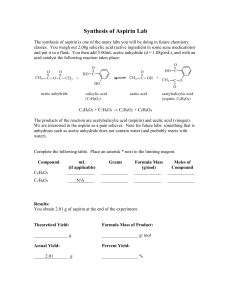
The Titration of Aspirin Background Aspirin is slightly acidic and can
advertisement

The Titration of Aspirin Background Aspirin is slightly acidic and can be titrated with a base such as sodium hydroxide. PRELAB Read the entire lab and answer the following questions. You may need to consult the internet to answer some of the following questions. 1. What is the name of the acid included in aspirin? 2. What is the chemical formula of aspirin? 3. What are the inactive ingredients in aspirin? 4. What is aspirin used for? 5. Draw a structural formula for acetylsalicylic acid and label the carboxyl group and the acidic hydrogen. 6. Write the double displacement reaction for aspirin and sodium hydroxide. Problem Apply your knowledge of titrations, molarity, and the mole concept to indirectly determine the molecular weight of aspirin. Safety 1. Wear goggles 2. Wash your hands after completing the lab Procedure 1. Place a 325mg unbuffered aspirin tablet in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. 2. Add 20 mL of distilled water, gently swirl the flask. This will allow the tablet to break up as it absorbs water and swells. 3. Add 20mL of ethanol to dissolve the aspirin, gently swirl the flask. 4. Add 3 – 4 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution. 5. Titrate with 0.100 M NaOH to the endpoint. 6. Perform two trials. Lab Report Data and Calculations 1. Summarize your experimental measurements in a data table. 2. Show all calculations to determine the molecular weight of aspirin. Post Lab Questions 1. If there was another additive to the aspirin tablet, say vitamin C, how would this affect the results for the titration of the aspirin? 2. If titrated properly, the neutralized aspirin solution color will fade over time. Why might this be? (Hint: relates to CO2 in the air). 3. An impure sample of benzoic Acid (HC7H5O2), with a mass of 2.06 grams is dissolved in water. It is titrated with 0.200 M sodium hydroxide. The sample required 46.0 mL to reach an endpoint using phenolphthalein as the indicator. a. Write the balanced neutralization reaction that occurs. b. Calculate the number of moles of benzoic acid in the sample. c. Calculate the mass of benzoic acid in the sample (Hint: you need the molar mass of benzoic acid). d. Calculate the % purity of the sample (Hint: (mass of benzoic acid/ mass of sample) X 100). 4. Calculate the concentration of acetic acid (HC2H3O2), if an average of 67.0 mL of .468 M magnesium hydroxide is required to titrate 50.0 mL of the acid in order to reach the endpoint. a. Write the balanced neutralization reaction that occurs. b. Calculate the concentration of acetic acid. 5. Calculate the concentration of potassium hydroxide if 65.0 mL of the base are used to titrate a 15.0mL sample of 1.0M sulfuric acid. a. Write a balanced neutralization reaction. b. Calculate the concentration of potassium hydroxide.