CardiovascularDrugsf..
advertisement
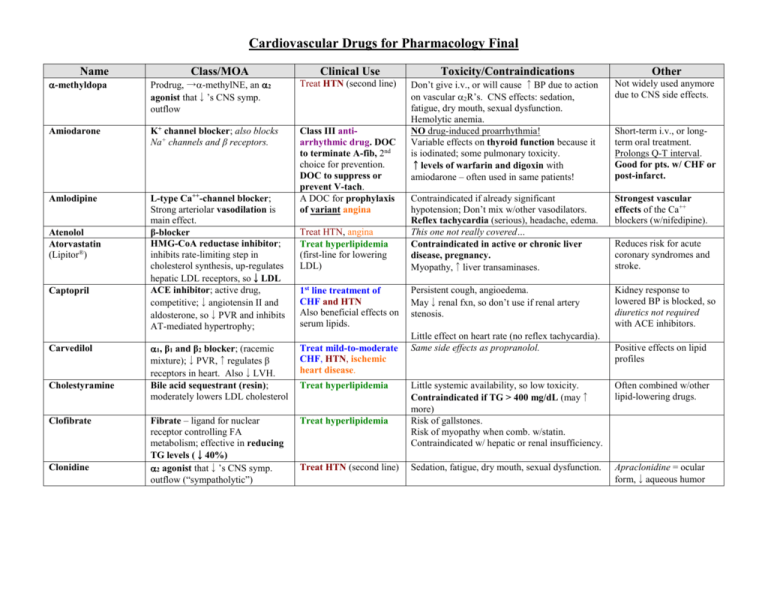
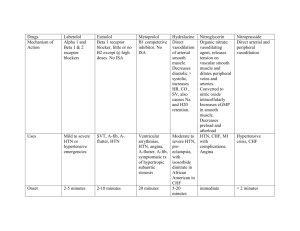
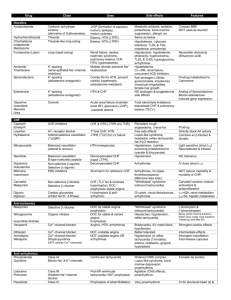
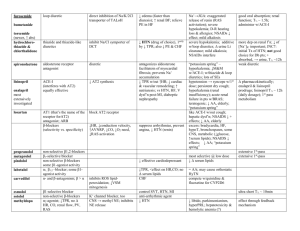
Cardiovascular Drugs for Pharmacology Final Name Class/MOA Clinical Use -methyldopa Prodrug, →-methylNE, an 2 agonist that↓’s CNS symp. outflow Treat HTN (second line) Amiodarone K+ channel blocker; also blocks Na+ channels and β receptors. Amlodipine L-type Ca++-channel blocker; Strong arteriolar vasodilation is main effect. β-blocker HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor; inhibits rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis, up-regulates hepatic LDL receptors, so↓LDL ACE inhibitor; active drug, competitive;↓angiotensin II and aldosterone, so↓PVR and inhibits AT-mediated hypertrophy; Class III antiarrhythmic drug. DOC to terminate A-fib, 2nd choice for prevention. DOC to suppress or prevent V-tach. A DOC for prophylaxis of variant angina Atenolol Atorvastatin (Lipitor®) Captopril Carvedilol Cholestyramine Clofibrate Clonidine Treat HTN, angina Treat hyperlipidemia (first-line for lowering LDL) 1st line treatment of CHF and HTN Also beneficial effects on serum lipids. 1, β1 and β2 blocker; (racemic mixture);↓PVR,↑regulates β receptors in heart. Also↓LVH. Bile acid sequestrant (resin); moderately lowers LDL cholesterol Treat mild-to-moderate CHF, HTN, ischemic heart disease. Fibrate – ligand for nuclear receptor controlling FA metabolism; effective in reducing TG levels (↓40%) 2 agonist that↓’s CNS symp. outflow (“sympatholytic”) Treat hyperlipidemia Treat hyperlipidemia Treat HTN (second line) Toxicity/Contraindications Other Don’t give i.v., or will cause ↑BP due to action on vascular 2R’s. CNS effects: sedation, fatigue, dry mouth, sexual dysfunction. Hemolytic anemia. NO drug-induced proarrhythmia! Variable effects on thyroid function because it is iodinated; some pulmonary toxicity. ↑levels of warfarin and digoxin with amiodarone – often used in same patients! Not widely used anymore due to CNS side effects. Contraindicated if already significant hypotension; Don’t mix w/other vasodilators. Reflex tachycardia (serious), headache, edema. This one not really covered… Contraindicated in active or chronic liver disease, pregnancy. Myopathy,↑liver transaminases. Strongest vascular effects of the Ca++ blockers (w/nifedipine). Persistent cough, angioedema. May↓renal fxn, so don’t use if renal artery stenosis. Kidney response to lowered BP is blocked, so diuretics not required with ACE inhibitors. Little effect on heart rate (no reflex tachycardia). Same side effects as propranolol. Short-term i.v., or longterm oral treatment. Prolongs Q-T interval. Good for pts. w/ CHF or post-infarct. Reduces risk for acute coronary syndromes and stroke. Positive effects on lipid profiles Little systemic availability, so low toxicity. Contraindicated if TG > 400 mg/dL (may↑ more) Risk of gallstones. Risk of myopathy when comb. w/statin. Contraindicated w/ hepatic or renal insufficiency. Often combined w/other lipid-lowering drugs. Sedation, fatigue, dry mouth, sexual dysfunction. Apraclonidine = ocular form,↓aqueous humor Digoxin Cardiac glycoside, inhibits