RATES OF REACTION – SURFACE AREA

1.
RATES OF REACTION – SURFACE AREA
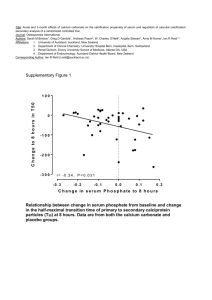
A small quantity of hydrochloric acid was added to a large quantity of marble chips in an evaporating dish, which was placed on the pan of a balance. The mass of the dish and its contents was recorded every half minute. The results are shown in the graph below. a. b.
Explain why the evaporating dish and contents loses mass .
What was the mass of the evaporating dish and its contents (i) at the start and (ii) at the end c. of the experiment?
What mass of carbon dioxide was produced? d. How long did the reaction last? f. During which of these times in the experiment was the rate of reaction most rapid:
0 - 1 minutes?
1 - 2 minutes?
2 – 3 minutes? g. On the graph sketch the curve you would expect if the acid had first been chilled.
(Label it A) h. Now sketch the curve you would expect if the chips had first been crushed to powder.
2.
(Label it B) i. What apparatus could be used instead of an evaporating dish, to prevent any loss of acid by splashing?
Sam is investigating the reaction between calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid.
The lump of calcium carbonate she uses has a mass of 5.0 g.
She also uses 50 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid in the experiment.
The temperature of the acid is 20 oC.
Look at the diagram. It shows the apparatus that Sam uses.
Sam writes down the mass of the calcium carbonate and acid every two minutes.
Look at her results.
Time
(mins ) mass of calcium carbonate and
Time
(mins ) mass of calcium carbonate and
0 acid ( g )
53.0 12 acid ( g )
51.8
2
4
6
8
52.8
52.6
52.4
52.2
14
16
18
20
51.6
51.5
51.4
51.3
10
12
52.0
51.8
22
24
51.3
51.3
Here is the equation for the reaction. calcium carbonate
+ hydrochloric acid
calcium chloride
+ carbon dioxide
+ water
(a) Look at the results.
The mass of calcium carbonate and acid gets smaller during the experiment.
Explain why.
(b) Sam knows that the reaction stops after twenty minutes.
Explain how she can tell from her results.
[1]
[1]
(e) Sam does the experiment a second time. Again she makes just one change.
She uses calcium carbonate powder instead of a lump.
Explain why the reaction is faster.
Use ideas about collisions between particles. [1]
(f) Sam now investigating the reaction between calcium and dilute hydrochloric acid .
The calcium metal she uses has a mass of 2.0 g.
She also uses 50 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid in the experiment.
The temperature of the acid is 20 oC.
She uses exactly the same apparatus as before .
(i) When calcium reacts with hydrochloric acid calcium chloride and hydrogen are produced. Write down the word equation for this reaction. [2]
(ii) Sam decides to test the gas.
She decides to burn the gas with a lighted splint.
What will happen if she does this ?
(iii) What is the name of the gas produced in this reaction ?
[1]
[1]