoxin levels Prophylaxis of atrial fibrillation (especially ischemic heart dz) Pulmonary toxicity, hypothyroidism OR thyrotoxicosis Torsade de pointes, bronchoconstriction DOC for rate control of atrial fibrillation Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, AV nodal reentry tachycardia Flushing, cardiac arrest (SA/AV nodal block), bronchoconstriction A1 (negative inotropism) A2 (vasodilation) A3 (histamine release) ONLY for severe arrhythmias OR low risk of proarrhythmias Diuretics, ACEIs (1st-line), AT1-blockers (1st-line), -blockers (1st-line), Ca2+-channel blockers, 2-agonists HTN w/ benign prostatic Fluid retention, 1st-dose Selective 1-blocker syncope, orthostatic hyperplasia (HDL & LDL) hypotension Arterial-selective vasodilator Severe HTN Lupus-like syndrome, Combo w/ -blockers & headache, Na+/H2O retention, diuretics reflex tachycardia Direct vasodilator Severe HTN Hair growth (Rogaine) Stimulates K+ channels to hyperpolarize SM Balanced vasdodilator HTN emergency (quickest IV infusion VS. Diazoxide Thiocyanate toxicity, ICP (arterial & venous) onset & shortest duration) (IV bolus) Combo therapy (Statin + Resin + Niacin) can LDL >70% HMG-CoA reductase 1st-line LDL, HDL, TGs inhibitor Upregulate liver LDL (reversible, competitive) receptors BA sequestrants Moderate LDL (younger (anion exchange resins) persons & pregnancy), slight HDL, NO effect TGs Niacin Selective cholesterol absorption inhibitor Nicotinic acid LDL, HDL, TGs (additive effect w/ Statin) Atherogenic dyslipidemia, Modest LDL, HDL, Marked TGs Gemfibrozil (Lopid) Fibrates Modest LDL, HDL Marked TGs Ezetimibe (Zetia) depressed LV fxn Minimal CI—liver dz, pregnancy & nursing GI upset, reduced drug absorption CI—TGs >400mg/dL familial dysbetalipoproteinemia CI—liver dz, pregnancy & nursing Flushing, hyperglycemia, gout, GI upset (combine w/ ASA/NSAID or titer up) CI—liver dz, PUD, gout, DM Dyspepsia, GI upset, gallstones, myopathy Lovastatin & Pravastatin prodrugs Extensive 1st-pass p450 Combo w/ Statins for very high LDL NOT absorbed b/c so large NOT effect fat-soluble vitamins Niaspan (extendedrelease) Mono OR combo therapy Mono OR combo therapy risk for acute pancreatitis CI—liver OR renal insufficiency Anti-thromboembolics Aspirin Irreversible COX-1 & 2 inhibitor MI, unstable angina, TIA, stroke Dipyridamole Platelet phosphodiesterase inhibitor (cAMP) Thienopyridines Irreversible platelet ADP receptor inhibitors Stroke prevention Abciximab (antibody) Eptifibatide (peptide) Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors Heparin Unfractionated anticoagulant Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Fractionated (LMWH) anticoagulant Acute coronary syndromes, prevent restenosis following intervention DVT, PE, MI, arrhythmias, CABG or valve replacement, stroke prevention Same as above Fondaparinux Factor Xa selective inhibitor (Pentasaccharides) Direct thrombin inhibitor (blocks thrombin binding sites on Factors) (blocks thrombin receptors on platelets) Oral anticoagulants (vit.K-dependent carboxylation inhibitor) Clopidogrel (Plavix) Ticlopidine Bivalirudin Argatroban Aprotinin Warfarin (Coumadin) Stroke prevention (patients intolerant to ASA) CI—ulcer, hypersensitivity, thrombocytopenia, bleeding disorder, <16yo, concurrent anticoagulants GI upset, hypersensitivity CI—asthma, bleeding Bone marrow suppression (Ticlopidine), bleeding, GI upset CI—bleeding, liver dz, kids Bleeding, hypotension, hypersensitivity