otes
advertisement

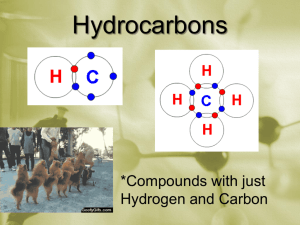
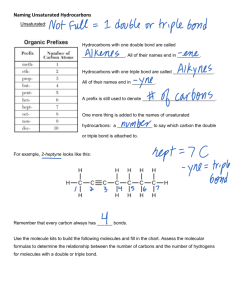
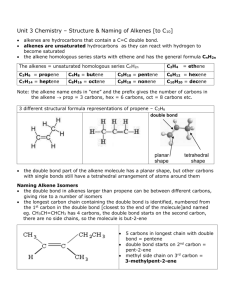
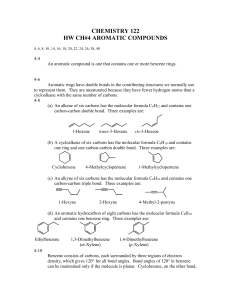
Chapter 22: Organic Chemistry HYDROCARBONS: compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen 4 categories: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes & aromatic Alkanes: hydrocarbons that only contain SINGLE bond Straight Chains – Carbons are all in a line Methane (1 Carbon): CH4 Ethane (2 Carbons): CH3-CH3 Propane (3 Carbons): CH3-CH2-CH3 Butane (4Carbons): CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 Pentane (5 Carbons): CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 Hexane (6 Carbons): CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 Heptane (7 Carbons) Octane (8 Carbons) Nonane (9 Carbons) Decane (10 Carbons) Cyclic Compounds - molecular formula has 2 less H atoms than straight chain Alkenes: hydrocarbons that contain a Carbon-Carbon DOUBLE bonds Alkynes: hydrocarbons that contain a Carbon-Carbon TRIPLE bond Aromatic: hydrocarbons that all involve the molecule benzene C6H6 – a special ring of carbons with alternating single and double bonds, has a special degree of stability FUNCTIONAL GROUP – a portion of a molecule that is a recognizable/classified group of bound atoms. Alcohol: characterized by the hydroxy, –OH group. It is a very important group in monosaccharides (carbohydrates). Sulfide: carbon groups bounded to a sulfur atom Alkyl Halide: hydrocarbon containing a halogen (F, Cl, Br, or I) Ketone: defined by a carbon double bound to an oxygen (different than an aldehyde because it can only be found in the inside of a molecular chain- the carbon does not have to be attached to a hydrogen). Ketones, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids contain the carbonyl functional group: C double bound to O. Aldehyde: defined by a carbon double bound to an oxygen and single bound to a hydrogen; because it is characterized by a bond to hydrogen, it can only be found at the ends of molecular chains Carboxylic Acid: characterized by the carboxyl group; RCO2H (R being any subset of a molecule); any molecular chain bound to a carbon, this carbon has a double bond to oxygen and also attached to an alcohol group Ester: produced by a reaction between an acid and an alcohol (RCO2R) Ether: defined by an oxygen bounded to two carbons. Nitrogen Functional Groups: Amine: a carbon molecule bound to a nitrogen. Amide: contains the double bond between a C and O. The carbon is also bonded to a N Nitrile: