BUILDING BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES
advertisement

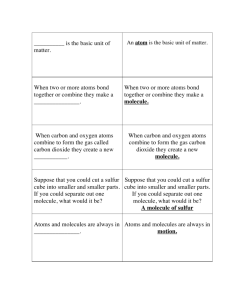
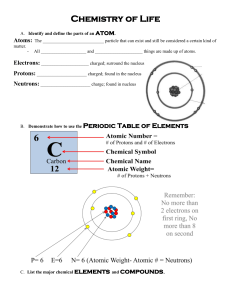
BUILDING BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES Ball and Stick Models Name: For each molecule, draw a colored picture of the structure you built. Remember: carbons atoms usually like to stay together. Date: Period: Hydrogen Peroxide - H2O2 Glycerol - C3H8O3 Produced as a byproduct in the body and will continue to build up and become toxic to body if not broken down. Forms backbone of fatty acids Diatomic Oxygen – O2 Ammonia - NH3 Oxygen gas is produced by plants during photosynthesis. It is also used to break down food to attain energy. Plays a role in waste products. Dihydrogen Monoxide - H2O Butane – C4H10 Essential to the survival of all forms of life. Often used as refrigerants. Lighter fluid. Methane – CH4 Glucose - C6H12O6 Principal component in natural gas. Produced by plants in photosynthesis. Used by all cells for cellular metabolism. QUESTIONS: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 1. For each of the molecules below, write the number of atoms of each element in the formula. The subscripts indicate the number of each atom. Sometimes, groups of atoms act as a single unit. This is called a radical. If a radical is used more than once, it is put in parentheses and the subscript appears outside the parentheses. For example: (OH2)2 would consist of 2 oxygen and 4 hydrogen atoms. Formula for Element Hydrogen Peroxide - H2O2 Glycerol - C3H8O3 Calcium Carbonate – CaCO3 Ammonia - NH3 Number of Atoms H=2 O=2 Aspirin – C9H8O4 Magnesium Hydroxide Mg(OH)2 Cellulose – C6H7O2(OH)3 Glucose - C6H12O6 Use Byproduct in body Backbone of fatty acids Limestone Waste Product of protein breakdown Pain Reliever, blood thinner Found in milk of magnesia Found in wood products. Sugar made in photosynthesis 2. Which 4 elements do you think play the largest role in living organisms? 3. a. What are the fewest number of atoms needed to construct a molecule? Define the term molecule. b. Provide an example of a molecule you made that is not a compound. 4. a. What is a compound? b. Give an example of a compound you made. 5. a. Which element used in the activity seemed to be able to make the largest number of different compounds? b. Why is this element a major component of organic (biological) molecules? 6. a. What is the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond? b. What type of bond was formed in this lab? 7. a. What is a double bond? How many electrons are involved? b. What is a triple bond? How many electrons are involved? c. Which type of bond is the hardest to break? 8. a. Explain the “octet rule”? b. Why is this concept important in chemical bonding?