APOPTOSIS
advertisement

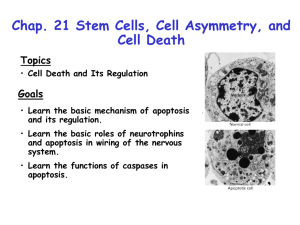
APOPTOSIS “Cell Death” By Brian Abadie, Emily Anderson, andJohn Ramsey Characteristics of Apoptosis Shrinks Blebbing Nucleus breaks down, breaks into small membrane wrapped fragments Phagocyte signals Apoptosis Video Importance of Apoptosis Maturing organisms Virus Immune System DNA damage What is a Caspase? Single chain of pro-enzymes Contains an N-terminal domain, a small subunit and a large subunit (similar to a ribosome) Apoptotic stimulus Activation Substrate Cleavage Enzyme 3 Types of Caspases Inflammatory Caspases: -1, -4, and -5 Initiator Caspases: -2, -8, -9, and -10 Long N-terminal domain Interact with effector caspases Effector Caspases: -3, -6, and -7 Little to no N-terminal domain Initiate cell death Two Caspase Pathways Extrinsic Pathway Death Ligand Death Receptors Caspases Cell Death Two Caspase Pathways Intrinsic Pathway Mitochondria Cytochrome C Apoptosome Complex Caspases Cell Death Two Caspase Pathways Cancer and Apoptosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qjjHKDn12qI Evasion of apoptosis can lead to cancer Treatment Options Activate apoptosis in cancer cells, problem solved. Finding useful mechanisms Needs to be selective Pathways (trail) IAPs Seaweed? IAPs Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins Neutralize them or prevent their production Inhibit one part in the cascade = failure to apoptose Smac mimetics Bcl proteins Elevated Bcl Confers resistance to chemotherapy Gene Expression Down regulation of XIAP Most potent endogenous IAP Using Adenovirus vector ShRNA achieves delivery And long term inhibition