myocardial Na+-K+ ATPase (competitive inh. of K+), causes↑ intracell. Na+, inhibiting exchange of Na+ (in) for Ca++ (out), so ↑ intracellular Ca++ (positive inotropism) Slows SA and AV nodal conduction. Digitoxin Diltiazem Dipyridamole Treat CHF, Anti-arrhythmic (for supraventricular tachyarrhythmias) Limited therapeutic index. N/V, visual disturbances, various arrhythmias. Renal disease ↓’s clearance, may lead to toxic buildup. Amiodarone, quinidine and verapamil ↓renal clearance of digoxin. Cholestyramine ↓’s bioavailability. Hypokalemia ↑’s likelihood of toxicity (beware diuretics!). Hypoxia also ↑’s toxicity. Elderly more sensitive! Same as digoxin, except: 90-100% GI absorption; Hepatic metabolism, renal excretion.; t½ = 4-6 days L-type Ca++-channel blocker; A DOC for prophylaxis See others of variant angina moderate↓in cardiac contraction, slowed conduction @ SA and AV nodes, moderate vasodilation (art.) Phosphodiesterase (PDE) Prevents clot formation; Therarpy for MI, angina; inhibitor; ↑cAMP, inhibits platelet activation, promotes arterial Variable GI absorption. Excreted unchanged by kidney. t½ = 36-48h Treat toxicity w/ phenytoin, lidocaine, K+, Fab fragments to digoxin. Intermediate cardiac & vascular effects (compare other Ca++ blockers.) Adjunct for anticoagulation therapy. relaxation β1 & β2 agonist,↑force of myocardial contraction. ACE inhibitor; prodrug, metabolized to active enalaprilat. Na+ channel blocker (strongest!) Treat cardiogenic shock, CHF Same as captopril… Long term use can cause downregulation & desensitization of receptors. Give i.v. only. Racemic mixture, is 1 agonist & antagonist, too. Class IC anti-arrhythmic drug – a DOC for prophylaxis of A-fib. Significantly widens QRS Furosemide Loop diuretic (sulfonamide): inhibits Na/K/2Cl transporter in TALH cells, ↑ GFR Treat HTN Relatively high incidence of proarrhythmia – contraindicated with structural heart disease (ischemic damage or hypertrophy). Also avoid with depressed ventricular fxn (↓ejection fraction). Alkalosis, hypokalemia (beware digoxin/digitoxin!), hypovolemia, dehydration, shock. CN VIII damage (deafness). Gemfibrozil Guanethidine Fibrate – see clofibrate Sympatholytic, inhibits Ca++dependent release of NE in periphery Arterial selective vasodilator; ↑’s smooth muscle levels of cGMP; result is ↓PVR,↓cardiac afterload, ↑ cardiac output. Thiazide diuretic, ↓s plasma volume and↓s PVR long-term. Treat HTN Hypotension, bradycardia. Not widely prescribed – “historical interest”. Treat CHF and HTN Lupus-like symptoms, headache, reflex tachycardia (blocked by co-administered βblockers), water and salt retention (co-administer diuretics). Hypokalemia, may cause ventricular arrhythmias (not a major impediment to therapeutic use). Use is decreasing due to safer, more effective drugs (ACE inhibitors and AT-R antagonists) Especially effective in African Americans and the elderly. Dobutamine Enalapril Flecainide Hydralazine Hydrochlorothiazide Treat HTN, often in combination w/other antihypertensives. In CHF, even before diuresis, eases breathing, ↓pulmonary resistance and pulmonary artery BP. Inamrinone (previously amrinone) PDE inhibitor (cardiac/vascular isoform); effectively ↑’s cAMP levels,↑cardiac output,↓PVR; Isoproterenol β1 & β2 agonist (more affinity than Epi or NE) Organic nitrate, slow onset, medium duration↓’s preload on heart due to vasodilation of large veins. 1, β1 and β2 blocker Na+ channel blocker (weakest, safest). Competitive angiotensin II (AT1) receptor antagonist; inhibits vasoconstriction, aldosterone release and hypertrophic growth. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor Selective β1 blocker PDE inhibitor Primarily an arterial vasodilator by↑cGMP, stim. outward K+ channels, hyperpolarizes vascular sm. muscle. β-blocker Decreases fatty acid mobilization from adipose to liver.↓plasma TG,↓VLDL and LDL and ↑ HDL. L-type Ca++-channel blocker; Strong arteriolar vasodilation is main effect. Isosorbide dinitrate Labetalol Lidocaine Losartan Lovastatin Metoprolol Milrinone Minoxidil Nadolol Nicotinic acid (niacin) Nifedipine Nitroglycerin Nitroprusside (sodium nitroprusside) Organic nitrate, ↓’s preload on heart due to vasodilation of large veins. Balanced vasodilator; ↑’s smooth muscle levels of cGMP; result is ↓ cardiac preload and afterload, ↑ cardiac output, ↓ pulmonary congestion. Short-term treatment of CHF. (Positive inotropic agent). Potential to induce arrhythmias, thrombocytopenia, nausea/vomiting. Reserved for patients who don’t respond to vasodilators or other positive inotropic agents. NOT effective in reducing morbidity and mortality a/w heart failure VERY low affinity for receptors (“pure β-ag”) 2nd choice for angina prophylaxis Treat HTN Class IB anti-arrhythmic drug. 1st line treatment of CHF and HTN Headache, hypotension, reflex tachycardia. Nitrate tolerance with continuous exposure. Don’t combine w/sildenafil (Viagra®)! Some risk of proarrhythmia (less than other Na+ blockers). Fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors. See atorvastatin Like propranolol, but without β2-mediated side effects. Like inamrinone, but with less toxicity. Reserved for treatment of Headache, hypotension, reflex tachycardia (counter w/β-blockers), edema (counter moderate to severe HTN. w/diuretics). Reflexes may blunt effect of ↓ PVR. Treat HTN, angina This one not really covered… Treat hyperlipidemia; Glucose intolerance (avoid high doses w/type 2 Most effective at raising DM), hepatotoxicity, hyperuricemia: HDL levels. contraindicated w/severe liver disease or gout. A DOC for prophylaxis of variant angina Sublingual = DOC to terminate anginal episode (stable or variant) Patch = 2nd choide for angina prophylaxis Acute management of CHF. Useful in hypertensive emergencies (diastolic BP > 120 w/ end-organ Contraindicated if already significant hypotension; Don’t mix w/other vasodilators. Reflex tachycardia (serious), headache, edema. Use extended release formulation. Headache, hypotension, reflex tachycardia. Nitrate tolerance with continuous exposure (i.e., with patch). Minimal effect on ECG. Parenteral use only. Diuretics not required. Also causes hair growth (marketed as Rogaine®) Strongest vascular effects of the Ca++ blockers (w/amlodipine). Don’t combine w/sildenafil (Viagra®)! Translingual spray or sublingual tab = rapid onset, short DOA; Patch = slow onset, long DOA Hypotension, risk of cyanide