Economic Engagement Powerpoint
advertisement

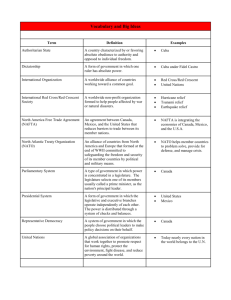
Economic Engagement USING ECONOMIC TOOLS TO BUILD RELATIONSHIPS 2012-13 Debate Resolution RESOLVED: THE UNITED STATES FEDERAL GOVERNMENT SHOULD SUBSTANTIALLY INCREASE ITS ECONOMIC ENGAGEMENT TOWARD CUBA, MEXICO, OR VENEZUELA QUIZ: WHEN WERE THE OTHER TIMES THAT LATIN AMERICA HAS BEEN DEBATED? ANSWER: 1987-88 POLITICAL STABILITY 1994-95 IMMIGRATION Implications of topic wording USFG must be the actor and determiner of economic engagement Question: What are the current policies that the USFG has towards these countries? Must know that first Current policies are like the three bears Cuba “Papa Bear” (too hard) No economic engagement now Embargo since the mid- ”60’s Policy as the the three bears Venezuela “Mama bear” (too soft) Some engagement, especially with oil With the passing of Hugo Chavez, some shifting will take place Policy as the three bears Mexico “Baby bear” (Just right) Although domestically we have issues, tied directly with Mexico Open to significant relationships What is included in economic engagement? We could define both “economic” and “engagement” Why would that not be the best approach? Answer: Very broad; would allow for a very large topic and not exclude much of anything Best is a contextual definition One that would include “positive incentives to achieve an objective” What does economic engagement include Haas & Sullivan with the Brookings Institute in 2000 argued that economic engagement included the following: Export credits Investment insurance or promotion Access to technology Loans and economic aid Removal of penalties such as embargoes, investment bans, high tariffs Facilitate entry into global economic arena and institutions Economic engagement Arda Celik, professor of international relations at Uppsala University in 2011 book Economic Sanctions and Engagement Policies defined as follows: The purpose of economic engagement is to “deepen the economic intersection, interconnectedness and mutual dependence and finally seeks economic interdependence. This interdependence serves the sender state to change the political behavior of target state.” Other types of engagement Political engagement Diplomatic recognition Access to regional or international institutions Summits between leaders Commercial interests that include people to people; humanitarian concerns; historical ties (extra topical?) Other types of engagement Military engagements Extension of military or educational training Human rights among armed services Establish relationships between US and other foreign military officers Arms exchanges; offering security services Other considerations ALTHOUGH THE TOPIC REQUIRES USFG ACTION, IT DOES NOT SPECIFY ACTION WITH THE GOVERNMENTS OF THE TARGET COUNTRIES Learn the Latin America alphabet NAFTA ALBA North America Bolivarian Free Trade Agreement-Agreement between Canada, US, and Mexico Alternative for the Americas-Member countries includes Venezuela, Cuba, Bolivia, Nicaragua, and island countries in the Bahamas Latin America Alphabet CELAC FTAA Community of Latin Free Trade Area of American and Caribbean StatesFounded in 2011, includes 33 countries, but excludes the US & Canada Founded as an alternative to the OAS the Americas Proposed agreement to expand to all of the nations in the Western Hemisphere excluding Cuba. Opposed by members of ALBA Possible Affirmative Advantages Hegemony Oil dependency Could defend an increase Energy development of or decrease in US leadership and/or influence; improved relations with various countries would increase soft power any one of the three countries would help with decreasing dependence on Middle East sources Possible affirmative advantage areas Economic growth Solving social issues Improving conditions in any of these countries would be beneficial to both the country and the US in terms of opening new markets, allowing for corporate expansions, and developing local economies Increased engagement would lead to addressing other issues such as immigration, health care, trafficking in humans and drugs, and nuclear proliferation Have fun with these countries