STUDENT DICTIONARY
advertisement
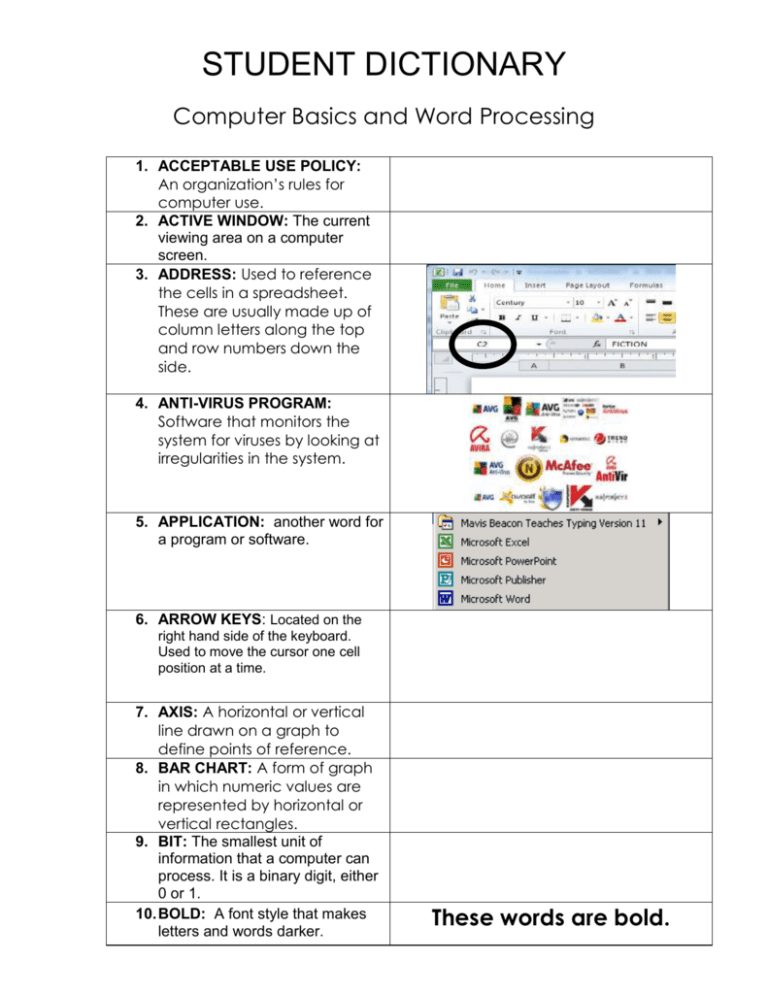
STUDENT DICTIONARY Computer Basics and Word Processing 1. ACCEPTABLE USE POLICY: An organization’s rules for computer use. 2. ACTIVE WINDOW: The current viewing area on a computer screen. 3. ADDRESS: Used to reference the cells in a spreadsheet. These are usually made up of column letters along the top and row numbers down the side. 4. ANTI-VIRUS PROGRAM: Software that monitors the system for viruses by looking at irregularities in the system. 5. APPLICATION: another word for a program or software. 6. ARROW KEYS: Located on the right hand side of the keyboard. Used to move the cursor one cell position at a time. 7. AXIS: A horizontal or vertical line drawn on a graph to define points of reference. 8. BAR CHART: A form of graph in which numeric values are represented by horizontal or vertical rectangles. 9. BIT: The smallest unit of information that a computer can process. It is a binary digit, either 0 or 1. 10. BOLD: A font style that makes letters and words darker. These words are bold. These words are not. 11. BROWSER: Software that allows users to access and navigate the contents of the Internet. Firefox and Google Chrome are the two most popular examples of this type of software. 12. BUG: An error or defect in software or hardware that causes a program to malfunction. 13. CELL: The intersection of a row and a column; the smallest element in which you can enter data. 14. CELL POINTER: Highlights the current active cell. 15. CELL RANGE: Two cell references, usually separated by a colon, defining a cell block. The first reference must be to the cell in one corner of the block and the second reference to the cell in the diagonally opposite corner. (A1:C3) 16. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT or CPU: where all of the information you put into the computer is stored. 17. CHAT: An electronic conversation. 18. CLICKING: Pointing to something on the screen and then pushing the button on the mouse is called clicking. 19. CLIENT: A computer that is controlled by the server. 20. CLOSE BOX: Located in the upper right-hand corner of a window and will exit a window. 21. COLD BOOT: Starting the computer by turning on the power source of the computer. 22. COLUMN: Vertical selection of cells identified by one or more letters. 23. COLUMN WIDTH- The distance from one side of a cell to the other side. 24. COOKIE: A small file on your computer that has information and identification allowing you faster access to a website. 25. CRASH: A serious computer failure. It means that the computer itself stops working or that a program aborts unexpectedly. It signifies either a hardware malfunction or a very serious software problem. 26. CURSOR: A marker on the screen that shows where current input or output is going to happen. 27. DELETE: Removing an item of data from a file or removing a file from a disk. 28. DESKTOP: The screen you see first when your computer turns on. This screen has many icons. 29. DIALOGUE BOX: A window that opens and asks you questions. 30. DIGITAL CAMERA: A still or video device that stores images in digital form. 31. DISK DRIVE: The place where you put your floppy disk so that you can save files on it. 32. DISKS: One way to save your work, like recording on a video tape. 33. DOCUMENT: Anything you create in Microsoft Word is called a document. 34. DRAGGING: Moving objects around the screen. 35. EMAIL: Electronic messages and mail sent over the Internet. 36. ENTER KEY: The key (on a computer keyboard) that causes the current entry to be accepted by the program, or that ends a paragraph/line. 37. FILE: a piece of computer information such as a document or part of a computer program. Stored information. 38. FOLDER: like a file folder in a filing cabinet, a file is where documents (letters, spreadsheets, etc.) are kept. 39. FONT: The way letters and words look. 40. FONT SIZE: The size of text. 41. FORMAT: Changing the way that text looks on the page. 12 point 16 point THIS is formatted. This is not formatted. 