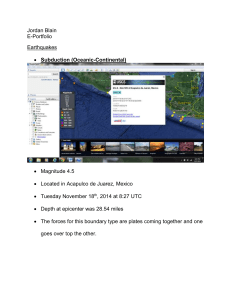
Plate Boundary: Oceanic-Continental Convergence - E-CADE
advertisement
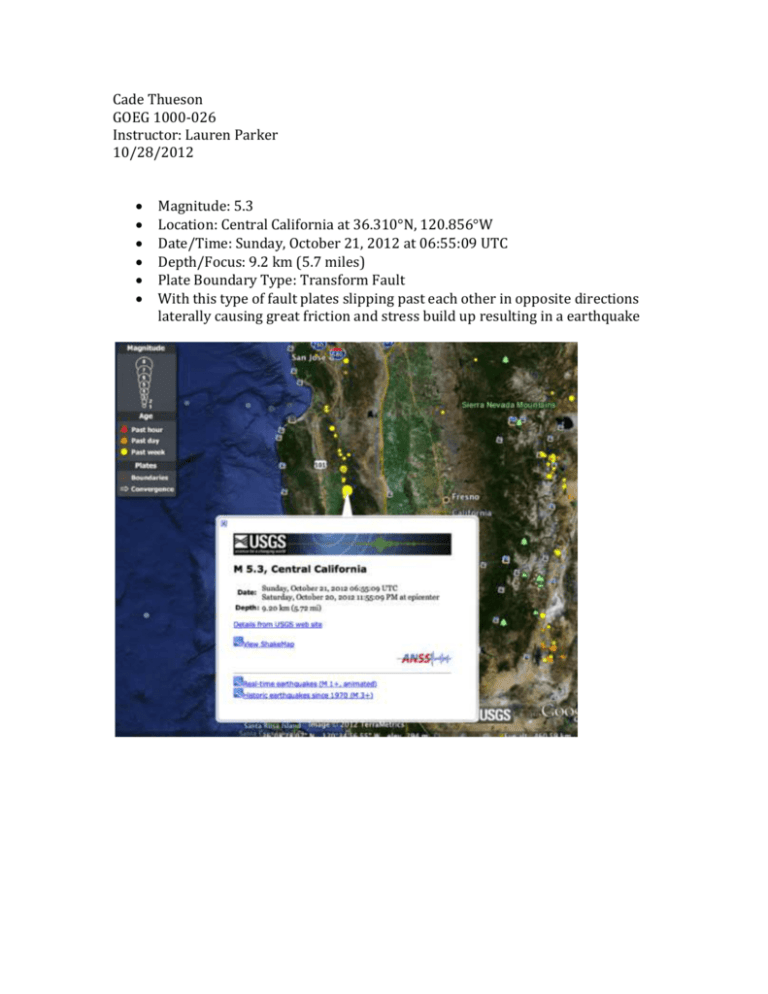
Cade Thueson GOEG 1000-026 Instructor: Lauren Parker 10/28/2012 Magnitude: 5.3 Location: Central California at 36.310°N, 120.856°W Date/Time: Sunday, October 21, 2012 at 06:55:09 UTC Depth/Focus: 9.2 km (5.7 miles) Plate Boundary Type: Transform Fault With this type of fault plates slipping past each other in opposite directions laterally causing great friction and stress build up resulting in a earthquake Magnitude: 4.6 Location: 2.150°N, 92.447°E, off the west coast of N. Sumatra Date/Time: Tuesday, October 23, 2012 19:11:52 UTC Depth/Focus: 29.00 km (18.02 mi) Plate Boundary: Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent When two converging plates come together one sliding under the other (subduction) causing a trench and earthquake. Magnitude: 6.5 Location: 10.121°N, 85.314°W, Costa Rica Date/Time: Wednesday, October 24, 2012 00:45:34 UTC Depth/Focus: 20.10 km (12.49mi) Plate Boundary: Continental-Continental Convergence When two continental plates converge together, causing great stress and because the continental crust is to buoyant to subduct this type of earthquake often forms large mountain ranges. Magnitude: 5.2 Location: 8.169°S, 123.431°E, Flores region, Indonesia Date/Time: Monday, October 29, 2012 06:28:33 UTC Depth/Focus: 9.70 km (6.03 mi) Plate Boundary: Oceanic-Continental Convergence On this boundary the oceanic lithosphere subducts under the continental lithosphere when they converge together causing the earthquake. Magnitude: 4.8 Location: 50.133°S, 113.885°E Southeast Indian Ridge Date/Time: Thuesday, October 25, 2012 22:33:49 UTC Focus/Depth: 9.10 km (5.65 mi) Plate Boundary: Divergent In this situation we are looking at mid-ocean ridge divergent boundary. What happened here was a shallow focus earthquake. In the asthenosphere we have upwelling of molten material along the mid-ocean ridge as it breaks through the lithosphere it causes separation and the earthquake. Also forming addition to the crust.