Vocabulary and Big Ideas
advertisement
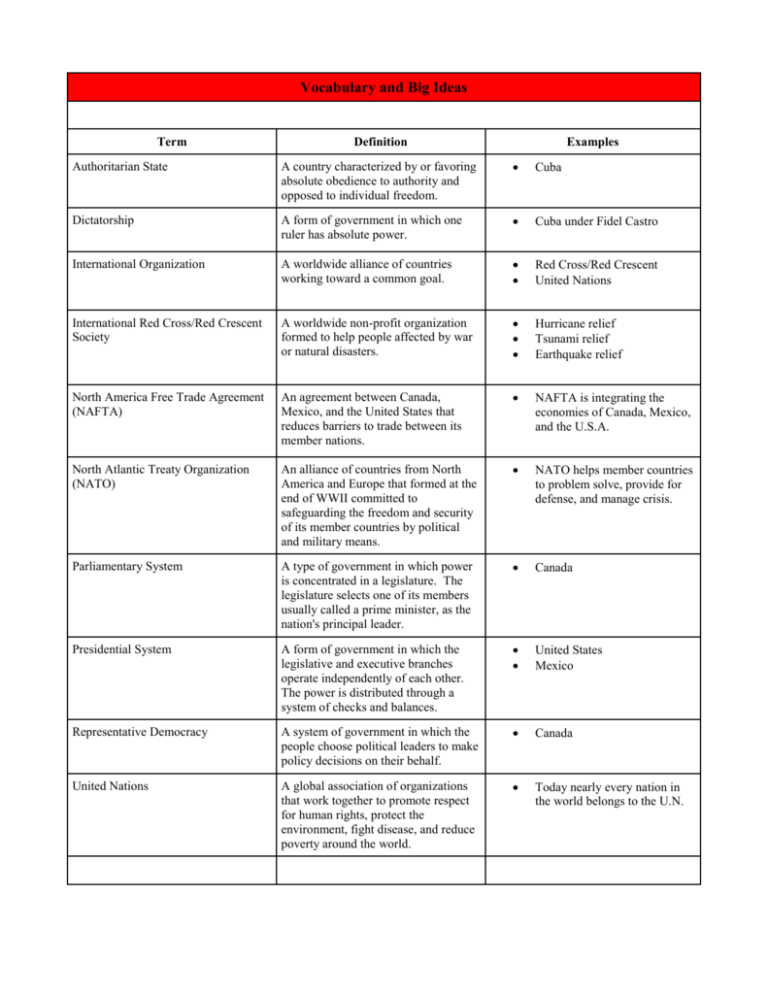
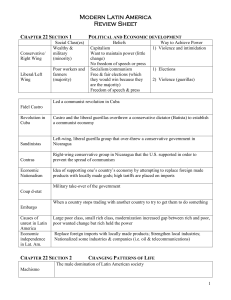
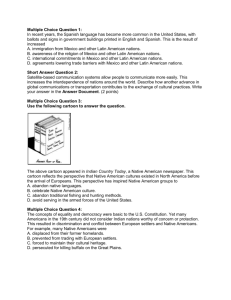
Vocabulary and Big Ideas Term Definition Examples Authoritarian State A country characterized by or favoring absolute obedience to authority and opposed to individual freedom. Cuba Dictatorship A form of government in which one ruler has absolute power. Cuba under Fidel Castro International Organization A worldwide alliance of countries working toward a common goal. Red Cross/Red Crescent United Nations International Red Cross/Red Crescent Society A worldwide non-profit organization formed to help people affected by war or natural disasters. Hurricane relief Tsunami relief Earthquake relief North America Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) An agreement between Canada, Mexico, and the United States that reduces barriers to trade between its member nations. NAFTA is integrating the economies of Canada, Mexico, and the U.S.A. North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) An alliance of countries from North America and Europe that formed at the end of WWII committed to safeguarding the freedom and security of its member countries by political and military means. NATO helps member countries to problem solve, provide for defense, and manage crisis. Parliamentary System A type of government in which power is concentrated in a legislature. The legislature selects one of its members usually called a prime minister, as the nation's principal leader. Canada Presidential System A form of government in which the legislative and executive branches operate independently of each other. The power is distributed through a system of checks and balances. United States Mexico Representative Democracy A system of government in which the people choose political leaders to make policy decisions on their behalf. Canada United Nations A global association of organizations that work together to promote respect for human rights, protect the environment, fight disease, and reduce poverty around the world. Today nearly every nation in the world belongs to the U.N. Economics Vocabulary and Big Ideas Term Definition Examples Business Firm An organization that produces and sells goods and services. Nike Toyota Command Economy An economy in which the government makes the decisions about what, where, how and how much is produced and who will get what is produced. Cuba Economic Institution An organization created for a specific economic purpose, making decisions about the consumption and production of resources that influence the economy. Households Businesses Banks Labor Unions Federal Reserve U.S. Treasury Economic Role of the Government Government actions that influence what is produced, how it is produced, and who recieves the benefit of production by making rules and enforcing them. Trade embargo Taxation Import/export regulation Trade agreements Economy All the producers and consumers interacting in a society to produce, distribute, and consume goods and services, including the management of the income, supplies, and expenses of a society. Production of Life Savers ( 2004 - headquarters moved from Holland, MI to Canada): Farmer Raw materials buyer Accountant Machine operator Inspector Truck driver Store clerk Children/parents as consumers Financial Institution An established organization that deals with money. Bank Credit Union Investment Company Households Individuals or family units who live together and buy and consume goods and services. The people with whom you live International Trade The exchange of goods and services between/among nations around the world. United States buys: Tomatoes from Mexico Lumber/paper from Canada Beef from Argentina Labor Unions An organization that represents workers to help improve their wages and working conditions. UAW (United Auto Workers) Teamsters Market Economy An economic system in which producers and consumers decide what is produced, how, and for whom. United States Canada Great Britain Mixed Economy An economic system that combines elements of market and command economic systems. Canada and many other countries Potential Contribution The possible good, service or item that can be given beyond the current contribution. A Latin American country that presently supplies cacao beans to the U.S. and could also provide beef if ranching was developed Scarcity The condition that occurs when wants are unlimited, while resources needed to produce those goods and services are limited. Oil/gasoline