42. FORMULA- Used to perform calculations in Excel. 43. FREEWARE & SHAREWARE: Copyrighted software distributed on a free-will donation; can usually be found on the Internet or passed along from person to person. 44. HACKING: The practice of breaking into a computer’s stored data, usually by gaining access to administrative controls. 45. HARDWARE: All the parts of the computer that you can touch: the monitor, CPU, printer, mouse, and keyboard. 24 point 46. HARDCOPY: Printed output or a piece of paper with data on it. 47. HARD DRIVE: the place inside your computer where programs and files are stored. 48. HEADSET: earphones and a microphone that you wear on your head. 49. HIGHLIGHT/SELECTING: Click and drag across a word or sentence to highlight it. When it is highlighted you can make changes to it. 50. HOME PAGE: The first(opening) page of a website. 51. HTML: HyperText markup language. The computer language that is used to create a website. 52. HYPERLINK: A highlighted word or graphic in a website that takes a user to ta different location on the Internet. 53. ICON: Symbols or pictures that you can click on to perform an action. Each program has its own icon. 54. INPUT: Information or data that is entered into the computer. This may be entered by the use of a mouse, keyboard, microphone, scanner, memory stick or card, digital camera, etc. 55. ITALICS: A font style that slants words to the right. 56. ISP(INTERENT SERVICE PROVIDER): Any organization that provides access to the Internet. 57. KEYBOARD: Like a typewriter, it’s where you type and enter numbers. It is one way to tell the computer what you want it to do. 58. LAPTOP: a portable computer that you can carry with you. 59. Left and Right Arrows: Moves the contents of a window horizontally. 60. LINE GRAPH- An axis-type graph in which data points are joined by a line. 61. Mac or MACINTOSH: A computer that is made to use the Macintosh operating system. There are two basic kinds of computers: PCs and Macs. 62. MEMORY: Data stored on a computer either temporarily or permanently. 63. MENU BAR: The words at the top of the screen. Click on these words and you see menus of other things you can do. 64. MENU: A list of commands you can do. You see a menu when you click on one of the words on the Menu Bar. 65. MICROSOFT: A software company owned by Bill Gates. 66. MICROSOFT POWERPOINT: a software program for making presentations that you can show to others. 67. MICROSOFT WINDOWS: an operating system made by the Microsoft company. 68. MICROSOFT WORD: A wordprocessing program for typing letters, resumes, school papers and more. 69. MINIMIZE: to collapse a window to the bottom of the screen/task bar without closing the window. 70. MAXIMIZE: to expand a window to the full size of the screen. 71. RESTORE: to make a window smaller so that you can change the size or position. 72. MODEM: A device that provides a computer a gateway to the Internet. 73. MONITOR: Your computer’s screen 74. MOTHERBOARD: The printed circuit board that is the foundation of a computer, this board contains a computer’s CPU, RAM chips, and expansion slots. 75. MOUSE: The tool you can use tell the computer what to do. For example you can open programs and files by clicking or double clicking. 76. MULTIMEDIA: Any combination of audio, video, animation, text, and graphics. 77. NETIQUETTE: The set of manners and rules of conduct for Internet users. 78. NETWORK: A group of connected computers that allows people to share information and equipment. 79. NUMERIC- Anything that is a number. 80. OPEN: A command on the File Menu that brings files onto the screen so that you can see them. 81. OPERATING SYSTEM: the most important program in your computer. This program is like the “manager” of all of the other programs. 82. OPTICAL DRIVE: Uses a laser to rewrite CDs or DVDs. Protects your data on a disk by keeping it in a sleeve. 