LESSON 10: ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS
advertisement

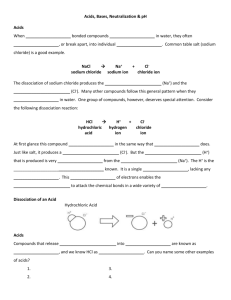
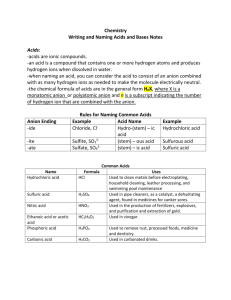
13. ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS - Key 2. What is the PH scale? What does it measure? acidity / basicity 3. a) Put the strips of papers with food items along the scale, according to their PH factor, from high alkaline, to alkaline, low alkaline, low acid, acid to high acid. HIGH ALKALINE LOW LOW ACID HIGH ALKALINE ALKALINE ACID ACID vegetable Carrots, lettuce, Goat milk, Bananas, Canned Beef, pork, juices, zucchini, soy milk, plums, fruit, canned parsley, raw dates,blackcurrent, lentils, wild processed white rice, tuna, spinach, grapes, kiwi, rice, fruit juices, white canned broccoli, apples, pears buckwheat, liver, bread, sardines, celery, garlic, strawberries, oyster, pastries, parmasan, herbal teas, lemons, whole pasta, black tea, lemon water, avocadoes, milk, fish, coffee, beer, dried figs, tomatoes, butter, lamb, liquor raisins oranges yoghurt, poultry, white eggs, sugar ketchup, mustard b) What problems might consuming too many acidic foods cause? obesity, allergies, fatigue 4. Acids, bases and salts – definitions. Watch the video1and complete the text below with missing pieces of information. The Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius introduced the theory of ionization and used this theory to explain much about the behaviour of acids and bases. An Arrhenius acid is defined as any compound that dissociates in aqueous solution to form hydrogen ions. HNO3(aq) → H+(aq) + NO3-(aq) An Arrhenius base is defined as any compound that dissociates in aqueous solution to form hydroxide ions. KOH(aq) → K+(aq) + OH - (aq) Salts are compounds that dissociate in aqueous solution releasing neither H+ nor OH ions. KCl → K+ (aq) + Cl – (aq) 1 5. Classifying compounds Using the Arrhenius definition, classify the following examples as acids, bases and salts HBr – A (hydrogen bromide) Mg(OH)2 – B (magnesium hydroxide) HCl – A (hydrochloric acid) KNO2 - A (potassium nitrite) HFO4 - S (perfluoric acid) Ba(OH)2 B (barium hydroxide) KCl – S (potassium chloride) H3 PO4 – A (phosphoric acid) HClO – A (hypochlorous acid) Al(OH)3 – B (aluminium hydroxide) KC2 H 3O2 – S (potassium acetate) NaCl – S (sodium chloride) 6. Naming acids and bases a) Watch the video1 and complete the text below Since bases are simply ionic compounds, they are named in the usual way: NH4 OH – ammonium hydroxide Al(OH)3 – aluminium hydroxide Binary acids consist of 2 elements, the first being hydrogen. Binary acids are named using the format: hydro+(root word of second element)+IC acid Ternary acids consist of 3 elements. Do not use a prefix. Simply change the ending of the polyatomic ion’s name and add the word acid. –ate ending becomes -ic and –ite becomes ous. b) Now name the following acids: HBr hydrobromic acid HNO3 - nitric acid HNO2 – nitrous acid HI – hydroiodic acid (viz VIDEO) H3 PO3 phosporous acid HC2 H3 O2 acetic acid H2 CO3 carbonic acid HClO2 chlorous acid HF hydrofluoric acid H2 SO3 sulfurous acid 7. Naming salts; a) Read the text below, and according to the information given, name the salts underneath, as in the example. The name of a salt has two parts. The first part comes from the metal in the base or carbonate, or the metal itself if a reactive metal like magnesium or zinc is used. The second part of the name comes from the acid used to make it. The names of salts made from hydrochloric acids end in –chloride, while the name of salts made from sulfuric acid end in –sulfate. metal acid 1. sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid 2. copper oxide hydrochloric acid 3. sodium hydroxide sulfuric acid 4. zinc oxide sulfuric acid 5. ammonia hydrochloric acid 2 to make salt sodium chloride copper chloride sodium sulfate zinc sulfate amonium chloride b) Write formulas of the reactions above 1. NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O 2. Cu2O + 2 HCl → 2 CuCl + H2O 3. 2 NaOH + H2 SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O 4. 2 ZnO + H2 SO4 → Zn2SO4 + 2 H2O 5. NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl 8. Give formulas of these acids, bases and salts boron silicide sodium hydroxide iron(III)chloride sulfuric acid B2Si NaOH FeCl3 H2SO4 magnesium phosphide Mg3P2 zinc hydroxide Zn (OH)2 aluminium sulfide Al2S3 sulfurous acid H2SO3 9. Chemistry quiz2 1. A solution has a pH of 4 - what does this mean? It is acidic. It is neutral. It is alkaline. 2. Which of the statements below is correct? Bases are acids that dissolve in water. Bases are alkalis that dissolve in water. Alkalis are bases that dissolve in water. 3. A liquid has a pH of 7. What does this tell you about the liquid? It is water. It is sodium chloride solution. It is neutral. 4. Which salt is made when calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid? sodium chloride calcium chloride calcium sulphate 5. Which pair of substances will react together to make copper sulfate? copper and sulfuric acid copper oxide and sulfuric acid copper oxide and hydrochloric acid 6. Which is the correct order of methods for making a salt from an acid and an insoluble base? filtration ==> evaporation ==> neutralisation neutralisation ==> evaporation ==> filtration neutralisation ==> filtration ==> evaporation 3 4