Chapter 16: Apoptosis - Introductory & Human Biology
advertisement

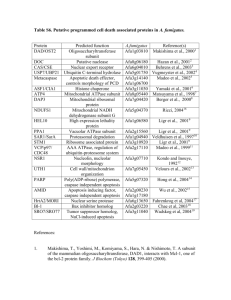
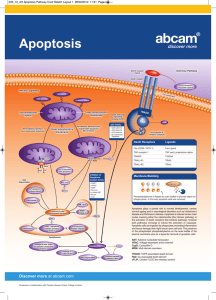
Chapter 16 16.1 Introduction Review Kerr, J. F., Wyllie, A. H., and Currie, A. R., 1972. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer v. 26 p. 239–257. Wyllie, A. H., Kerr, J. F., and Currie, A. R., 1980. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. v. 68 p. 251–306. 16.2 Caspases orchestrate apoptosis by cleaving specific substrates Review Fischer, U., Jänicke, R. U., and Schulze-Osthoff, K., 2003. Many cuts to ruin: A comprehensive update of caspase substrates. Cell Death Differ. v. 10 p. 76–100. 16.3 Executioner caspases are activated by cleavage, whereas initiator caspases are activated by dimerization Review Boatright, K. M., and Salvesen, G. S., 2003. Mechanisms of caspase activation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. v. 15 p. 725–731. Fuentes-Prior, P., and Salvesen, G. S., 2004. The protein structures that shape caspase activity, specificity, activation and inhibition. Biochem. J. v. 384 p. 201–232. Lahm, A., Paradisi, A., Green, D. R., and Melino, G., 2003. Death fold domain interaction in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. v. 10 p. 10–12. Research Berglund, H., Olerenshaw, D., Sankar, A., Federwisch, M., Mcdonald, N. Q., Driscoll, P.C. 2000. The Three-Dimensional Solution Structure and Dynamic Properties of the Human Fadd Death Domain. J. Mol. Biol. v. 302 p. 171–188. Boatright, K. M., et al., 2003. A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol. Cell v. 11 p. 529–541. Huang, B., Eberstadt, M., Olejniczak, E. T., Meadows, R. P., Fesik, S. W. 1996. NMR structure and mutagenesis of the Fas (APO-1/CD95) death domain. Nature v. 384 p. 638–641. Riedl, S. J., Fuentes-Prior, P., Renatus, M., Kairies, N., Krapp, S., Huber, R., Salvesen, G. S., and Bode, W., 2001. Structural basis for the activation of human procaspase-7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA v. 98 p. 14790–14795. Vaughn, D. E., Rodriguez, J., Lazebnik, Y., Joshua-Tor, L., 1999. Crystal structure of Apaf-1 caspase recruitment domain: An alpha-helical Greek key fold for apoptotic signaling. J. Mol. Biol. v. 293 p. 439–447. 16.4 Some inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) block caspases Review Shi, Y., 2004. Caspase activation, inhibition, and reactivation: A mechanistic view. Protein Sci. v. 13 p. 1979–1987. Vaux, D. L., and Silke, J., 2005. IAPs, RINGs and ubiquitylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. v. 6 p. 287–297. 16.5 Some caspases have functions in inflammation Review Martinon, F., and Tschopp, J., 2004. Inflammatory caspases: Linking an intracellular innate immune system to autoinflammatory diseases. Cell v. 117 p. 561–574. 16.6 The death receptor pathway of apoptosis transmits external signals Review Bodmer, J. L., Schneider, P., and Tschopp, J., 2002. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. v. 27 p. 19–26. 16.7 Apoptosis signaling by TNFR1 is complex Review Aggarwal, B. B., 2003. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. v. 3 p. 745–756. Research Barnhart, B. C., and Peter, M. E., 2003. The TNF receptor 1: A split personality complex. Cell v. 114 p. 148–150. 16.8 The mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis Review Green, D. R., 2000. Apoptotic pathways: paper wraps stone blunts scissors. Cell v. 102 p. 1–4. 