Acute Asthma - Cardiff PICU
advertisement
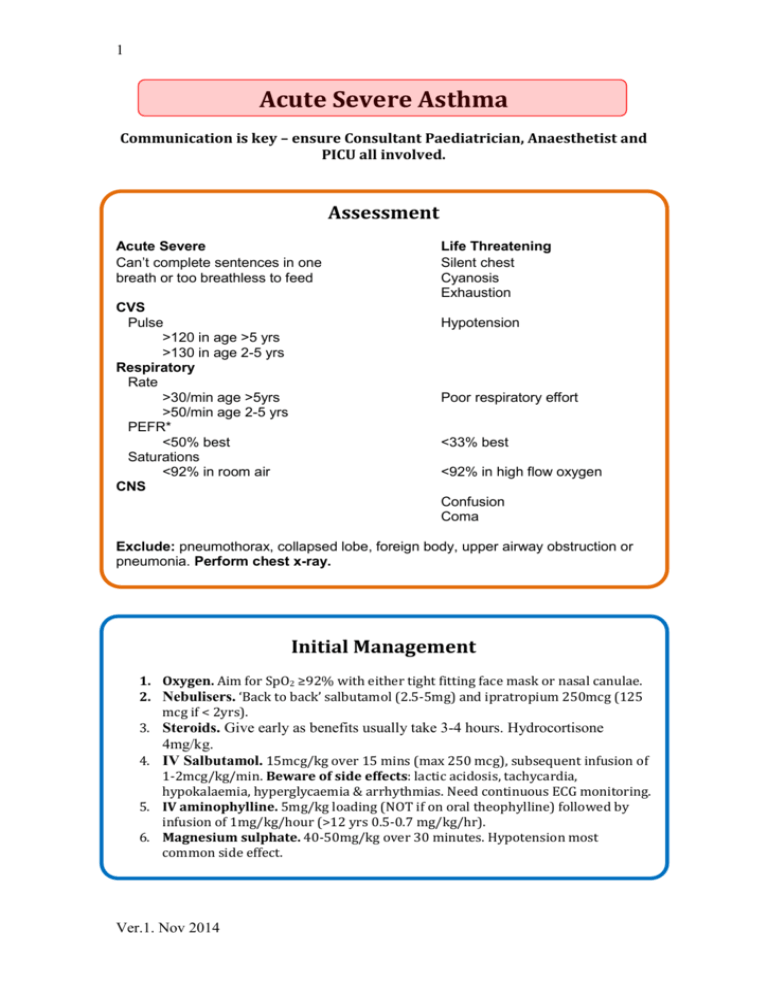
1 Acute Severe Asthma Communication is key – ensure Consultant Paediatrician, Anaesthetist and PICU all involved. Assessment Acute Severe Can’t complete sentences in one breath or too breathless to feed CVS Pulse >120 in age >5 yrs >130 in age 2-5 yrs Respiratory Rate >30/min age >5yrs >50/min age 2-5 yrs PEFR* <50% best Saturations <92% in room air CNS Life Threatening Silent chest Cyanosis Exhaustion Hypotension Poor respiratory effort <33% best <92% in high flow oxygen Confusion Coma Exclude: pneumothorax, collapsed lobe, foreign body, upper airway obstruction or pneumonia. Perform chest x-ray. Initial Management 1. Oxygen. Aim for SpO2 ≥92% with either tight fitting face mask or nasal canulae. 2. Nebulisers. ‘Back to back’ salbutamol (2.5-5mg) and ipratropium 250mcg (125 mcg if < 2yrs). 3. Steroids. Give early as benefits usually take 3-4 hours. Hydrocortisone 4mg/kg. 4. IV Salbutamol. 15mcg/kg over 15 mins (max 250 mcg), subsequent infusion of 1-2mcg/kg/min. Beware of side effects: lactic acidosis, tachycardia, hypokalaemia, hyperglycaemia & arrhythmias. Need continuous ECG monitoring. 5. IV aminophylline. 5mg/kg loading (NOT if on oral theophylline) followed by infusion of 1mg/kg/hour (>12 yrs 0.5-0.7 mg/kg/hr). 6. Magnesium sulphate. 40-50mg/kg over 30 minutes. Hypotension most common side effect. Ver.1. Nov 2014 2 Intubation Indications Tired Reduced level of consciousness Worsening hypoxaemia N.B. Laboratory investigations are less important than clinical picture Practicalities Most experienced person available should perform Pre-oxygenate Have 10-20mls/kg of fluid attached and ready to go. Consider administering a fluid bolus pre-emptively. Use a cuffed ETT as high airway pressures are likely to be required. Ketamine is a useful induction agent (1-2mg/kg) due to its bronchodilator activity. Sevoflurane also has bronchodilator activity therefore useful for maintenance. Avoid morphine & atracurium (histamine release). Ventilation Sedate & paralyse. Sevoflurane can be used or infusion of midazolam and fentanyl. Vecuronium can be used for paralysis. Avoid peak inspiratory pressure > 35 cmH2O. Permissive hypercapnea to keep pH ≥7.2. Ensure long enough expiratory time to avoid gas trapping – i.e. low rate (10—15 breaths/min), I:E ratio of at least 1:2. PEEP. A PEEP of 5-7cmH2O often necessary to overcome intrinsic PEEP and prevent gas-trapping. Regular suction to prevent mucus plugging. Check CXR for ETT position (between clavicles). Beware of auto-PEEP. Disconnect from ventilator if suspected and consider manual decompression. Beware of pneumothorax. Acute bronchospasm can be relieved by adrenaline (O.1mg/kg = 0.1ml/kg of 1:10,000 solution). Cardiovascular Commonest complication is hypotension caused by high intrathoracic pressure limiting venous return. Use 10-20ml/kg alloquats of iv fluid as required. Ver.1. Nov 2014