Mod 7 drugs - Student Nurse Laura
advertisement

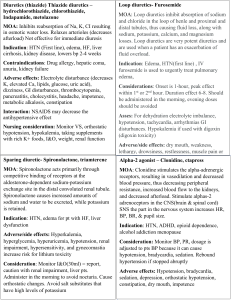
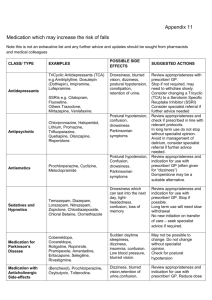
Medications Actions Advantage Contraindication AD/SE Nursing Indications Thiazide Diuretic increase sodium & water excretion by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule of the kidney. Used for hypertension and peripheral edema. Not effective for immediate dieresis. Used in clients w/normal renal function. Hydrochlorothiazide Relatively Gout, known dry mouth, thirst, Monitor for signs inexpensive, sensitivity to weakness, drowsiness, of electrolyte effective orally. sulfonamidelethargy, muscle aches, imbalance because Thiazide diuretics Effective longderived muscular fatigue, this causes loss of should be used term admin. Mild medications, tachycardia, GI sodium, K+, Ma. w/caution in clients side effects. severely disturbance. Encourage intake taking lithium Enhances other impaired of K+ rich foods. Postural hypotension because lithium antihypertensive kidney GerI: risk of may be potentiated by toxicity can occur in meds. Counter function, and postural alcohol, barbiturates, client taking digoxin, sodium retention history of hypotension. opioids, or hot corticosteroids, or effects of other hyponatremia. weather/baths, strenuous Measure BP in 3 hypoglycermice antihypertensive positions. Caution exercise meds. meds. pt to rise slowly. sulfa-based – allergic i/o, lytes, FUN Cr. reaction Give in AM, Diet, - at risk for hypokalemia, BUN, uric acids. hyperglycemia, Hypercalcemia, hyperlipidemia and hyperuricemia. Loop Diuretic Inhibit sodium and chloride reabsorption. More potent than Thiazide diuretics. Causing rapid dieresis, and thus decreasing vascular fluid volume, cardiac output and BP Gout, known risk of volume Geri: risk of postural Rapid Action. Potent. sensitivity to and elect. hypotension. Measure BP Used when Thiazides sulfonamideDepletion from in 3 positions. Caution pt fail or pt needs rapid derived the profound to rise slowly. dieresis. medications, diuresis severely impaired occurring. kidney function, Fluid & elec and history of replacement hyponatremia. may be req. Bumetanide – diuretic used to decrease venous return when client is in bed.(paroxysmal nocturnal Dyspnea due to increased venous return) adverse – hypotension. monitor BP Put on K+ supplements. Furosemide – Administer Lasix slowly - may cause hearing loss if injected too rapidly. 1 Medications Actions Advantage Contraindication AD/SE Nursing Indications Potassium Sparing Diuretic – promotes sodium and water excretion and potassium retention. Used for edema and HTN to increase urine output, fluid retention, and overload associated w/heart failure, ascites. Causes Potassium retention Contraindicated in Drowsiness, lethargy, Monitor for Renal Disease, headache. Hyperkalemia, Hyperkalemia if Azotemia, severe N & V, diarrhea. Rash, given with ACE Spironolactone - Considered an hepatic disease, Dizziness, weakness, dry inhibitor or Aldosterone Receptor Blocker as hyperkalemia mouth photosensitivity, Angiotensin well as Potassium sparing diuretic. anemia, thrombocytopenia. receptor blocker. Diarrhea & GI symptoms – admin. meds after meals Monitor Vital signs. Monitor Urine Output. Avoid foods high in K+. Avoid salt substitutes – high in K+. Centrally Acting Sympatholytic (Adrenergic Blockers) Alpha Agonist – stimulate alpha receptors in the CNS to inhibit vasoconstriction – reducing peripheral resistance. slows pulse, history of Sodium and water retention, Monitor VS. Not to which counteracts depression, drowsiness, dizziness, dry discontinue med – can tachycardia of psychosis, mouth, Bradycardia, edema, cause severe rebound Hydralazine obesity, impotence, hypotension, hypertension. Monitor chronic depression. liver function tests. Use sinusitis, peptic May cause severe with caution if history of ulcer gallbladder, renal, or depression – but mainly cardiac disease, or those with depression; report manifestations, as seizure disorder. Geri: this may require that drug depression and postural be omitted. Nasal hypotension common in congestion. elderly Methyldopa – drowsiness, dizziness, dry Geri: May produce mouth; nasal congestion. mental and behavioral Dopa-decarboxylase, inhibitor; displaces (troublesome at first but changes in the elderly. norepinephrine from storage sites. then tends to disappear) Use Drug of choice for pregnant women w/HTN (Laura’s with caution w/Renal METH-Pregnant Lady) Useful in patients w/renal Disease. failure or prostate disease. Does not decrease cardiac output or renal blood flow. Does not induce oliguria. Liver disease Clonidine through CNS, little or no Drowsiness, dry mouth, monitor BP when produces blood orthostatic withdrawal phenomenon. stopping medication Patch pressure reduction. effect. Moderately sometimes is effective If BP is above 160 potent, when other meds fail to give Clonidine – lower blood pressure. Centrally acting. 