Solubility Product of Calcium Hydroxide Experiment
advertisement

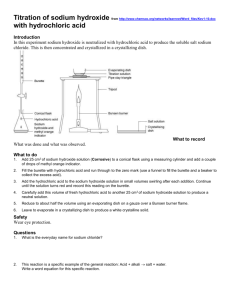
EXPERIMENT: Determination of solubility product ASSESSMENT CRITERIA: DCP, CE Aim: To determine the solubility product of calcium hydroxide. Theory: When a sparingly soluble salt is dissolved in water at a definite temperature, equilibrium is established and the rate of dissolution of ions from the solid equals to the rate of precipitation of ions from the saturated solution. For example, when calcium hydroxide is dissolved in water, equilibrium exists between solid Ca(OH)2 and the calcium and hydroxide ions present in the saturated solution. Ca(OH)2 = Ca2+ + 2OHRequirements: Apparatus: Conical flasks (250ml) 6, filter funnels 3, beakers (100ml) 3, measuring cylinder (100ml) 1, pipette (10ml) 1, burettes 2, burette stands 2. Chemicals: Calcium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, sodium carbonate, methyl orange indicator. Procedure: Take about 2.0 grams of powdered calcium hydroxide in each of the three conical flasks(250ml). Add 100ml of distilled water in each. Shake well and allow to stand overnight. Filter the solution into the beaker (250ml). Discard about 5 ml of filtrate in the beginning because the filter paper absorbs solute until it attains equilibrium with the solution. Take 10ml of the filtrate in a conical flask with the help of a pipette and titrate it with standardized hydrochloric acid, using methyl orange as an indicator. Repeat the same procedure for the other two solutions. Preparation of Standard Hydrochloric Acid Solution Prepare 0.1 M sodium carbonate solution by weighing 3.1g solid sodium carbonate and dissolving it in distilled water and making it 250ml in a standard flask. Prepare 250 ml of approximately 0.1 M hydrochloric acid. Now titrate hydrochloric acid against the standard solution of sodium carbonate using methyl orange as an indicator. Record your observations and determine the solubility product of calcium hydroxide.