2.7-2.8RxnsAlkenes
advertisement

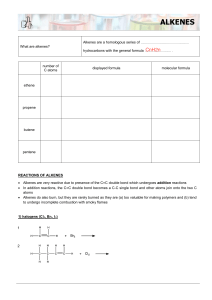
2.7 Physical Properties of Alkenes 1 • • • • Nonpolar Insoluble in water Soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. Less dense than water: they float on water. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES LIKE ALKANES 2 2.8 Chemical Properties of Alkenes 3 REACTIONS OF ALKENES Combustion Addition reactions : hydrogenation halogenation hydrohalogenation hydration (addition of water) 4 • Addition reactions: A substance adds to the multiple bond of an unsaturated reactant to yield a saturated product that has only single bonds. 5 In an addition reaction the atoms of the reactant molecule attach to the carbon atoms originally joined by a double bond. The double bond becomes a single bond. 6 1. Symmetrical Addition Reactions: In which identical atoms are added to each carbon of the double bond. 2. Unsymmetrical Addition Reactions: In which different groups are added to each carbon of the double bond. For example, hydration or hydrohalogenation. 7 1. Symmetrical addition reactions HYDROGENATION: The addition of H-H to C=C HALOGENATION: The addition of Cl2 or Br2 to C=C 8 HYDROGENATION C + C H H catalyst catalyst = Pt, Pd, Ni C C H H Hydrogenation is the addition of hydrogen (H2) to a functional group. It requires a catalyst (cat) + H2 Pd H3C CH3 + H Pt H2 CH3CH2CH2CH3 H NO REACTION WITH C=C IN AROMATIC RINGS! 9 HALOGENATION Addition of Cl2 and Br2 to alkenes: • Alkenes react with the halogens Br2 and Cl2 to give the 1,2-dihaloalkanes. D:\Chem 11\movies\addition.mov 10 Bromine in water is a reddish brown solution. Br2 Bromine adds to the alkene to form colorless dibromo compounds. 11 2. UnSymmetrical addition reactions HYDROHALOGENATION : The addition of H-Cl, HBr or H-I to C=C Hydration: The addition of H2O to C=C 12 HYDROHALOGENATION Addition of HCl and HBr to alkenes: • Alkenes react with hydrogen bromide and hydrogen chloride to give alkyl bromide or alkyl chloride products. 13 •Markovnikov rule: In the addition of HX to an alkene, the H becomes attached to the carbon that already has the more H’s, and X becomes attached to the carbon that has fewer H’s. D:\Chem 11\movies\HCLadddition.mov 14 HYDRATION Addition of water (H-OH) to alkenes An alcohol is produced on treatment of the alkene with water in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, such as H2SO4. Markovnikov’s rule applies. 15 16