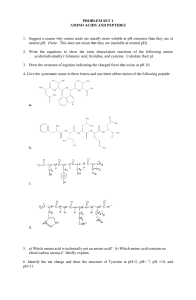
3-4 WKST

3-4 P
EPTIDE
B
ONDS
1.
Describe the primary structure of a protein.
2.
The linkage between amino acid residues is an _______________ bond called a
_______________ bond.
3.
What type of reaction occurs to form a peptide bond? What functional groups react on the two different amino acids? What side product is formed?
4.
What helps to overcome the thermodynamic barrier of peptide formation?
5.
Draw reaction equations and name the dipeptide that forms between the following pairs of amino acids. Assume the second one listed retains its carboxyl group. a.
Gly-Ile b.
Phe-Thr c.
Met-Glu d.
Asn-Ser
6.
Why are amino acids numbered from the N-terminus to the C-terminus?
7.
Why is most of the ionic charge of a polypeptide contributed by the side chains?
8.
What four things are affected by the charge of the side chain?
9.
Match the peptide with its biological importance.
_____ a. toxins X. 200x sweeter than table sugar
_____ b. endorphins
_____ c. aspartame
Y. regulate pain in vertebrates
Z. snake venom and poisonous mushrooms
10.
(#6 pg 81) The tripeptide glutathione (GSH) (
-Glu-Cys-Gly) serves as a protective function in animals by destroying toxic peroxides that are generated during aerobic metabolic processes.
Draw the chemical structure of glutathione (the
symbol indicates that the peptide bond between
Glu and Cys is formed between the
-carboxyl of Glu and the amino group of Cys).
11.
(#7 pg 81) Melittin is a 26-residue polypeptide found in bee venom. It its monomeric form, melittin is thought to insert into lipid-rich membrane structures. Explain how the amino acid sequence of melittin accounts for this property.
H
3
N + -Gly-Ile-Gly-Ala-Val-Leu-Lys-Val-Leu-Thr-Gly-Leu
Pro-Ala-Leu-Ile-Ser-Trp-Ile-Lys-Arg-Lys-Arg-Gln-Gln-NH
2