Matter Notes: Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, Properties
advertisement
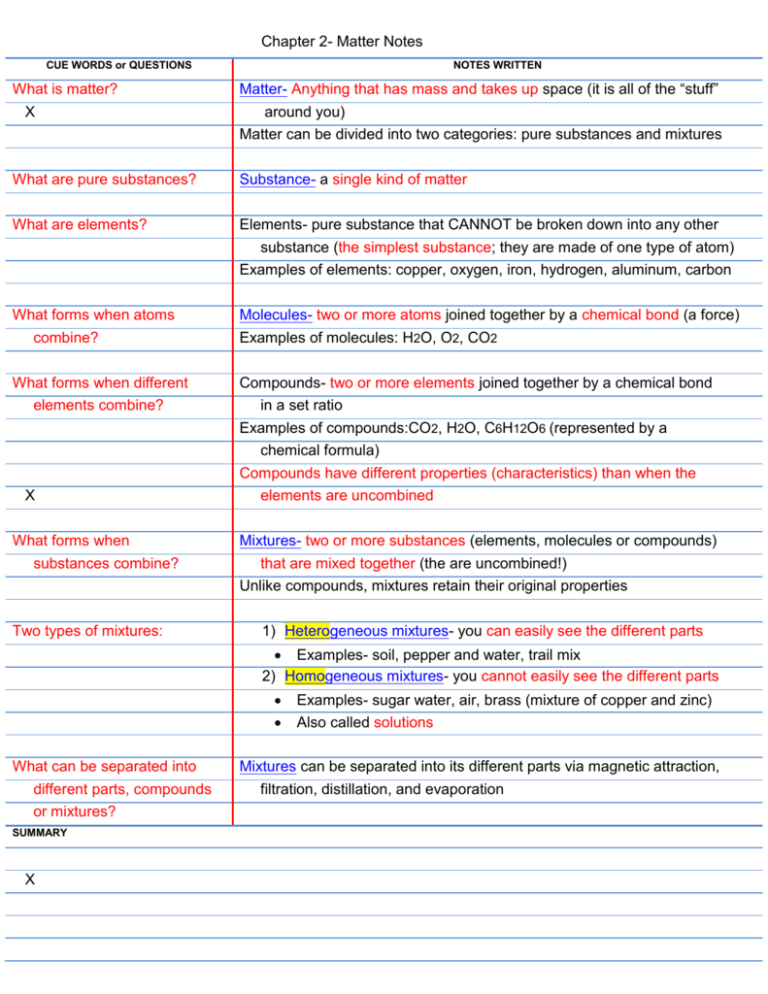
Chapter 2- Matter Notes CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS What is matter? X NOTES WRITTEN Matter- Anything that has mass and takes up space (it is all of the “stuff” around you) Matter can be divided into two categories: pure substances and mixtures What are pure substances? Substance- a single kind of matter What are elements? Elements- pure substance that CANNOT be broken down into any other substance (the simplest substance; they are made of one type of atom) Examples of elements: copper, oxygen, iron, hydrogen, aluminum, carbon What forms when atoms combine? Molecules- two or more atoms joined together by a chemical bond (a force) Examples of molecules: H2O, O2, CO2 What forms when different elements combine? Compounds- two or more elements joined together by a chemical bond in a set ratio Examples of compounds:CO2, H2O, C6H12O6 (represented by a chemical formula) Compounds have different properties (characteristics) than when the elements are uncombined X What forms when substances combine? Two types of mixtures: Mixtures- two or more substances (elements, molecules or compounds) that are mixed together (the are uncombined!) Unlike compounds, mixtures retain their original properties 1) Heterogeneous mixtures- you can easily see the different parts Examples- soil, pepper and water, trail mix 2) Homogeneous mixtures- you cannot easily see the different parts What can be separated into different parts, compounds or mixtures? SUMMARY X Examples- sugar water, air, brass (mixture of copper and zinc) Also called solutions Mixtures can be separated into its different parts via magnetic attraction, filtration, distillation, and evaporation CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS What are physical and chemical properties? X NOTES WRITTEN All matter has two kinds of properties: physical and chemical 1) Physical property- characteristic of a substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance Examples of physical property: color, texture, melting point, boiling point, density, flexibility… 2) Chemical property- characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into different substances Cannot be simply observed with the senses, you must try to change it to another substance Examples of chemical property: flammability, ability to react or produce gases How can matter change? Two ways that matter can change: physical and chemical 1) Physical change- any change that alters the form or appearance of matter but does not change into a different substance Substance remains the same after the change Examples of physical change: Ex: tearing paper, bending a nail, changes of state (solid to liquid to gas), change in shape X 1) Chemical change- a substance is changed into one or more new substances new substance formed has different properties from the original substance (known as a chemical reaction) Conservation of matter- SUMMARY X Example: CH4 +2O2 CO2 + 2H2O Conservation of matter- matter is not created or destroyed and mass is not gained or lost











