Chapter 14 – From Organic Molecules to Medicines
advertisement

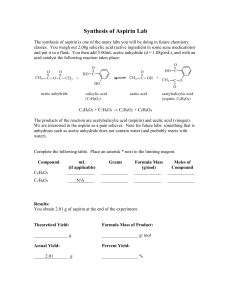
Chapter 14 – From Organic Molecules to Medicines Aspirin • Pharmaceutical products are often developed from substance found in a plant that has been used for traditional medicine. • Aspirin is one of these products. • Salicylic acid is the active substance that helps helps to reduce pain and fever. • However, salicylic acid irritates the lining of the stomach. • So when salicylic acid is reacted with ethanoic acid,it produces acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). • This reaction, however, is slow and the yield is low as the water formed tends to drive the reaction backwards. • An alternative reaction pathway, that is faster and produces higerh yields, is one between ethanoic anhydride (acetic anhydride) and salicylic acid. • Once the acid has passed through the stomach it reacts with water in the small intestine and returns to the more effective salicylic acid. Reaction Pathways for Aspirin Soluble Aspirin • Pure acetylsalicylic acid is not very soluble in water, despite have a –COOH functional group. • Though converting the carboxylic acid functional group into the sodium salt changes the molecule into an ion and makes it much more soluble. • Buffered aspirin provides further protection against stomach irritation. Identifying Aspirin - IR • The analytical techniques IR, NMR and Mass Spectrometry can be used to analyse aspirin. • The molecular structure of acetylsalicylic acid is shown below: • There are two C=O groups present. • One is part of an ester and the other is part of the carboxyl group. • These correspond to the two absorptions at 1760 and 1770cm-1 in the IR spectrum. Identifying Aspirin - NMR • There are four hydrogen around the benzene ring, three Hs in the CH3 group and one in the OH group. • The four hydrogen attached to the benzene ring give four separate peaks. • The three hydrogen atoms of CH3 all experience the same environment so they are the large peak. • The single hydrogen atom in the COOH group would give a small peak, it is not shown in the spectrum over. Identifying Aspirin cont… Identifying Aspirin – Mass Spec • The peak at 180 is the molecular formula ion peak, this is the Mr of Aspirin. • The masses of the various fragments are used to confirm the structural formula.