Name: Date: Block
advertisement

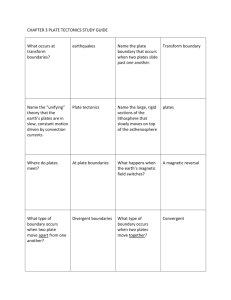
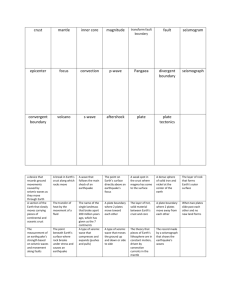
Name: ___________________________ Date: _______________ Block: ____________ Topics to Review For The Final Big Idea 3 & 4 Date of TEST: ________________________ Big Idea #3 1. What percentage of the Earth’s atmosphere is made up of nitrogen gas? Carbon Dioxide gas? 2. Study your Ocean Acidification Activity. What causes ocean acidification? What relationship does it have with climate change? What are some consequences of ocean acidification? 3. What is biogeochemical cycling? Why is it important to the biosphere? 4. What is the correct order of processes that are involved in the formation of sedimentary rocks? Terms to use: deposition, erosion, weathering, cementation and compaction. 5. What energy sources drive the rock cycle? 6. Sedimentary rocks are primarily formed by processes powered by what energy source? Explain. 7. Metamorphic and igneous rocks are primarily formed by processes powered by what energy source? Explain. 8. What are minerals? What are rocks? 9. Explain how humans are affecting the carbon cycle? 10. What are the three types of rocks? 11. Biological systems do not use up matter, they transform it. Explain what this statement means. What law does it satisfy? 12. How are the three types of rocks classified? Based on what? 13. Explain the nitrogen cycle. 14. What do coal, oil and natural gas have in common? 15. What are some processes that decrease the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? 16. What are some processes that increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? 17. What is the role of decomposers? 18. What is transpiration? 19. What are sphere interactions? If trees are cut down in an ecosystem would that affect other spheres? Why or why not? 20. Know the water cycle and all the possible ways water can move between spheres. Draw a picture of it. 21. Know the rock cycle and all the possible ways rocks can change, how they form and move from one place on the rock cycle to another. Draw a picture of it. 22. Know the different spheres that make up earth’s system. 23. What do greenhouse gasses, such as CO2, do to the Earth? 24. How does the transfer of solar energy throughout an ecosystem start? Explain. 25. What is a closed system? What is an open system? What would Earth be an example of? Explain. 26. Why do organisms need nutrients? Why are the biogeochemical cycles so important to the biosphere? 27. What is the difference between a carbon source and a carbon sink? 28. What is an ecosystem? 29. Know the carbon cycle. Draw and image. Big Idea #4 1. What instrument records earthquake waves? 2. What region are deep ocean trenches associated with? 3. What type of boundary occurs where two plates move together, causing one plate to descend beneath the other plate? 4. At what type of plate boundary is oceanic lithosphere destroyed? 5. What kind of plate boundary occurs where two plates grind past each other without destroying or producing lithosphere? 6. What are lithosphere plates made of? 7. What type of geologic features would you see at an oceanic continental plate boundary? 8. What evidence is there to support Wegener’s hypothesis? 9. Where is new ocean crust formed? 10. Describe the theory of plate tectonics. 11. What is the name of the process when one plate descends beneath another? 12. Why does magma rise and melt at divergent plate boundaries? 13. Where is an earthquake’s epicenter? 14. Continental volcanic arcs are associated with what type of plate boundary? 15. What is an earthquakes magnitude a measure of? 16. What is the first wave to show on a seismogram? Why? 17. How were the Hawaiian Islands formed? 18. What layers of the Earth make up the lithosphere? 19. What was the main reason Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis was rejected? 20. What volcanic landforms occur at divergent ocean plate boundaries? 21. Which seismic waves travel most rapidly? 22. What affects the amount of destruction caused by earthquake vibrations? 23. Describe each of the Earth’s layers. 24. What landform develops at plate boundaries where one oceanic plate descends beneath another? 25. How does the age of seafloor sediments change with increasing distance from the ocean ridge? 26. Where are most of the active volcanoes on Earth located? 27. What do tectonic plates consist of? 28. What results when divergence occurs between two oceanic plates? 29. How is the distance between a seismic station and the earthquake epicenter determined? 30. What is the supercontinent in the continental drift theory called? 31. Why does magma tend to rise toward Earth’s surface? 32. What is the minimum number of seismic stations that is needed to determine the location of an earthquake’s epicenter? 33. Volcanic island arcs are associated with what type of plate boundary? 34. What is a fault? 35. Overall, which seismic waves are the most destructive? 36. What landforms can be produced at an oceanic-continental convergent boundary? 37. What metals is Earth’s core made of? 38. Which seismic waves compress and expand rock in the direction the waves travel? 39. What is a tsunami? 40. When an earthquake occurs, energy radiates in all directions from its source, which is called the ____________.