Orange juice after a hurricane Vaccines and medicines in some countries Traditional Economy An economy that is based on customs and traditions; the way things have been done in the past. Bartering in remote areas of Latin America; primarily agriculture, fishing, hunting. Geography Vocabulary and Big Ideas Term Definition Examples Belief System A set of opinions about what is considered to be true and trustworthy. Communism Catholicism Democracy Climate Region An area that shares similar long-term trends in weather including temperature, precipitation, winds, etc. Desert Tundra Cultural Region An area of earth that shares common human characteristics such as language, religion, history or politics. Mexico is a predominately Spanish-speaking country Economic Connection A person or group's relationship to the production, and distribution of goods and services. A wheat farmer and a flour mill Economic Region An area of the Earth that shares the method of organizing, the production, consumption, and distribution of goods and services. Silicon Valley in California Coffee and bananas in Latin America Medicines from the South American rainforests Ecosystem A system formed by the interaction of all living organisms (plants, animals, and humans) with each other and with the factors of the environment in which they live. Rainforest in Brazil Gender Roles A particular belief or view of males and females in a group based on cultural values and traditions. Only men can be priests in the Catholic religion Global Consequences Outcomes that are experienced throughout the world. Global Warming Human/Environment Interaction How people interact with and change their environment; how people depend on, modify, and adapt to their environment. People build a bridge across a river Deforestation Language A standard oral or written means of communicating ideas or feelings. In Panama a major way of speaking or writing (communicating) is Spanish Physical Feature A natural characteristic of the earth. A landform A mountain Physical Region An area that shares similar natural The Great Lakes features. Prairie provinces/bread basket Andes Mountain region Maritime provinces Political Region An area where a group of people share a similar belief about the role of government. Quebec Political Connection A person or group's relationship with a set of ideas or particular government official. Democrat NAFTA members Population Total number of people in an area. Number of students in your class 20 million people in Mexico City Regional Environment The characteristics of an area such as climate and vegetation. Western Hemisphere The half of the earth located west of the Prime Meridian to the 180* meridian. Carnival in Rio de Janeiro Fireworks on the 4th of July in the U.S.A. Quincinera Includes North and South America History Vocabulary and Big Ideas Term Contemporary Condition Definition A recent or modern social issue in the Western Hemisphere. Examples Immigration Quebec independence movement Global warming Water rights and division Drug Trade Deforestation Crimes against Humanity Actions that are agreed to universally horrible by all people. Enslavements Massacres Native peoples forced to leave their land and change their cultural practices Discrimination A showing of favoritism or prejudice based on category or class. Treatment of Native peoples by invading groups (Acadians, Mestizo, Native American tribes) Historical Origins People and events of the past that influenced future events. French colonization of Quebec Spanish colonization of Latin America Introduction of slavery into the American colonies Causing pain or suffering to an individual or group of people based on their race, religion, political beliefs, or gender. Imprisonment of the people who spoke out against Castro Civil war in Guatemala Responses of Individuals How and individual responds to a specific situation or event Crimes against Humanity Discrimination Violation of Human Dignity The disrespectful or offensive treatment of a person's human rights. Child labor Slavery Persecution Grade 6 Inquiry and Decision Making Vocabulary Term Definition Examples International Public Policy Issues An issue the government must discuss and make decisions on, based on how it affects the lives of citizens between and among various nations Deforestation Water Pollution Global Warming Tariffs National Public Policy Issues An issue the government must discuss and make decisions about, based on how it affects the lives of citizens in a nation Welfare/Poverty Immigration