notes for colligative properties
advertisement

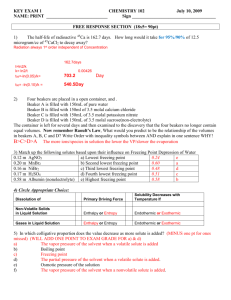
Standard 6 Notes--Solutions Solutions The solvent is what does the dissolving and the solute is what is dissolved in the solvent. For example, if sugar is dissolved in water, then sugar is the solute and water is the solvent. In a solution, the solute particles are evenly spread out through the solvent so that the mixture has the same composition throughout. See page 401—402. Solutions don’t always have to be liquids. Gases can be dissolved in liquids, gases can be dissolved in other gases, and solids can be dissolved in other solids. Examples -- page 402. The concentration of a solution is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solvent. A dilute solution has a relatively small amount of solute and a concentrated solution has a relatively large amount of solute. Concentration can be expresses in molarity or molality. Molarity is the number of moles of solute in one liter of solution. Read about molarity on page 418. Molality is the concentration of a solution expressed in moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. See page 422. The rate at which a solute dissolves in a solvent depends on temperature, agitation (stirring or shaking), and particle size (powdered sugar dissolves faster than a sugar cube.) The concentration of pollutants in the environment is often expressed in ppm (parts per million). Colligative Properties Properties that depend on the concentration of solute particles but not on their identity are called colligative properties. The temperature at which a solution boils or freezes is a colligative property. For example, dissolving sugar in water raises the boiling point and lowers the freezing point. See graph on page 446. Study “Electrolytes and Colligative Properties” on page 453. Pay careful attention to Figure 9 at the bottom of the page. Which salt would lower the freezing point the most-NaCl or CaCl2? Which one would raise the boiling point the most? If you want to melt ice should you lower the freezing point or raise the freezing point? Why do we put salt on icy roads? Which salt would be best for this purpose? Acids and Bases An acid increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) when it dissolves in water and a base increases the hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration when it dissolves in water. If there is more H+ than OH- then the solution is acidic. If there is more OH- than H+ then the solution is basic. When H+ = OH- then the solution is neutral. On the pH scale, a pH of 0 is very acidic, a pH of 14 is very basic, and a pH of 7 is neutral. See the pH scale on page 512. A pH indicator is a compound that will change colors as the pH of a solution changes. Learn how to perform a titration by reading pages 515—521.