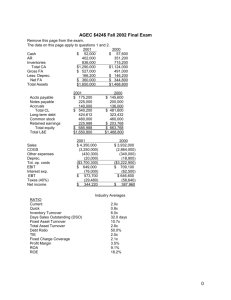
THE RATIOS AT A GLANCE
advertisement

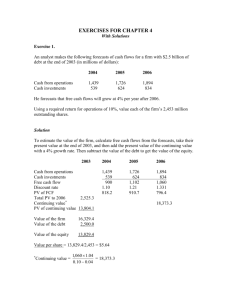
Appendix 8 THE RATIOS AT A GLANCE LIQUIDITY RATIOS Current Ratio Current Assets Current Liabilities Quick Ratio (Acid test) Current Assets – Inventory Current Liabilities - Bank Overdraft Current Liquidity Ratio (Current liabilities - bank overdraft) - liquid assets x 365 Cash flow from operations Defensive Interval Liquid assets x 365 Projected Expenditures FINANCE / LEVERAGE RATIOS Gearing ratio Debt Debt and Equity (Debt means long term and short term debt) Debt to equity ratio Total Debt Shareholders’ Equity Interest Cover EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) Interest paid Fixed Charges Coverage Ratio EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) Annual Financial Fixed Charges (interest + lease payments) Cash Coverage Ratio EBIT + non cash expenses Interest paid Fixed Charges Coverage Ratio EBIT + Lease Payment Annual Financial Fixed Charges (interest + lease payments) Capital Expenditure Ratio Cash from Operation Capital Expenditures Effective Interest Rate There are two methods of calculating the effective interest rate, these being: (i) Calculating the total cost of debt (internal measure): Interest Payments x 100% Average total debt (ii) Calculating interest rate on interest bearing debt: Interest Payments x 100% Average interest bearing debt Dividend Cover Net Profit Dividend ACTIVITY RATIOS Inventory Turnover Cost of Goods Sold Average Inventory (beginning year inventory + end of year inventory divided by two) Debt Collection Period / Debtor Days Accounts Receivables x 365 Credits Sales (Accounts receivable as at year end can be used or the average receivables) Trade Payable Period Trade Creditors x 365 Cost of Goods Sold Average days to convert inventory to cash Raw material turnover in days + Days to produce an item + Finished goods inventory turnover in days + Days between dispatch and invoice preparation + Debt collection period Net Current Assets to Sales (Debtors + Inventory - Creditors) Sales Tangible Fixed Assets to Sales Net Book Value of Tangible Fixed Assets x % Sales Capital Expenditure versus Depreciation Capital expenditure in year (gross) Depreciation charge for year x % Fixed Asset Turnover Sales Average Fixed Assets Capital Expenditure vs Depreciation Capital expenditure in year (gross) Depreciation charge for year Average Age of Fixed Assets Current Net Book Value Original Cost PROFITABILITY Gross profit margin (%) Gross profit Sales Mark Up % Selling price - costs of goods sold Cost of goods sold Costs of Goods Sold % Cost of goods sold Sales Net operating margin Gross profit - operating expenses – administration expenses Sales Or EBIT Sales Profit per employee Net operating profit Number of employees Breakeven point Fixed expenses ((Sales - Variable expenses)/Sales) Margin of safety (%) (Sales - Breakeven point) Sales SHAREHOLDER RETURN Return on total assets - management perspective EBIT (earnings before interest & tax) Average assets Return on assets - shareholder perspective NPAT (net profit after tax) Average assets Return on net operating assets (RONOA EBIT Net operating assets (operating fixed assets + stock + debtors - creditors) Earnings per share (EPS) Net income after tax Number of shares on issue A variation of EPS is Cash EPS which is defined as Cash flow (Net profit + Depreciation) Number of shares on issue Price Earnings Ratio Market price per share Earnings per share Dividend yield Dividends per share Market price per share Shareholders return i. Capital return Current market share price - Cost of shares purchased Cost of shares purchased ii. Dividend yield Dividend per share Current market share price iii. Total return Capital return + Dividend yield Net Asset Backing (NAB) Net assets less intangibles Number of shares on issue This analysis can be further refined by comparing the market value of the shares to their net asset backing : Market value per share Net asset backing Return on equity (ROE) Net profit after tax Total equity Cost of debt Interest rate (1 - tax rate) Cost of equity Re = Rf + βe (Rm - Rf)