2 Medications Actions Advantage Contraindication AD/SE Nursing Indications CNS – Quick. Beta Blockers block the sympathetic nervous system, especially the sympathetic to the heart, producing a slower heart rate and lowered blood pressure. Reduces Hearts Contractility work load and oxygen demands. Reduce pulse Bronchial asthma, Mental depression I/O, Wt, HR Avoid Glucose monitoring. rate in patients allergic rhinitis, manifested by sudden discontinuation, with right ventricular insomnia, lassitude, check HR before giving. Used for angina, tachycardia failure from weakness, and Geri: Risk of toxicity is Dysrhythmia, and BP pulmonary fatigue. Light increased for elderly hypertension, elevation. hypertension, headedness & patient w/decreased migraine headaches, Indicated for heart failure, occasional N & V, renal and liver function. prevention of patients who depression , DM, Epigastric distress Take BP in 3 positions myocardial also have Dyslipidemia, and observe for infarction, and stable angina Heart block, PVD, hypotension. Antacids glaucoma. pectoris and HR < 50bpm, may cause silent apical malabsorption. ischemia. BP < 110 Atenolol Propranolol – watch out for bronchospasms indicated by audible expiratory wheezes. Metoprolol Calcium Channel Blockers – Inhibit CA ion influx across membranes. Vasodilating effects on coronary and peripheral arteriole. Decrease cardiac work and energy consumption, increase delivery of O2 to myocardium VASODIALATORS, relax smooth muscle in vessel walls – sexual dysfunction. Used as Antirhythmic agents. Rapid action. Effective by oral or None (except Muscle cramps, joint Monitor for hypotension, sublingual route. To tendency to slow Heart Failure stiffness, sexual Bradycardia and pedal SA nodal activity or prolong AV for Nifedipine) difficulties may edema. Administer on empty node conduction. Isolated systolic disappear when dose stomach. Use w/caution in hypertension. decreased. diabetic patient w/diabetes. Small frequent meals if Used in Raynaud’s Disease May cause dizziness nausea. Report irregular Heartbeat, hyperglycemia. constipation, SOB, edema. Amlodipine Felodipine Nifedipine- for blood pressure Nisoldipine Diltiazem - Bradycardia due to affect on AV and SA nodes. CA blockers used to treat Arrhythmias. Verapamil Bradycardia due to affect on AV and SA nodes. CA blockers used to treat Arythmias. slows velocity of conduction of cardiac impulse. Effective antiarrhythmic Rapid IV onset. Blocks SA and AV Sinus or AV node disease; severe heart failure; severe hypotension Bradycardia. Administer on empty stomach or before meal. Do not discontinue suddenly. Depression may subside when medication is discontinued. To relieve headaches, reduce noise, monitor electrolytes. Decrease dose for patients 3 Medications Actions AD/SE Advantage Nursing Indications node channels. Contraindication with liver or renal failure. Peripherally Acting Alpha Blocker – Decrease sympathetic vasoconstriction by reducing the effects of norepinephrine at peripheral nerve endings, resulting in vasodilation and decreased BP Doxazosin Orthostatic hypotension, Monitor VS, Fluid Prazosin reflex tachycardia, sodium retention , edema. Terazosin and water retention, GI change positions disturbances, N, slowly. drowsiness, nasal congestion edema Weight Gain. Combined alpha & beta blocker Carvedilol Labetalol Peripheral Vasodilators – work directly on the vessels to cause vasodilation, given for chest pain. decrease Peripheral Resistance. Increased blood flow to extremities. Effective for disorders resulting from vasospasm Reynaud’s disease.. May decrease symptoms of cerebral vascular insufficiency. Hydralizine light-headedness, Assess Headaches Minoxidil dizziness, Orthostatic Monitor for Orthostatic Hypotension, hypotension. BP VS HR. Tachycardia, inadequate blood flow – pallor, Palpitations, Flushing, feeling cold, pain. Instruct patient GI distress. it may take up to 3 months for desired therapeutic response. Quit smoking – increases vasospasm.. Avoid Aspirin or aspirin-like compounds. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme ACE Inhibitors and) – lowers total peripheral resistance. by blocking Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II. Good for Heart Failure. Reduces Cardiac workload. Prevents Peripheral Vasoconstriction. Used to treat HTN, PRIL Causes N & V, diarrhea, check urinary protein HF, cardioprotective Play right in Decrease Persistent dry cough Monitor VS, WBC, effect after Las vegas you Aldosterone hypotension Protein, Albumin, myocardial need a ACE Avoid use Hyperkalemia BUM, Creatinine, K+. infarction. with tachycardia Hypoglycemic potassium headache dizziness, reactions. supplements fatigue, insomnia Inform pt food may and hypoglycemic reaction in diminish taste during potassium=sp pt w/DM, bruising, 1st month of therapy. aring Petechiae, bleeding diuretics. Diminished Taste. Benazepril Captopril – take 20 – 60 minutes before a meal. Enalapril Fosinopril 4 Medications Actions Advantage Contraindication AD/SE Nursing Indications Lisinopril Ramipril Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)– sit at receptor site on II, blocks so I can’t go to II. Produces Vasodilation. “artan” Irbesartan Losartan Olmesatrtan Valsartan Normal BUN 7 – 20 Normal Creatinine 0.8 – 1.4 K+ 3.5 – 5.5 Norm PT 11 – 13, or PTT is 1-2 times the pt’s control for warfarin INR prophylaxis and Tx of venous thrombosis 2-3 Tx pulmonary, Prevention of systemic embolism 2-3 all other INR 3-4.5 Digoxin therapeutic 0.5 – 2ng. 5