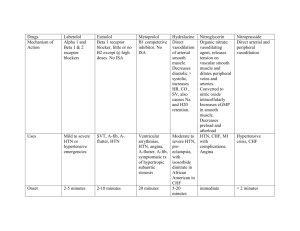
Class Aldosterone Antagonists Common Names Sprinolactone (Aldactone) Eplerenone (Inspra) K sparing diuretic Alpha-1 Blockers alpha Prazosin (minipress) Terazosin (Hytrin) Doxazosin (Cardura) Angiotensin Converting Enalapril (Vasotec) Enzyme Inhibitor (ACE) Ramipril (Altace) Captopril (Capoten) Lisinopril (Zestril/Prinivil) Transolapril (Mavik) Quinapril (Accupril) Benazepril (Lotensin) Angiotensin II Receptor Candesartan (Atacand) Blockers/Antagonists Irbesartan (Avapro) Losartan (Cozzar) (ARBs) Valsartan (Diovan) adrenergic agonists Beta Blockers aka Beta Adrenergic Blockers Calcium Channel Blockers Vasodilators Digoxin Atenolol (Tenormin) Carvedilol (Coreg) Labetalol (Normodyne) Metroprolol (Lopressor or Toprol) Propranolol (Inderal) Sotalol (Betapace) Verapamil (Calan) Diltiazem (Cardizem) Amlodipine (Norvasc) Felodipine (Plendil) Nifedipine (Procardia, Adalat) Digoxin Not used much Loop Diuretics (not K sparing) Nitrates Thiazide Diuretic (not K sparing) Furosemide (Lasix) Torsemide (Denadex) Action/Use Uses CHF Action: Blocks action HTN of aldosterone, causing excretion of Na, Cl, and water BUT hold onto K HTN Action: Blocks alpha-1 vasoconstriction (reduce peripheral resistence) Action: Blocks conversion of HTN angiotensin I to angiotensin CHF II, promoting vasodilation. CAD Action: Similar to ACE resulting in vasodilation, decreased blood volume and prevention of ventricular remodeling. Action: Blocks sympathetic nervous system (fight/ flight): decreases HR, BP, contractility & oxygen demand of heart Triglycerides Cholesterol absorption inhibitors HMG Co-A reductase inhibitors “- statins” - Ezetimibe (Zetia) NOT 1st line treatment! Monitor BP, esp for orthostasis HTN CHF (If ACE not tolerated) Same as ACE, but no cough and less likely to cause angioedema Same as ACE CAD CHF HTN Severe bronchospasm – do NOT give to asthma pt, bradycardia (<60),depression/fatigue, may mask signs of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients Monitor: HR, BP, and heart rhythm, check for orthostasis, assess lung sounds Check for peripheral edema and wt gain, esp in HF patients Teach diabetic pt to closely monitor glucose levels Check for orthostasis if pt is dizzy/light headed Hypotension, Dizzy CHF Angina (CAD) Digoxin toxicity, esp if low toxic s/s non specific, antacids K levels. affect absorption, kindey probs cause body to hold onto it, increases workload of the heart Ototoxicity Hypotension, Monitor for electrolytes (esp dehydrate, decreased K, K), ototoxicity Mg, and Na Pt on Falls Precautions Low K + digoxin = renal failure Headache (ok to treat w/ Tylenol) Hypotension, syncope HTN CHF Same as above, but NO ototoxicity Action: blocks reabsorption HTN CHF of Na, Cl and water Action: relaxation of smooth muscle, significant vasodilation, some coronary artery dilation Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) Action: blocks reabsorption 1st Line – CHEAPEST of Na, Cl and water Nursing Implications Monitor for hyperkalemia No grapefruit juice or St. John’s Wort Cough, headache and angioedema (swelling of lips or mouth) Action: blocks initial calcium HTN influx into cardiac cells and CAD vascular smooth muscle cells. Slows conduction in the atria and ventricles. Vasodilates coronary arteries Action: Improves heart CHF contractility and slows AV conduction, decreases HR Nitroglycerin (NTG), many routes: Sub lingual, PO, patch, IV Adverse Effects Hyperkalemia, Gynecomastia Same as above Encourage foods high in K Low K + digoxin = renal failure Omega 3 fatty acids Bile acid-binding resins Fish Oil Omacar Cholestyramine (Questran) Colestipol Colesevelam (Welchol)