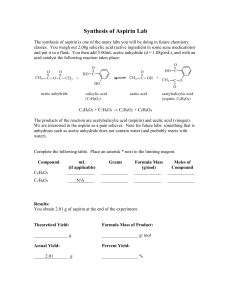
Name - Seattle Central College
advertisement
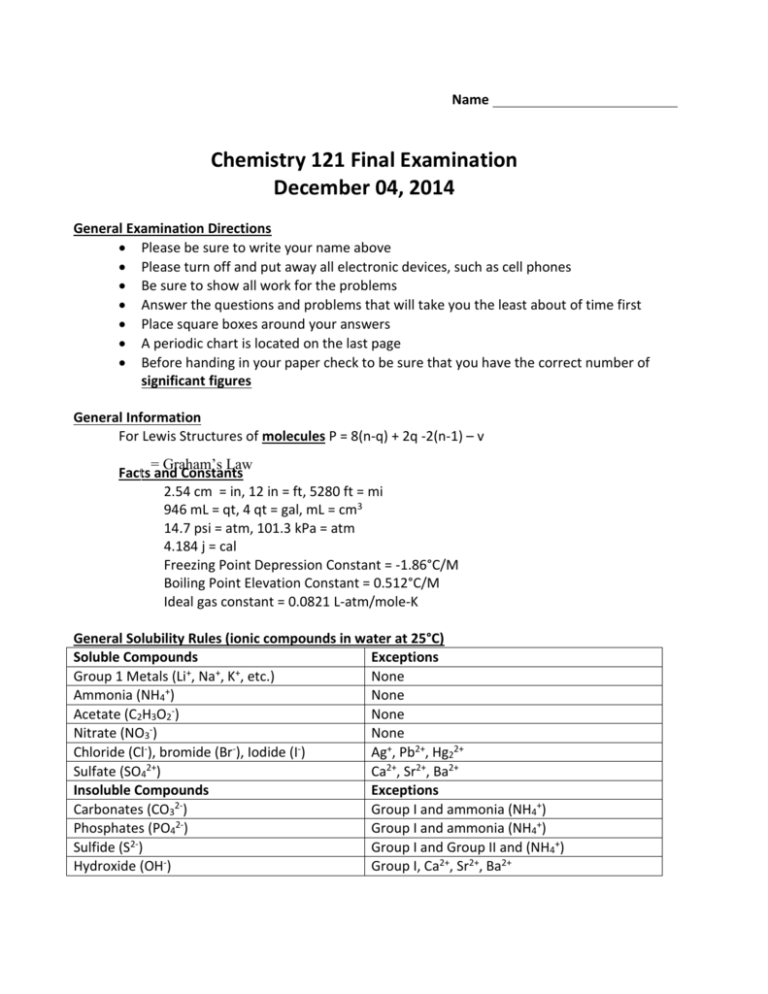
Name Chemistry 121 Final Examination December 04, 2014 General Examination Directions Please be sure to write your name above Please turn off and put away all electronic devices, such as cell phones Be sure to show all work for the problems Answer the questions and problems that will take you the least about of time first Place square boxes around your answers A periodic chart is located on the last page Before handing in your paper check to be sure that you have the correct number of significant figures General Information For Lewis Structures of molecules P = 8(n-q) + 2q -2(n-1) – v = Graham’s Law Facts and Constants 2.54 cm = in, 12 in = ft, 5280 ft = mi 946 mL = qt, 4 qt = gal, mL = cm3 14.7 psi = atm, 101.3 kPa = atm 4.184 j = cal Freezing Point Depression Constant = -1.86°C/M Boiling Point Elevation Constant = 0.512°C/M Ideal gas constant = 0.0821 L-atm/mole-K General Solubility Rules (ionic compounds in water at 25°C) Soluble Compounds Exceptions + + + Group 1 Metals (Li , Na , K , etc.) None + Ammonia (NH4 ) None Acetate (C2H3O2 ) None Nitrate (NO3 ) None Chloride (Cl-), bromide (Br-), Iodide (I-) Ag+, Pb2+, Hg22+ Sulfate (SO42+) Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ Insoluble Compounds Exceptions 2Carbonates (CO3 ) Group I and ammonia (NH4+) Phosphates (PO42-) Group I and ammonia (NH4+) 2Sulfide (S ) Group I and Group II and (NH4+) Hydroxide (OH-) Group I, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ 1. Label the following as chemical or physical changes. a. Ice melting e. Snow forming in clouds b. Iron rusting f. Iron being magnetized c. gasoline burning g. Salt being formed from an acid and a base d. Sugar dissolving in water h. Milk turning sour 2. List the memorized strong acids. 3. What is an indicator and what does it do? 4. Give the conjugate acid and the conjugate base for NH3. 5. Label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base in the following reactions: PO43- + HOH <----> HPO42- + OH6. What substances are normally produced in a neutralization reaction? 