Enzyme Kinetics Sample Questions: Michaelis-Menten & Lineweaver-Burke
advertisement

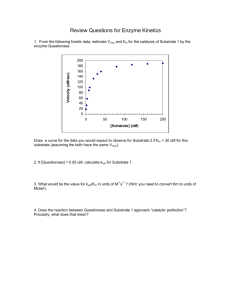
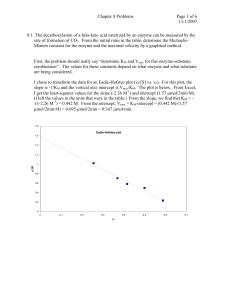
Biochemistry 2000 (1) Sample Questions x Kinetic graphs For an enzyme (5 M) , the following initial velocities have been reported depending on the substrate concentration: v0, mM s-1 10.83 18.57 26.76 32.50 39.00 43.33 48.75 54.17 56.88 [Substrate], mM 0.02 0.04 0.07 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.3 0.5 0.7 (a) Draw a Michaelis-Menten plot for this enzyme. (b) Draw a Lineweaver-Burke plot for this enzyme. (c) Determine KM and vmax for this enzyme (d) Indicate in both graphs (a & b) where vmax and KM can be recognized. (e) Calculate the catalytic constant and the catalytic efficiency for this enzyme. (2) You are trying to reproduce experimental data from the previous student in the lab. He/she had reported that the enzyme under investigation has a kcat of 1875 s-1 and a catalytic efficiency of 7.5 107 M-1 s-1. (a) What is the KM of this enzyme? (b) In repeating the measurement, you want to have a vmax of 10 mM s-1 (as this is easy to measure). How much enzyme should you use? Provide your result in M. (c) Calculate at which substrate concentrations in M you should measure the initial rate v0 to obtain the following values: v0, mM s-1 [Substrate], M 2.50 4.50 6.00 9.00 (d) Create a predicted Michaelis-Menten plot for your enzyme. (e) Draw a predicted Lineweaver-Burke plot for your enzyme. 1 Biochemistry 2000 Sample Questions x Kinetic graphs Answers: (1) (a) 70 vmax v0, mM/s 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 KM [Substrate], mM (b) 0.10 -1 1/v0, mM s 0.08 0.06 0.04 1/vmax 0.02 -1/KM -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 1/[Substrate], mM-1 (c) KM and vmax can be most precisely determined from the intercepts in the Lineweaver-Burke plot: 1/vmax = 0.015385 mM-1 s vmax = 65 mM s-1 -1/KM = -10 mM-1 KM = 0.1 mM (d) kcat = vmax / [E]total = 65 mM s-1 / 5 M = 65 mM s-1 / 0.005 mM = 13000 s-1 catalytic efficiency: kcat/KM = 13000 s-1 / 0.1 mM = 13000 s-1 / 0.0001 M = 1.3 108 M s-1 2 Biochemistry 2000 Sample Questions x Kinetic graphs vmax 25 KM 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250 [Substrate], M (e) 1/[Substrate], M-1 0.1200 0.0489 0.0267 0.0044 1/v0, mM-1 s 0.4000 0.2222 0.1667 0.1111 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 -1 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1/v0, mM s v0, mM/s (2) (a) From kcat/KM and kcat, you can calculate KM as KM = 1/(kcat/KM) * kcat = KM/kcat * kcat = 1/7.5 107 M s-1* 1875 s-1 = 2.5 10-5 M = 0.025 mM = 25 M (b) From kcat and vmax, you can calculate [E]total vmax / [E]total = kcat [E]total = vmax/kcat = 10 mM s-1 / 1875 s-1 = 0.00533 mM = 5.33 M (c) Rearranging the Michaelis-Menten equation: [S] = v0 * KM / (vmax – v0) Inserting the given values for KM, vmax and v0 will give you [S] in mM. Mulitplying by a factor of 1000 converts [S] in M. v0, mM s-1 [Substrate], M 8.333333 2.50 20.45455 4.50 37.5 6.00 225 9.00 (d) 0.25 0.20 0.15 1/vmax 0.10 0.05 -1/KM -0.04 -0.02 3 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 1/[Substrate], M-1 0.10 0.12 0.14