4-1 Protein 3D Structure and Function
advertisement

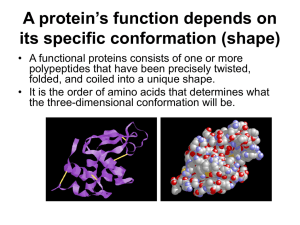
4-1 PROTEINS: THREE–DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Introduction The primary structure of proteins is the linear _______________ of amino acid residues in a polypeptide. Polypeptide chains do not have linear conformations, but contain _______________, _______________, _______________, and _______________. Recall that in order to change conformation, a _______________ bond must be broken. Also recall that each amino acid can exist in ___ and ___ conformations, and since there are many _______________ in a protein, there is an _______________ number of potential conformations. Under physiological conditions, each protein _______________ into a single stable shape known as its _______________ conformation. o The biological _______________ of a protein depends completely on its native conformation. Rotation around covalent bonds is restricted by _______________ bonds and other weak _______________ between amino acid residues. Protein Size A protein may be a _______________ polypeptide chain, or it may be composed of _______________ polypeptide chains bound to each other by _______________ interactions. In general, each polypeptide chain is encoded by a single _______________, but there are exceptions. In some species, the _______________ and _______________ of every polypeptide can be determined from the sequence of the _______________. Types of Proteins Many proteins are _______________ proteins, which are __________ - soluble, _______________, roughly _______________ macromolecules whose polypeptides are tightly _______________. o The interior is _______________ and the surface is _______________. o They possess _______________ or indentations that specifically recognize and bind other compounds. o Many are _______________, _______________ proteins, and _______________ proteins. Polypeptides can be _______________ components of large subcellular or extracellular structures. o _______________ proteins are structure proteins that provide mechanical _______________ to cells or organisms. They are typically large cables or threads. o Examples: -keratin, the major component of __________ and __________. Collagen, the major component of __________, __________, __________, and __________. Many proteins are integral components of _______________, or they are somehow associated with them.