7. What acid and base are required to form NH4Cl (SHOW A BALANCED EQUATION SUPPORTING YOUR ANSWER) and is ammonium chloride an acidic, basic or neutral salt? 8. For the following molecules, or ions, draw a three dimensional shape, name the geometrical shape, list bond angles, describe polarity, give hybrid orbital of the central atom. HCO31- 9. Aluminum metal shavings (10.0 g) are placed in 100 mL of 6.00M hydrochloric acid. What is the maximum volume of hydrogen, measured at STP, which can be produced? Assume there are 22.4 L/mole of hydrogen gas at Standard Pressure and Temperature (STP) 2Al(s) + 6 HCl → 2 AlCl3 + 3H2 (g) 10. NAME THE FOLLOWING: II. WRITE FORMULAS FOR THE FOLLOWING a. H2SO3 (aq) a. CALCIUM HYDROXIDE b. CuS b. AMMONIUM SULFITE c. Fe3P2 c. IODINE TETRAOCHLORIDE d. I2O3 d. PERIODIC ACID e. MnS2 e. HYDROCHLORIC ACID 11. Find the [OH -] and pH of a solution when [H+] = 4.22 X 10 –4. 12. Find the molarity when 123 ml of water is added to 15.0ml of 7.00 M HCl. 13. What volume of water, ft3, would have a mass of 2.00 lbs? Assume the density of water to be 1.00 g/mL 14. A non-SI unit of mass used in pharmaceutical work is the grain (gr) (15 gr = 1.0 g) An aspirin tablet contains 5.0 gr of aspirin. A 155 lb arthritic individual takes two aspirin tablets per day. a. What is the quantity of aspirin in two tablets, expressed in milligrams? b. What is the dosage rate of aspirin, expressed in milligrams of aspirin per kilogram of body mass? c. At the given rate of consumption of aspirin tablets, how many days would it take to consume 1.0 lb of aspirin? 15. A at 25°C and 788 torr has a volume of 2.00L. What would be its volume at STP. 16. A 0.1340 g sample of gas is collected in a 122 mL flask at 25°C and one atmosphere of pressure. Calculate the molecular weight and identify the gas. 17. Predict the products, balance and then give the formula, ionic, and net ionic equation when Na3PO4 (aq) combines with Fe(NO3)2(aq). 18. A sample of 4.00 g of methane (CH4) is mixed with 15.0 g of chlorine (Cl2) according to the following equation: CH4 + 4Cl2 → CCl4 (l) + 4 HCl (g) a. Determine the mass of HCl formed. b. Determine the mass of the excess reactant left at the end of the experiment. 19. A solution is prepared by combining 2.33 g of AlCl3 with 125 mL of water. If the density of the solution is 1.12 g/mL give answers to the following. a. Is the solution an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte (circle the correct one)? b. Find the molarity of the solution c. How many equivalents are in the 2.33 g sample of AlCl3 d. Calculate the boiling point. e. Calculate the osmotic pressure. f. Give the %m/m g. Give the %m/v