Acids, Bases, Neutralization, & pH Outline
advertisement
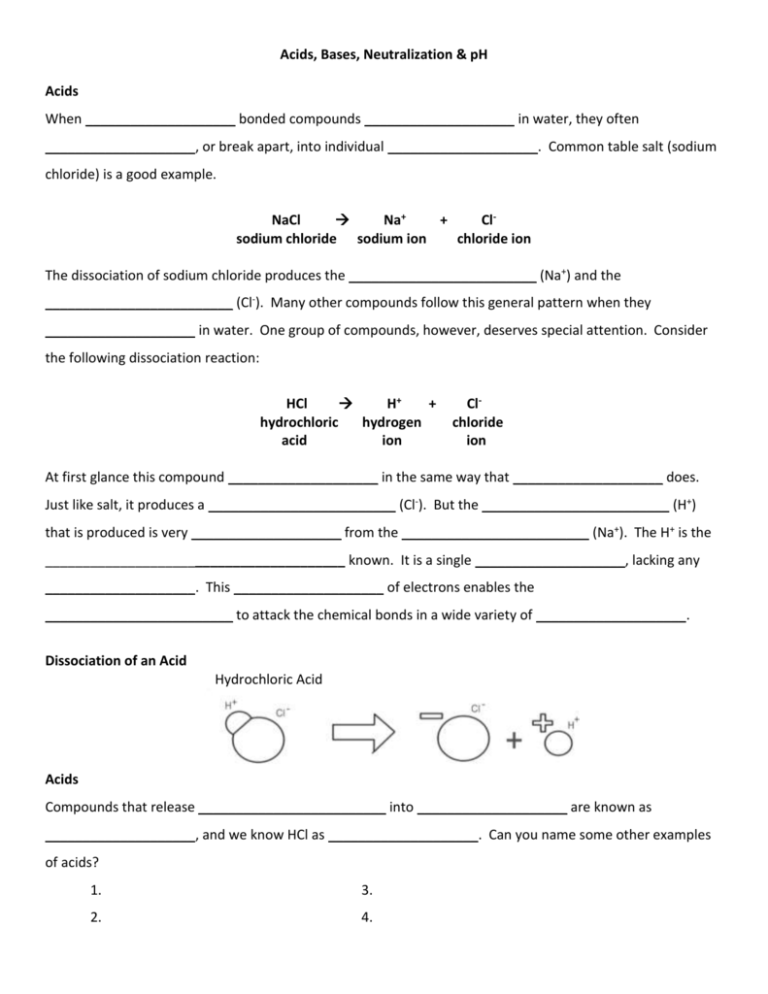
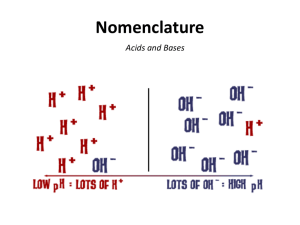
Acids, Bases, Neutralization & pH Acids When ____________________ bonded compounds ____________________ in water, they often ____________________, or break apart, into individual ____________________. Common table salt (sodium chloride) is a good example. NaCl Na+ + Clsodium chloride sodium ion chloride ion The dissociation of sodium chloride produces the _________________________ (Na+) and the _________________________ (Cl-). Many other compounds follow this general pattern when they ____________________ in water. One group of compounds, however, deserves special attention. Consider the following dissociation reaction: HCl H+ + hydrochloric hydrogen acid ion Clchloride ion At first glance this compound ____________________ in the same way that ____________________ does. Just like salt, it produces a _________________________ (Cl-). But the _________________________ (H+) that is produced is very ____________________ from the _________________________ (Na+). The H+ is the ________________________________________ known. It is a single ____________________, lacking any ____________________. This ____________________ of electrons enables the _________________________ to attack the chemical bonds in a wide variety of ____________________. Dissociation of an Acid Hydrochloric Acid Acids Compounds that release _________________________ into ____________________ are known as ____________________, and we know HCl as ____________________. Can you name some other examples of acids? 1. 3. 2. 4. Bases ____________________ are compounds that release _________________________ (OH-) into solution. _____________________________ is an example of a base. NaOH Na+ + OHsodium sodium hydroxide hydroxide ion ion Dissociation of a Base Acids & Bases Strong ____________________ and ____________________ are highly ____________________ chemical compounds. They can attack and ____________________ a variety of ____________________, thus making them potentially dangerous to _________________________. Neutralization & pH Mixing a _________________________ and a _________________________ results in a reaction in which _________________________ and _________________________ react to form ____________________. This type of reaction is called a ____________________ reaction. Can you guess the reason for this name? H+ + OH hydrogen hydroxide ion ion H2O water If the quantities of acid and base being mixed are in ____________________, the neutralized solution that results is neither ____________________ nor ____________________. The concentrations of _________________________ and _________________________ are ____________________. The relative ____________________ of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in a ____________________ is an important indicator of the ____________________ of the solution. A measurement system known as the ____________________ indicates the relative concentrations of these ____________________. The pH scale ranges from _____ to _____. _________________________, in which the concentrations of H+ and OH- ions are ____________________, has a pH value of _____. Acids have pH values of _________________________. _________________________, such as those used to help _________________________ in the stomach, have pH values of ____________________. Bases have pH values _________________________. _________________________, like _________________________, have high pH values, ranging from ____________________. The pH values within most ____________________ range from ____________________. These _________________________ values are maintained by ____________________ that help prevent sharp, sudden swings of _____, which might cause ________________________________________within living tissues.