File
advertisement

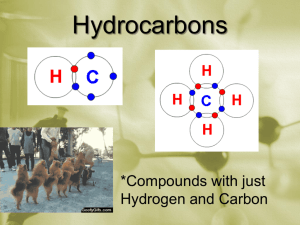
Organic means containing carbon. Originally, scientists believed that the only substances to contain organic compounds were living things as they were not able to manufacture organic substances in lab. Why did nature choose carbon? Carbon is not the most abundant element. Nature chose carbon because of its versatility. Forming covalent bonds, it is able to combine with itself forming long chains, make aromatic compounds, form isomers, and combine with almost every other atom. In drawing structural formulas of organic substances you will notice that carbon has four bonds. Each line represents a carbon bond. Each of these carbon bonds represents two electrons being shared by the two atoms. Carbon will have four bonds, making it have 8 valence electrons and a full outer shell. One class of organic compounds are hydrocarbons. These are substances that contain only carbon and hydrogen. This is different from the CARBOHYDRATES, which have C,H,O in a 1:2:1 ratio. There are a tremendous number of hydrocarbons. Three types of hydrocarbons we will study are the Alkanes-these hydrocarbons contain only single bonds between carbons The formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2 Alkenes-an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one double bond The simplest alkenes have one double bond and the formula of CnH2n Alkene - In general, a double bond is shorter in length and stronger than a single bond. If more than one double bond is present the name changes. For example, two double bonds would be a “diene”, three a “triene”. Alkynes-are substances that have at least one triple bond The simplest alkynes have one triple bond and follow the formula of CnH2n-2 The prefixes in organic chemistry are the same for the alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. Meth-1 But-4 Hept-7 Eth-2 Pent-5 Oct-8 Dec-10 Prop-3 Hex-6 Non-9 Try these practice problems to test how well you know the prefixes: A. (Eth + Meth) X (Hept -Pent) = B. (Oct + But)/Prop = C. (Dec X Hex) - Non = Eth Answers next slide. Answers: A. (2+1) X (7-5) = 6 B. (8+4)/3 = 4 C. (10X6)-9 = 25.5 2 If you look at alkanes, they can be anywhere from one to one million atoms long. If the carbon atoms are in a continuous line, the substance is said to be “normal” so an N is used to identify the substance. For example, n-butane. This means you have a straight chained 4 carbon alkane. If you have an isomer of butane, it will have a different name but it will not be n-butane. Here you see the first compound is a straight chain. This would be “normal butane”. The second compound, an isomer, is isobutane. These are saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula of: CnH2n+2 This means that if you know the number of Carbons, n, then the formula for the hydrogens is H=2n + 2. Alkanes are the only saturated hydrocarbons. This is because they have only single bonds between each of the carbons. If a double or triple bond is added then the hydrocarbon becomes UNSATURATED. Now you can try these practice problems: A. Calculate the number of hydrogens if an alkane has 45 carbons. B. How many hydrogens does an alkane with 345 carbons have. C. What is the molecular formula for Heptane. Answers next slide. Answers: H=2n+2 A. C45H92 B. C345H692 C. C7H16 Alkenes are UNSATURATED hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond. Alkenes that have two double bonds are called DIENES. An alkene with three triple bonds is called a TRIENE. Unless you are told otherwise, we will work with alkenes that have ONE double bond. The general formula for an alkene is as follows: CnH2n Notice that the +2 is missing from the alkane formula. This is because with every carbon to carbon bond made, you must lose 2H atoms. Calculate the number of carbons or hydrogens for each: A. An alkene with 56 Hydrogens. C=? B. An alkene with 56 Carbons. H=? C. Give the formula for Butene. Answers next slide. Answers to previous slide: H=2n A. C28H56 B. C56H112 C. C4H8 These are also unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkynes differ from alkenes in that they contain at least one triple bond between carbons. This means that if you started with an alkane, you would lose 4 hydrogens making a triple bond. The resulting formula would be: CnH2n-2 Try these practice problems: Calculate the number of C or H for each: A. 34 carbon alkyne. H=? B. An alkyne with 344 hydrogens. C=? C. Give the molecular formula for Propyne. Answers next slide. Answers to previous slide: H=2n-2 where n=no. of carbon A. H=66 B. C=173 C. C3H4 Remember that in going from an alkane to an alkene to an alkyne, you are adding carbon to carbon bonds. Every time you make a carbon to carbon bond, you remove two hydrogen atoms. If you remove a carbon to carbon bond, you must add two hydrogen atoms. What would be the molecular formula if you combined the following: A. ethyne + pentene + butane B. Octane + octyne Answers next slide. A. C2H2 + C5H10 + C4H10 so your initial formula is C11H22. However, you have two carbon to carbon bonds so you have to substract 4 more hydrogens. The final answer is C11H18. B. C16H30