16.9 Bcl-2 family proteins mediate and regulate MOMP and apoptosis Research Liu, X., Dai, S., Zhu, Y., Marrack, P., and Kappler, J.W. 2003. The structure of a Bclxl/Bim fragment complex: Implications for Bim function. Immunity v. 19 p. 341– 352. Suzuki, M.,Youle, R. J., and Tjandra, N. 2000. Structure of Bax: Coregulation of dimer formation and intracellular localization. Cell v. 103 p. 645–654, McDonnell, J. M., Fushman, D., Milliman, C. L., Korsmeyer, S. J., and Cowburn, D. 1999. Solution structure of the proapoptotic molecule BID: A structural basis for apoptotic agonists and antagonists. Cell v. 96 p. 625–634, 16.11 The activation of Bax and Bak are controlled by other Bcl-2 family proteins Review Danial, N. N., and Korsmeyer, S. J., 2004. Cell death: Critical control points. Cell v. 116 p. 205–219. 16.12 Cytochrome c, released upon MOMP, induces caspase activation Review Hill, M. M., Adrain, C., and Martin, S. J., 2003. Portrait of a killer: The mitochondrial apoptosome emerges from the shadows. Mol. Interv. v. 3 p. 19–26. Research Bao, Q., Riedl, S. J., and Shi, Y., 2005. Structure of Apaf-1 in the auto-inhibited form: A critical role for ADP. Cell Cycle v. 4 p. 1001–1003. 16.15 MOMP can cause caspase-independent cell death Review Chipuk, J. E., and Green, D. R., 2005. Do inducers of apoptosis trigger caspaseindependent cell death? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. v. 6 p. 268–275. 16.16 The mitochondrial permeability transition can cause MOMP Review Halestrap, A., 2005. Biochemistry: A pore way to die. Nature v. 434 p. 578–579. 16.17 Many discoveries about apoptosis were made in nematodes Review Kinchen, J. M., and Hengartner, M. O., 2005. Tales of cannibalism, suicide, and murder: Programmed cell death in C. elegans. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. v. 65 p. 1–45. 16.18 Apoptosis in insects has features distinct from mammals and nematodes Review Hay, B. A., Huh, J. R., and Guo, M., 2004. The genetics of cell death: Approaches, insights and opportunities in Drosophila. Nat. Rev. Genet. v. 5 p. 911–922. 16.19 The clearance of apoptotic cells requires cellular interaction Review Lauber, K., Blumenthal, S. G., Waibel, M., and Wesselborg, S., 2004. Clearance of apoptotic cells: getting rid of the corpses. Mol. Cell v. 14 p. 277–287. Reddien, P. W., and Horvitz, H. R., 2004. The engulfment process of programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. v. 20 p. 193–221. 16.20 Apoptosis plays a role in diseases such as viral infection and cancer Review Clem, R. J., 2005. The role of apoptosis in defense against baculovirus infection in insects. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. v. 289 p. 113–129. Green, D. R., and Evan, G. I., 2002. A matter of life and death. Cancer Cell v. 1 p. 19– 30. Polster, B. M., Pevsner, J., and Hardwick, J. M., 2004. Viral Bcl-2 homologs and their role in virus replication and associated diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta v. 1644 p. 211–227. 16.21 Apoptotic cells are gone but not forgotten Review Munoz, L. E., Gaipl, U. S., Franz, S., Sheriff, A., Voll, R. E., Kalden, J. R., and Herrmann, M., 2005. SLE—a disease of clearance deficiency? Rheumatology (Oxford) v. 44 p. 1101–1107. Skoberne, M., Beignon, A. S., Larsson, M., and Bhardwaj, N., 2005. Apoptotic cells at the crossroads of tolerance and immunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. v. 289 p. 259–292.