CI—thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia, rash, osteoporosis Lower risk thrombocytopenia Prevention of DVT following hip/knee surgery Prevents Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), prevent bleeding after intervention Anemia, GI upset, injection rxn Bleeding, hypersensitivity w/ repeated exposure Long-term (delayed onset) therapy Hemorrhage, necrosis (early thrombosis w/ rapid protein C loss), GI upset, teratogenic, 7-10d duration Adjuvant w/ ASA (Aggrenox) Expensive Inhibit platelet aggregation (fibrinogen binding) IV dosing Rapid & short duration RES elimination Requires aPTT monitoring Easier SC dosing, NO monitoring, longer t1/2 Renal elimination Synthetic (less variable prep) Requires monitoring PT time (INR) drug interactions CI—liver dz Alteplase Anistreplase -Aminocaproic acid (EACA) Recombinant tPA (activates plasmin on fibrin) Streptokinase-plasminogen complex (NOT specific to fibrin) Competitive inhibitor of plasminogen & PAs DOC for acute MI DVT & PE Acute MI Serine protease inhibitor of plasmin & SK-plasminogen Antidote for excessive fibrinolytic therapy & hemophilia Antidote for excessive fibrinolytic therapy & postop Oral Fe (most common) Fe-deficiency Fe-deficiency Fe-hydroxide dextran Ferrous gluconate, fumarate, lactate, cholinate Parenteral Fe Deferoxamine Fe chelator Cyanocobalamin Hydroxycobalamin Stable vit.B12 Leucovorin Folic acid Epoetin- (Epogen or Procrit) Recombinant erythropoietin Aprotinin Anemia Ferrous sulfate Organic Fe salts Antihistamines Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Fe-deficiency (patients cannot tolerate OR absorb oral Fe) Acute & chronic Fe overload Dietary deficiency (rare), achlorohydria, Crohn’s dz, pernicious anemia Dietary deficiency, malabsorption, alcoholism, drug-induced (esp. due to antifolates) Renal failure, chemo, HIV, frequent blood donations 1st-generation H1-blocker (oral or topical) Nasal allergies, allergic dermatoses, direct suppression of cough center, insomnia (OTC sleep aids) Nasal allergies, dermatoses Fexofenadine (Allegra) 2nd-generation H1-blocker (oral) 2nd-generation H1-blocker (oral) 2nd-generation H1-blocker (oral) Promethazine (Phenergan) H1-blocker (less selective than 2nd-generation) Motion sickness, vomiting Proton pump inhibitors (selective, irreversible H+/K+ ATPase inhibitors in gastric parietal cells) Selective H2-blockers (competitive, reversible) GERD, combo therapy for H.pylori ulcers Cetirizine (Zyrtec) Loratadine (Claritin) GI Omeprazole (Prilosec) Pantoprazole (Protonix) Cimetidine (Tagamet) Ranitidine (Zantac) Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of magnesia) Aluminum hydroxide Bismuth (Pepto Bismol) Sucralfate (Carafate) Misoprostol (PG) Metoclopramide Cisapride Tetracyclines Ondansetron (Zofran) OTC antacids Nasal allergies, dermatoses Nasal allergies, dermatoses Duodenal ulcer healing, prevent nocturnal acid breakthrough (some PPIs) Acid neutralization IV dosing w/in 4-6h Derived from Strep Cheap GI upset, heartburn, constipation Fewer SE Anaphylaxis Allergic rxn, hypotension, ocular defects (histamine release) Cheap More expensive Complex dosing forms IM or IV (rapid buildup of Fe stores) IM or slow IV (prevent SE) Oral (IM for pernicious anemia) Rare Oral or IV Recovery w/in 10d HTN, seizure, headache, GI upset, edema, fatigue MUST maintain Fe levels w/ long-term therapy Sedation (crosses BBB), antimuscarinic (dry mouth, tachycardia, blurred