Plate Tectonic Test Use the pictures above to answer questions 1
advertisement

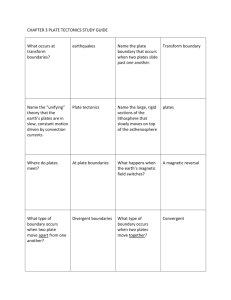
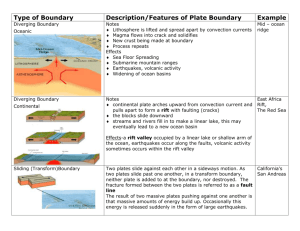
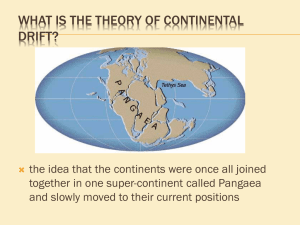
A. B. C Use the pictures above to answer questions 1-3. Each answer choice will be used once for this section. 1. Convergent Boundary 2. Transform Boundary 3. Divergent Boundary Use the same pictures above to answer questions 46. Each answer choice will be used once for this section. 4. Type of boundary where an EARTHQUAKE would occur. 5. Type of boundary where a VOLCANO or MOUNTAIN would occur. 6. Type of boundary where a MID OCEAN RIDGE would occur. ____7. The presence of ____ on several continents supports the hypothesis of continental drift. a. Fossils, and a puzzle- like fit b.. No life, rocks, and a puzzle-like fit c. Life, rocks, and a puzzle-like fit ____ 8. Earthquakes often happen at the boundary where two tectonic plates slide past each other. a. True b. False ____9. In the diagram of the earthquake simulation, which of the points would represent the epicenter or where the surface waves begin? a. A c. C b. B ____10. In the diagram of the earthquake simulation, which point would experience the weakest surface wave? a. D c. C b. B ____11. The youngest rocks on the ocean floor are located ____. a. near continents c. at mid-ocean ridges b. near Asia ____12. ____ currents inside Earth might drive plate motion. a. Vertical c. Convection b. Horizontal ____13. Active volcanoes are most likely to form at ____. a. transform boundaries c. the center of continents b. convergent boundaries where an ocean and continental plate collide ____ 14. A subduction zone occurs where . a. Two plates move away from one another. b. Two plates collide and the more dense plate sinks below the other. c. Two plates collided and raise up ____ 15. The lithosphere floats on the plastic-like layer of the upper mantle known as the ____. a. atmosphere c. core b. asthenosphere ____ 16. Continental drift occurs because of ____. a. seafloor spreading c. magnetic reversal b. Pangea ____ 17. Oceanic plates are pushed down into the upper mantle in ____. a. convection currents c. strike-slip faults b. subduction zones ____ 18. Seafloor spreading occurs because ____. a. Sediments accumulate on the ocean floor b. New material is being added to the asthenosphere c. Hot, less dense material below Earth’s crust is forced upward towards the surface. ____ 19. Over millions of years, the shape of the Earth’s surface can change from rugged mountains to low hills to flat pains. These changes are most likely caused by --. a. folding and faulting b. volcanoes and earthquake c. weathering and erosion ____ 20. One reason that melted material from the Earth’s mantle is rising up at location is because it isa. cooler than the surrounding material b. older than the surrounding material c. Less dense than the surrounding material ____ 21. The newest rocks are most likely found at a. Location c. Location b. Location ____ 22. Which of these best describes what is happening at location ? a. Oceanic plate is being created b. Oceanic plate is being subducted c. Continental plate is being destroyed ____ 23. Convection currents in the Earth’s mantle cause crustal plates to move. The drawing above shows a lab set up designed to model this process. If the two corks floating on the water represent the continents, which of the following outcomes is most likely to result from this investigation? a. b. ____ 24. Sea Floor spreading is most likely to cause-- a. land subsidence b. new ocean floor to form c. beach erosion ____ 25. While performing the investigation above, which of these safety rules is most important to follow? a. dispose of chemical as directed by teacher. b. do not reach across open flames c. clean glassware before returning it ____ 26. The map above shows three mountain ranges in the United States. Which of the following forces caused the mountain ranges to form? a. Glacial Drift c. Physical Weathering b. Crustal Plate Movement ____ 27. According to Figure 10-1, what type of plate boundary occurs between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate? a. transform boundary b. divergent boundary c. convergent oceanic-continental plate boundary 28. The tool shown in the diagram is best used to measure a. Force c. Volume b. Weight 29. The tool shown in the diagram measures in which units? a. Ounces c. Newtons b. Milliliters 31. Which of the following would be constants in the experiment? (Look to see what did not change during the experiment) a. Length of String c. Mass of Pendulum b. Distance String Pulled Back d. Both a and b 32. What is the independent variable in this investigation? (What you can Change) a. Completion time for 20 swings is pulled back b. Mass of the pendulum c. Distance string 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 33. In the photosynthesis equation above, how many atoms of oxygen are on each side? a. 18 atoms b. 2 atoms c. 36 atoms 34. Which side of the equation above is “ENERGY” found? a. Yields b. Reactant c. Arrow 35. What is the energy source that drives the photosynthesis equation above? a. Sun b. Clouds c. Automobile Write the letter of the topographic map that matches the following landscapes. 36. A. B. _37. __37. DIRECTIONS: Read the passage below, then complete the writing activity that follow on a SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER! Writing Prompt = Imagine you are a resident and have chosen not to leave your home island. Write a ½ (half) to 1 page narrative describing your reasons for staying, what you will do to prepare for an eruption, and what you will do if the volcano erupts again.