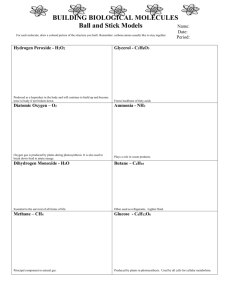
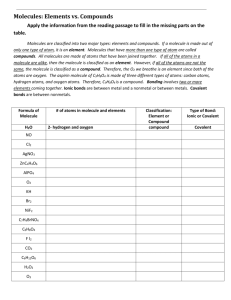
Molecules * a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds
advertisement

Molecules – a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. And a single molecule can exist on its own Chemical formula – indicated the relative numbers of atoms of each kind in a chemical compound by using atomic symbols and numerical subscripts Molecular compound – chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. The relative strength of attraction and repulsion- as hydrogen atoms get closer their potential energy rises until they are a molecule and then their potential energy is lowered Molecular Formula- shows the types and numbers of atoms combined in a single molecule of a molecular compound Bond Length- the distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy, that is, the average distance between two bonded atoms Bond Energy- the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral isolated atoms The Octet Rule- Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom by gaining losing or sharing electrons as an octet of electrons in its highest occupied energy level Exceptions to Octet Rule – other elements can be surrounded by more than eight electrons when they combine with the highly electronegative elements fluorine, oxygen, and chlorine. Models of molecules