vision, constipation), ED, appetite loss CI—nursing, babies Dose-dependent sedation (liver dz) Non-sedative (NOT cross BBB), NO tachycardia Minimal sedation, antimuscarinic, NO QT prolongation BP effects (central anti-ACh), rash, sedative Most effective prior to histamine release 4-6h duration Hypochlorhydria w/ gastric bacterial overgrowth, hypergastrinemia, gastric cancer (long-term) Mental confusion, renal disturbances, inhibits p450 (Cimetidine) GI upset, renal problems, altered drug absorption Protonix acid stable Omeprazole inhibits drug metabolism 12-24h duration >24h duration 1-12h duration Combo w/ cold meds Quick onset, 2-8h duration Structure similar to histamine basal acid secretion Diazepam absorption w/ AlOH & w/ MgOH (Amphojel) Mucosal protection & healing AlOH & sulfated sucrose complex Inhibits acid production (binds parietal cell receptor & cAMP) Serotonin receptor agonists Mucosal protection, promotes PG synthesis mucosal thickness, mucosal BF, HCO3secretion GERD (rarely used) Antibiotics 5-HT3-receptor blockers NOT neutralize acid Constipation, altered drug absorption Diarrhea, uterine stimulant CI—pregnancy Forms viscous suspension that binds mucosa H.pylori-associated PUD Parkinson’s-like Sx (Metoclopramide) Disruption of GI flora N&V (esp. w/ chemo) Constipation, diarrhea, Cisapride removed from market for arrhythmias Triple-component regimen (TCN, PPI, Bismuth, Metronidazole) for 14d Extensive p450 Granisetron (Kytril) Metoclopramide (Reglan) Prochlorperazine (Compazine) Sulfasalizine (Azulfidine) Prednisone Budenoside 6-Mercaptopurine Infliximab (Remicade) Entanercept (Enbrel) Mineral oil Docusates Phenolphthalein Bisacodyl Loperamide (Imodium) Diphenoxylate headache, light-headedness Extrapyramidal effects, restlessness, sedation, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea Masks gag reflex, tranquilizer, jaundice Fever, malaise, N&V, headaches, epigastric discomfort, diarrhea, allergic rxns metabolism Promote gastric emptying (peripheral) & suppress vomiting (central) Bone marrow loss, opportunistic infection, teratogenic SLE & lymphoma (long-term) May take 3-6m to work D2-receptor blocker, 5-HT3receptor blocker, & 5-HT4 agonist D2-receptor blocker (in CTZ) N&V (esp. w/ chemo) 5-aminosalicylates (inhibits arachidonic acid metabolism, scavenges ROS, immune effects) Glucocorticoids (outside US) Immunosuppressive (inhibits lymphocyte proliferation) Chimeric Ig (binds & neutralizes TNF-) Fusion protein of TNF-R & IgG1 Fc portion Stool softeners (lower ST) Mild UC & IBS Diphenylmethane derivative Constipation Removed from market over concerns w/ long-term use Diphenylmethane derivative (stimulates mucosal nerve plexus of colon) Opioid (improves anal sphincter tone) Opioid (metabolized to Difenoxin) Constipation & pre-op colonic cleanse Severe intestinal cramps, damaged colonic tone (longterm) CNS effects (overdose, esp. in kids) N&V 90% remission UC & 60-90% Crohn’s dz Severe UC & maintain UC remission Crohn’s dz Prodrug metabolized to Sulfapyridine (causes SE) & 5-ASA mesalamine (active portion) in colon Crohn’s dz Neutralizes TNF- Constipation Little efficacy Diarrhea (activity against cholera & some E.coli toxins) Diarrhea CNS effects Induce low-grade inflammation, fluid accumulation, & motility Stomach (>6h onset) Rectal (30-60min) Binds peripheral -opioid receptors & relaxes intestinal contractions Marketed w/ Atropine (Lomotil or Motofen) to discourage abuse