Low Blood Pressure And Whole Body Vibration
advertisement

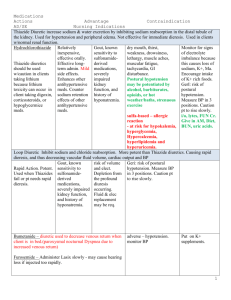
Low Blood Pressure and Whole Body Vibration Low blood pressure or hypotension results when blood pressure is lower than normal during and after each heart beat. Normal blood pressure tends to range from 90 systolic and 60 diastolic to 130 systolic and 80 diastolic. However, low blood pressure is not defined by a number but by symptoms. What may be low blood pressure for one individual may be normal for someone else. Hypotension can be caused by many factors, which include certain drugs as well as various heart issues, fainting, advanced diabetes, anaphylaxis, shock, and dehydration. There are three types of hypotension: orthostatic hypotension, neural-mediated hypotension, and severe hypotension. Orthostatic hypotension is a temporary lowering of blood pressure that last seconds or minutes. It usually occurs when an individual is moving from a lying to standing position. Symptoms of hypotension may include blurred vision, dizziness, confusion, syncope, light-headedness, and sleepiness. Treatment for low blood pressure in a healthy individual is not needed. Treatment is required if symptoms or signs of hypotension are present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Orthostatic hypotension can occur during exercise when the head moves from a position below the heart to an upright position. It can also occur when an individual stops an aerobic activity suddenly and the blood pools in the ankle. When an individual suffers from orthostatic hypotension, it is important during exercise that positions where the head is below the heart be avoided and care taken to ensure an adequate cool down is incorporated into a workout. Exercise is an important component when altering lifestyle behaviours to lower blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Research has suggested that the most important benefit to exercise with respect to hypertension is weight loss1. One study suggests that weight loss along with diet modifications are the most effective lifestyle changes for lowering blood pressure in hypertensive individuals1. Another literature review suggests that there are significant reductions in blood pressure with exercise, but the same decreases are not seen in individuals with normal blood pressure2. There is no research specifically looking at the impact of Whole Body Vibration (WBV) on individuals with hypotension. Two studies measured blood pressure changes from using WBV. One study found no change in blood pressure following its use, while the other study found an increase in blood pressure during use3, 4. Therefore, findings remain inconclusive. Regardless, it is important that any individual with a known medical condition discuss the addition of any type of exercise, including WBV, with his/her physician. This is so the physician can help an individual weigh the benefits of an exercise against any potential risk or contraindications. Once an individual, in consultation with a physician, determines it is safe to use WBV, it should be initiated at a reduced intensity and duration. This is so an individual can become accustomed to the THIS IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. WE DO NOT DIAGNOSE OR PRESCRIBE. PLEASE CONSULT YOUR HEALTH PROVIDER. 25 Curity Avenue, Unit 2A, Toronto, ON M4B 3M2 416-285-6055 fax 416-285-8918 info@t-zonehealth.com www.t-zonevibration.com -2machine and determine if it is contributing to any symptoms related to his/her hypotension. Once an individual adjusts to the platform, the intensity and duration can be increased and exercised added at the appropriate level of fitness. It is important that an individual with hypotension avoid any exercise that places his/her head below the level of the heart. An adequate cool down is also essential. Other exercises, such as squats, that may trigger symptoms without the platform, should be approached with caution or avoided. If an individual is concerned WBV may be impacting blood pressure levels, pre and post exercise blood pressure can be recorded and monitored for changes. If at any time an individual experiences any symptoms related to his/her hypotension while using the platform or following the use of WBV, it should be discontinued until the individual speaks to a physician. In general, if an individual experiences any dizziness, pain, or shortness of breath while using the machine, it should be discontinued. References 1. Hedayati SS, Elsayed EF, Reilly RF. 2011. Non-pharmacological aspects of blood pressure management: what are the data?, Kidney International, 79(10), 1061-70. 2. Gupta R, Guptha S. 2010. Strategies for initial management of hypertension, Indian Journal of Med Res, 132(5), 531-42. 3. Otsuki T, Takanami Y, Aoi W, Kawai Y, Ichikawa H, Yoshikawa T. 2008. Arterial stiffness acutely decreases after whole-body vibration in humans, Acta Physiologica (Oxf.), 194(3), 189-94. 4. Cochrane DJ, Sartor F, Winwood K, Stannard SR, Narici MV, Rittweger J. 2008. A comparison of the physiologic effects of acute whole-body vibration exercise in young and older people, Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 89(5), 815-21. THIS IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. WE DO NOT DIAGNOSE OR PRESCRIBE. PLEASE CONSULT YOUR HEALTH PROVIDER. 25 Curity Avenue, Unit 2A, Toronto, ON M4B 3M2 416-285-6055 fax 416-285-8918 info@t-zonehealth.com www.t-zonevibration.com