Acids and Bases
advertisement

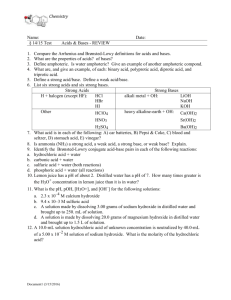
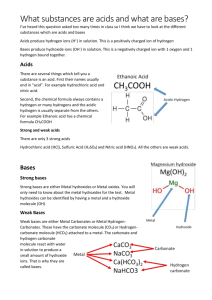
SNC 2D – Chemistry Acids and bases Acids and Bases – Properties, Names and formulas Properties of acids Acids are sour tasting, water-soluble substances. They are considered proton donors since the hydrogen ions that distinguishes them is displaced during the reaction. They are good electrical conductors. Ions disassociated when dissolved in water With metals, the H+ is displaced to form H2(g) zinc + hydrochloric acid hydrogen + Zinc chloride With carbonates, water and carbon dioxide are formed. Hydrochloric acid + calcium carbonate calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide Names and formula of acids Making Oxyacids Oxyacids are made when non- metal oxides are added to water. The cation is always a Hydrogen ion (H+). The name of the acid is based on the name of the cation non-metal oxide + water Acid Sulphate added to water Acid that begin with the prefix “hydro” are binary compounds in solution. The cation is always hydrogen while the anion is halogen. Hydrochloric acid - Identify the following acids names HClO3 __________________________ Carbonic acid _______________________ H3PO4 __________________________ Nitric acid _______________________ HF __________________________ Hydrobromic acid _______________________ HI __________________________ Hydrofluoric acid` _______________________ SNC 2D – Chemistry Acids and bases Properties of Bases Bases are bitter-tasting, water-soluble substances that feel slippery to the touch. They are good conductors of electricity because they release OH-, proton acceptors. Substances that are basic are described as alkaline. Bases are made when metal oxides are placed in water Non-metal oxide + water Add Sodium oxide to water The rules for naming and writing formula for bases is the same as basic nomenclature… Magnesium Hydroxide Potassium hydroxide LiOH Ca(OH)2 _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ Other Common Bases Draino: drain cleaner (sodium hydroxide – NaOH) breaks down protein in hair Bleach: Sodium hypochlorite – NaClO Baking soda: Sodium bicarbonate – NaHCO3 P. 271 1-8