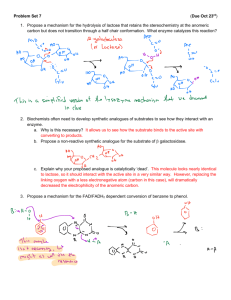
Review Questions for Enzyme Kinetics
advertisement
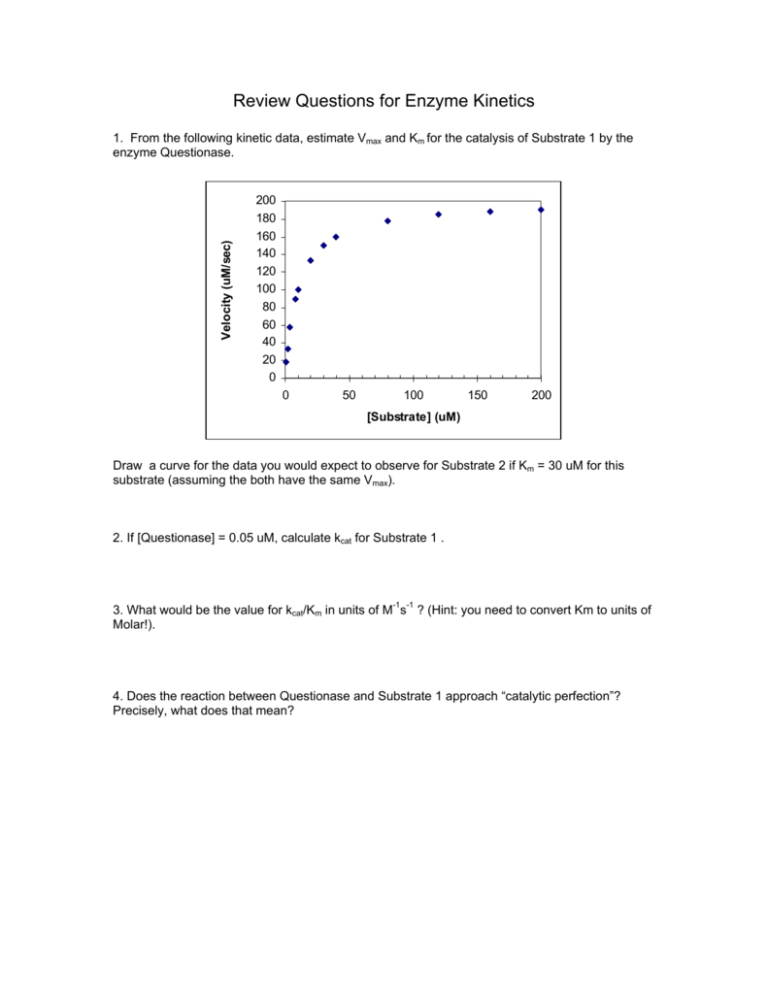
Review Questions for Enzyme Kinetics Velocity (uM/sec) 1. From the following kinetic data, estimate Vmax and Km for the catalysis of Substrate 1 by the enzyme Questionase. 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 50 100 150 200 [Substrate] (uM) Draw a curve for the data you would expect to observe for Substrate 2 if Km = 30 uM for this substrate (assuming the both have the same Vmax). 2. If [Questionase] = 0.05 uM, calculate kcat for Substrate 1 . 3. What would be the value for kcat/Km in units of M-1s-1 ? (Hint: you need to convert Km to units of Molar!). 4. Does the reaction between Questionase and Substrate 1 approach “catalytic perfection”? Precisely, what does that mean? Answers 1. From the following kinetic data, estimate Vmax and Km for the catalysis of Substrate 1 by the enzyme Questionase. Determining Vmax for Substrate 1 might vary, depending on how you draw the curve. The value of Vmax = 200 uM/sec) was used to calculate values for the data. What ever you chose, Km will be determined from the substrate concentration that gives you Vmax/2. Your curve for Substrate 2 might look a little different as well. 2. If [Questionase] = 0.05 uM, calculate kcat for Substrate 1 . Vmax = kcat [Etotal] so kcat = Vmax / [Questionase] = (200 uM/sec)/0.05 uM = 4000 s-1 3. What would be the value for kcat/Km in units of M-1s-1 ? (Hint: you need to convert Km to units of Molar!). Km = 10 uM = 10 x 10-6 M = 1 x 10-5 M kcat/Km = (4 x 103 s-1)/(1 x 10-5 M) = 4 x 108 M-1 s-1. 4. Does the reaction between Questionase and Substrate 1 approach “catalytic perfection”? Precisely, what does that mean? With a value of kcat/Km = 4 x 108 M-1 s-1, Questionase approaches very closely catalytic perfection. This means that not only does the enzyme tightly bind the substrate (the low value for Km) but it also catalyzes the reaction very rapidly (the high value for kcat).