Modern Latin America Review Sheet C 22
Modern Latin America
Review Sheet
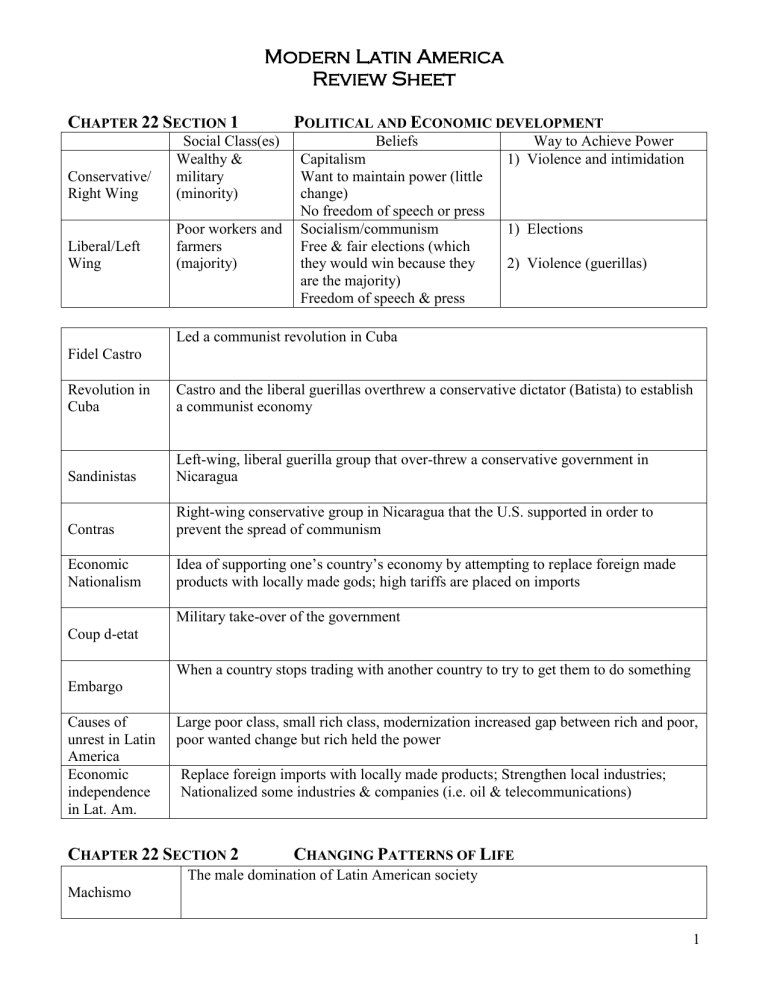
Sandinistas
Contras
Economic
Nationalism
Coup d-etat
Embargo
Causes of unrest in Latin
America
Economic independence in Lat. Am.
C
HAPTER
22 S
ECTION
1
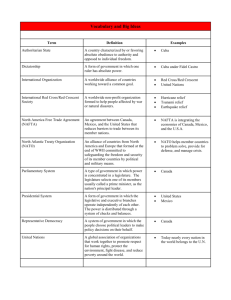
Social Class(es)
Conservative/
Right Wing
Liberal/Left
Wing
Wealthy & military
(minority)
Poor workers and farmers
(majority)
Fidel Castro
Revolution in
Cuba
P
OLITICAL AND
E
CONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
Beliefs
Capitalism
Want to maintain power (little change)
No freedom of speech or press
Socialism/communism
Free & fair elections (which they would win because they are the majority)
Freedom of speech & press
Led a communist revolution in Cuba
Way to Achieve Power
1) Violence and intimidation
1) Elections
2) Violence (guerillas)
Castro and the liberal guerillas overthrew a conservative dictator (Batista) to establish a communist economy
Left-wing, liberal guerilla group that over-threw a conservative government in
Nicaragua
Right-wing conservative group in Nicaragua that the U.S. supported in order to prevent the spread of communism
Idea of supporting one’s country’s economy by attempting to replace foreign made products with locally made gods; high tariffs are placed on imports
Military take-over of the government
When a country stops trading with another country to try to get them to do something
Large poor class, small rich class, modernization increased gap between rich and poor, poor wanted change but rich held the power
Replace foreign imports with locally made products; Strengthen local industries;
Nationalized some industries & companies (i.e. oil & telecommunications)
C HAPTER 22 S ECTION 2
Machismo
C HANGING P ATTERNS OF L IFE
The male domination of Latin American society
1
Effects of urban growth in Latin
America
Traditions effect women’s lives
Change in the role of the
Catholic Church
Difficulty finding jobs, housing shortage
Women are still considered inferior in many parts of society
Urbanization has caused more women to work outside of the home and become more educated
Idea of “Liberation Theology” – the Church should take a more active role in changing the conditions that contributed to poverty; They helped people organize for change (Romero)
C HAPTER 22 S ECTION 3
Porforio Díaz
M EXICO
Dictator of Mexico that implemented programs intended to modernize and strengthen Mexico’s economy (foreign investment, built railroads, developed mines,
Constitution of
1917
PRI bought land); the people eventually rebelled against him
Redistributed land to peasants, decreased the power of the Catholic Church , protected the rights of workers, gave government control of certain resources such as oil and silver
Institutional Revolutionary Party; political party that has dominated the country because it pays attention to the needs of many different groups
Ejido
Community-based farms that were established by government land & farm reform
Describe Mexico’s economic development (see notes)
Type of economy - mixed
Land reform – Mexico took land from wealthy land owners and redistributed it more equally
Oil resources – used them for development, when prices dropped, reliance on oil revenue hurt their economy
Dealing with Debt crisis – cut spending on health care, education, and other programs; laid off thousands of government workers; sold state-owned industries
NAFTA
What acronym stands for
3 countries in
NAFTA
Tariff
Free trade
Trade balance
North American Free Trade Agreement
U.S., Mexico, Canada
Tax on imports; it is designed to protect domestic products and make money for the government
No taxes or other restrictions on trade
Amount of exports compared to imports
2
Trade deficit
Trade surplus
Maquiladores
One argument for NAFTA
One Argument
Against NAFTA