83. OUTPUT: Any computer- generated information displayed on a screen or printed on a piece of paper. 84. PATH: The steps for navigating to a specific location on the Internet. 85. PC = PERSONAL COMPUTER a computer that is made to use the Windows operating system. There are two basic kinds of computers: PCs and Macs. 86. PIE CHART-A form of graph which represents numeric values as segments of a circle. 87. POINTING: The line or arrow that you control by moving the mouse. 88. POWER SUPPLY: Usually sits at the top of the computer case and supplies power. A high=end machine can burn up to 800 watts. 89. PROGRAMS: Another word for software or applications. 90. RAM or RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY: Sits on the motherboard. Holds the data of running software. 91. ROM or READ ONLY MEMORY: Computer memory on which data has been prerecorded. It is permanent memory that can be only be read and cannot be erased. 92. ROW- The horizontal cells in one line of a spreadsheet 93. SCANNER: A device that reads printed material and converts it into an image for the computer. 94. SCREEN SAVER: A design on the screen that turns on if you don’t use your computer for a few minutes. 95. SCROLL BARS: The bars on the sides of the screen that allow you to move up or down the page. 96. SEARCH ENGINE: A program that searches a database of websites for words that you enter into the program. Google, Bing, Yahoo 97. SELECTING: Pointing to an object and highlighting it. 98. SERVER: A computer or device on a network that manages network resources. 99. SOFTWARE: another word for programs, instructions in the computer that help it do different tasks 100. SOFTWARE PIRACY: The illegal use, copying, or distribution of software. 101. SPAM: Unwanted and unsolicited email. 102. SPELL CHECK: When you’re using Microsoft Word, you can click on this button to look for spelling and grammar mistakes. 103. SPREADSHEET: A worksheet arranged in a matrix allowing for computation and analysis in an easy-to-read format. 104. SURFING THE WEB: Moving from one website to another. 105. SURGE PROTECTOR: A device that connects a computer to an electrical outlet and protects the computer against sudden increases in electrical power. 106. TELECOMMUNICATIONS: Transmitting and receiving data over a long distance. 107. TITLE BAR: Located at the top of a window. The name of a window is located on this icon. 108. TOOL BARS: The bars across the top of the screen that have icons you click on to do different things. 109. Up and Down Arrows: Moves the contents of a window vertically. 110. URL(Uniform Resource Locator): The address required to connect to a website. 111. USB DRIVE: a disk that you can save information on. Also called a flash drive, jump drive, or thumb drive. 112. USERNAME: A code used by individuals, in addition to a password, that lets them access a network computer, an online service, etc. 113. VIDEO CARD: Creates the images that appear on the monitor. 114. VIRUS: A manmade program or piece of code that is loaded onto your computer without your knowledge and runs against your wishes. These can also replicate themselves. 115. WARM BOOT: Reloading a computer's operating system by using a reset operation. Like using the log-off/log -on function. 116. WEBSITE: A location on the Internet where information is presented using graphics, text, and sound. 117. WORD PROCESSING: Typing documents on a computer. Word processing also allows you to format, save, and edit your writing. 118. WORLD WIDE WEB: An information system on the Internet that allows documents to be connected to other documents by hypertext links, enabling the user to search for information by moving from one document to another. 119. WORM: A program or algorithm that replicates itself over a computer network and usually performs malicious actions such as using up the computer's resources and possibly shutting the system down. 120. Y-AXIS- The vertical axis of an axis-type graph 121. X-AXIS- The horizontal axis of an axis-type graph.