Chemistry of Life (biochemistry)
advertisement

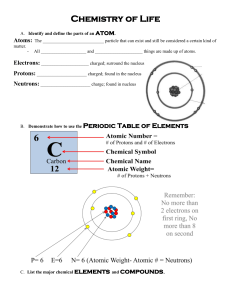
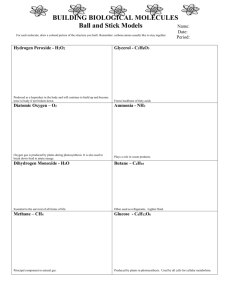
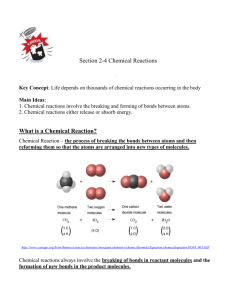
Chemistry of Life (biochemistry) Matter & Substances 3.1 NOTES!!!! ________: the smallest particle of an element that has the properties of the element; smallest unit of matter. Subatomic particles (+ charges and location): 1. 2. 3. _________: a substance made up of atoms that have the same number of protons. Vocab… Isotope: atoms of the same element that have different #s of _________. Chemical bonds: hold 2 or more atoms together (form in order to become __________). *break bonds energy is __________. *form bonds energy is ___________. ____________: a substance made of the bonded atoms of 2 or more different elements (ex. H2O) _______: an atom (or group of atoms) that has lost or gained an e-. lose an e- __ charge. gain an e- __ charge. examples… H+, OH-, Na+ 3 types of chemical bonds (1) Ionic bond: attractive force between ions w/ opposite charges…result: compound w/ no electrical charge…NaCl (Na+ & Cl-); fig. 3 pg. 53. (2) Covalent bond: occurs when atoms in a compound share valence e-; forms molecules (and compounds); strongest type of bonds *single bond: shares _____ pairs of e-. *double bond: shares _____ pairs of e-. *triple bond: shares _____ pairs of e-. *examples…H20, C02, 02, N2 (3) Hydrogen bond: a hydrogen bond is a region of charge or attraction between polar molecules. “polarity” or “polar molecules”: molecules with partial charges on opposite ends (or “poles”); example: water molecule. remember, opposite charges attract—this is true for “partially charged” atoms too! H-bonds play important roles in many of the molecules that make up living things (ex. DNA). Quick Lab…modeling! Using the Periodic Table of Elements Colored marshmallows Chalk