poisoning w/high concentrations (it is metabolized to cyanide). Unstable in solution, ultrashort DOA damage). Phenylephrine Prototype 1 agonist, causes vasoconstriction Pindolol β-blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) (partial agonist) Selective 1 antagonist (competitive),↓TPR & venous return Non-selective β-blocker (β1 & β2); ↓’s HR and force of contraction, so ↓’s O2 demand of heart. Slows conduction @ AV node. Prazosin Propranolol Quinidine Blocks Na+ and delayed rectifying K+ channels. Slows conduction through ventricles and prolongs ventricular action potential. Reserpine Sympatholytic, depletes NE from nerve endings in CNS & periphery. K+ channel blocker; also blocks β1 and β2- receptors. Sotalol Streptokinase Sulfinpyrazone Verapamil Hemorrhage control, treatment of hypotension. Treat HTN Treat HTN DOC for prophylaxis of stable angina and ischemia relief during acute coronary syndromes; also for HTN. Class II antiarrhythmic drug (DOC for ventricle rate control w/A-fib). Class IA anti-arrhythmic drug. Treat HTN Class III (and II) antiarrhythmic drug. DOC for prophylaxis of Afib. Binds, activates plasminogen Clot buster for acute MI, DVT, multiple PE (without cleavage)→fibrinolysis. Uricosuric agent: why is it on the cardiovascular drug list??? A DOC for prophylaxis L-type Ca++-channel blocker; Strong inhibition of cardiac of variant angina. contractility and conduction Class IV antiacross SA and AV nodes. arrhythmic drug. DOC for ventricular rate control in A-fib. Masks hypoglycemic emergency (prevents tachycardia) in diabetics, exacerbates AV node block. Renal reflex may → fluid retention, so give diuretic too. Orthostatic hypotension and 1st dose syncope. Contraindicated (due to β2 block) in patients with COPD (asthma) or peripheral vascular disease. Also masks hypoglycemic emergency (prevents tachycardia) in diabetics, exacerbates AV node block (due to β1-block). “Withdrawal syndrome” possible, →tachycardia… so↓dose gradually. Risk of drug-induced arrhythmias (torsades de pointe), cinchonism (tinnitus, visual disturbances and anticholinergic effects), negative inotropic effect. ↑digoxin levels and ↓elimination of same – can be life-threatening! Hypotension (↓PVR and CO), insomnia, sedation, depression Significant risk of drug-induced arrhythmias (torsades de pointe) – incidence 2-4%. Beware β2 effects with asthma, etc. Could aggravate CHF (β1-block, negative inotropism). Bleeding! Don’t combine w/other drugs that ↓cardiac fxn! (β-blockers, digoxin). Avoid w/CHF, SA or AV node block, or hypotension. Side effects include hypotension, bradycardia, AV node block. Less potent than Epi or NE, but orally active and longer t½ Blocking effect predominates over ISA as endog. NE is released. ↓BP does NOT cause reflex tachycardia. A DOC for supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (A-fib.), but secondary choice for V-tach. Widens QRS complex (Na+ block) and lengthens Q-T interval (K+ block) Not widely prescribed – “historical interest”. Prolongs Q-T interval. Good for patients w/ischemic heart disease due to β-block. Aprotinin may be used as antidote for excess bleed. Strongest cardiac effects of the Ca++ blockers. Prolongs P-R interval.