Study Guide for Continental Drift Test
advertisement

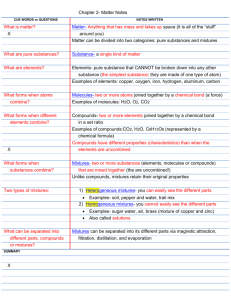
Name _________________________ Date ______________ Period _____ # _____ First Nine Weeks Study Guide This test will cover the material we have been studying since the beginning of the year. The concepts on the test include: Lab Safety Observations and Inferences Density, Mass, Volume, and Length Mixtures and Pure Substances Different parts of the atom, masses, charges, and where each part is located Isotopes and how to calculate number of neutrons Lewis Dot Structures—how many valence electrons elements have Periodic Table—how to read it, rows (periods), columns (families/groups), special group names, where metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are located Lab Safety (Ch. 1) You need to know basic rules of lab safety—I suggest going over your lab safety quiz and the lab safety rules. Observations and Inferences (Ch. 1) 1. You are expected to know the difference between an observation and an inference. Use the picture below to help you practice: A: Observations B: Inferences 1) 1) 2) 2) Density, Mass, and Volume You should know the basic metric units of measurement that we covered in class. Questions to guide your study include: 2. What is mass? 3. What is volume? 4. What are two ways to determine an object’s volume? 5. If an object is denser than the liquid it is in, what does it do? 6. If an object is less dense than the liquid it is in, what does it do? 7. How do you calculate density? 8. What are the metric units for mass? Units for volume? Units for density? Name _________________________ Date ______________ Period _____ # _____ Mixtures and Pure Substances (Ch. 18) 9. You should be aware of the properties of pure substances and mixtures. Classify the substances below as pure substances or mixtures: A) B) C) 10. Define pure substance: all of the particles are the same and cannot be physically separated 11. What are the two types of pure substances? 12. Define mixture: two or more substances that are not chemically combined and can be separated by their physical properties 13. What are the two types of mixtures? Atomic Structure (Ch. 19) 14. You need to know and be able to apply the following information about subatomic particles: Particle Name Proton Neutron Electron Charge Location Mass Isotopes (Ch. 19) You should be able to recognize that all atoms of the same element contain the same number of protons, and that elements with the same number of protons may or may not have the same mass. If they have different masses, they are called isotopes. You will be given questions to test your understanding of this concept. (There are two isotope questions on Ch. 19 test.) 15. Practice Problem: How are Hydrogen-1, Hydrogen-2, and Hydrogen-3 similar? How are they different? How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does each of these isotopes have? Lewis Dot Structures (Ch. 19) You should understand how to determine how many valence electrons different elements have and how to draw the dots around the element symbol. 16. Practice Problems: How many valence electrons do the following elements have? N, Be, Ra, Al, O? Periodic Table (Ch. 19) You will be expected to know that when elements are listed in order according to atomic number, the repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements. You should know how to read the periodic table and identify an unknown element when given its period number (AKA the row) and group number (AKA the column). You should know the four special names given to groups 1, 2, 7, and 8, and where metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are located on the periodic table. You will be given a periodic table to use during the test. 17. Practice Problems: What element is located in group 2, period 3? Group 7, period 4? Is Rb a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? What about S? Si? Kr? Be? Ge?