More imports (buy) than exports (sell)
More exports (sell) than imports (buy)
Factories built along the border between the U.S. and Mexico to take advantage of cheap Mexican labor
The availability of cheaper products will allow Americans to spend more in our own economy and it will improve
Because labor in Mexico costs less, many Americans are afraid it will result in the loss of American jobs
C HAPTER 22 S ECTION 5
Juscelino
B RAZIL
Leader of Brazil who helped create rapid development and moved its capital
Kubitschek
“Brazilian
Miracle”
Groups that make up populations
Rapid development and economic growth in Brazil
50% black (descendants of Africans); descendants of European colonists and immigrants, recent Japanese immigrants
Effects of development on the land & people
While the economy improves, development often increases the gap between the rich and the poor as only some benefit from the development, and the land and environment is often negatively impacted
C HAPTER 23 S ECTION 1
Mexican War
L ATIN A MERICA AND THE U NITED S TATES
War with Mexico that began over Texas, The U.S. won and gained Texas and other territories in the southwest (Arizona, New Mexico, southern California)
Spanish-
American War
Good Neighbor
Policy
Bay of Pigs
Cuban Missile
Crisis
U.S. wanted Spanish out of North and South America; U.S. defeated Spain; Cuba gained independence, Spain lost influence in Latin America; U.S. gained territories such as Puerto Rico, Guam, Etc.
No country should interfere with the internal or external affairs of another country
An attempt to oust (remove from power) Fidel Castro; the U.S. backed anti-Castro forces, but did not give them the support they needed and they were defeated
Soviet Union (USSR) placed nuclear weapons missiles on Cuba; The U.S. perceived a threat and threatened Cuba; USSR threatened the
U.S.; U.S. agreed to back off and USSR agreed to remove the missiles
3
Increase in US investment in
Latin America
Cold War effects on US-Latin
America relations
U.S. investment increased in the early 1900s; bought plantations and nines, built railroads and factories, invested in oil wells; unpaid debt, however, often caused the
U.S. to invade and occupy land in hoes they would get their money back.
U.S. did what was necessary to prevent the spread of communism including support conservative groups than were guilty of human rights violations in order to maintain power
C HAPTER 23 S ECTION 2
OAS & its Goals
Default
R EGIONAL AND G LOBAL I SSUES
Organization of American States; its goal was to increase regional cooperation (help settle regional disputes peacefully, discourage foreign intervention, and promote economic development and democracy)
When a country stops paying, or cannot pay, back its loans from other countries
Why regional common markets
Success of regional common markets
Global Issues in
Latin America
Many countries have joined together to create regional common markets; Common markets promote trade among the countries involved, and hopefully benefit their economies.
Limited success because of political differences
Debt, drug trade, environment, human rights
Effect of Foreign
Debt on Global
Economy
When Latin American countries cannot pay back money that was lent to them, it negatively impacts the countries that lent the money
BRAZIL’S RAINFOREST
Development of
Amazon
Rainforest
Developments often leads to the destruction of the rainforest; alternatives to this destruction have caused controversy and violence
A variety of plants and animals in a certain area
Biodiversity
Greenhouse effect
When gases and particles trap the sun’s energy in the Earth’s atmosphere
Rubber Tappers
They offer an ecological alternative to cutting down the rainforest by tapping the rubber trees to harvest natural latex; their efforts have caused controversy with people who want to develop the rainforest
4