Chromatography - Sheryl Hoffmann
advertisement

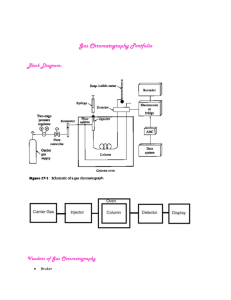
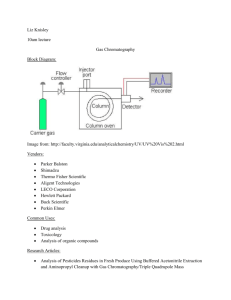
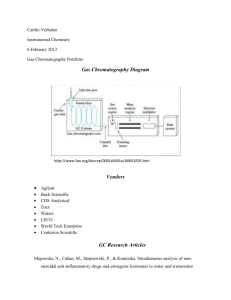
Hands-on Chromatography Presented by: Sheryl K. Hoffmann, B Sc., Grad Dip. O. H., MSIA Concordia College shoffmann@concordia.sa.edu.au CONASTA 60 – Darwin High School, 2011 Definition 1: Chromatography is a technique for separating similar compounds from one another by using differences in the strength of their adsorption on an inert material. Adsorb: hold (molecules of a gas or liquid or solute) to its surface Absorb: swallow up, incorporate, take in Definition 2: Chromatography is a technique which can be used to separate the components of a mixture. The method depends upon differences in the abilities of the components to adhere to a porus solid such as silica gel, called the stationary phase differences in the abilities of the components to be dissolved in a stream of liquid or gas, called the mobile phase, which is passed over the solid. Main Types 1. Paper Chromatography 2. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) 3. Column Chromatography 4. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) 5. Gas-Liquid Chromatography Basic Method for Paper Chromatography 1. Take a piece of chromatography paper and mark a pencil line 2 cm from the bottom. 2. Mark the positions of the samples evenly across the paper with a cross, leaving at least 2cm at each side. 3. Spot the samples on the positions marked, and allow to dry. 4. Pour < 1cm of solvent into a beaker, test tube or chromatography tank. 5. Lower the chromatography paper into the solvent in a beaker & support. 6. Allow the run until the solvent nearly reaches the top of the paper. 7. Mark final solvent height if Rf values are to be calculated. Spotting Methods To get good separation of bands, it is important to keep the spot as small as possible & as concentrated as possible. Capillary Tubes, Toothpick & Pasteur Pipettes can all be used to spot chromatography paper. Tips If the spot is large, components start from different origins and will thus blur any separation that would normally occur. Try a quick dabbing motion, the longer the liquid is in contact with the paper the larger the spot If the spot is not very concentrated the resulting bands, once spread over a wider area, will be even fainter. If the solution to be spotted is not very strong, spot several times, being sure to allow the spot to dry in-between, a hair drier will speed up the drying process. Suppliers SCIENCE SUPPLY AUSTRALIA PO Box 465, Glen Waverley, VIC 3150, Phone : 1300 857 544 Fax : 1300 857 533 Email : sales@ssapl.com.au Web: www.ssapl.com.au WESTLAB PO Box 1680, Ballarat, Vic 3354 Phone: 1800 358 101 Fax: (03) 5333 4144 Chromatography Paper 20 mm X 100m $44.15 30mm X 100m $60.30 50mm X 100m $87.15 TLC Sheets 200 X 200 mm box/25 200mm X 200mm box/100 sheets $80.40 Chromatography Column 355 X 14mm $35 Chromatography Paper 250mm X 250mm box/100 sheets LIVINGSTONE 106-116 Epsom Rd, Rosebery, NSW 2018 Phone:1300 780 078 Fax: (02) 9313 6444 Email: laboratory@livingstone.c om.au Web: www.livingstone.com.au Chromatography Paper 20 mm X 20mm $140.95 Capillary tubes Plain 75mm 100/vial $2.30 Different Styles & Support Methods for Paper Chromatography There are numerous examples of paper chromatography. Below are some pictures of various styles & different methods of supporting the paper. NB: A lid is only needed if the solvent is not water My Preferred Methods Paper Large battery tank, paperclips & skewer TLC 25ml McCartney bottle